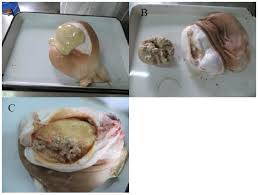
Testicular Abscess
A testicular abscess is a localized collection of pus within the testicle, typically caused by an infection. It is a serious condition that requires prompt medical attention to prevent complications.
---
Causes
1. Bacterial Infections:
Often results from untreated epididymo-orchitis (infection of the epididymis and testicle).
Common causative organisms include Escherichia coli, Staphylococcus aureus, and sexually transmitted pathogens like Chlamydia trachomatis and Neisseria gonorrhoeae.
2. Trauma:
Injury to the testicle may become infected, leading to abscess formation.
3. Immunocompromised State:
Conditions like diabetes, HIV/AIDS, or chemotherapy can increase susceptibility to infections.
4. Post-Surgical Complications:
Rarely, can occur after urological surgeries or procedures.
5. Spread of Infection:
From nearby structures, such as the prostate, urinary tract, or perineum.
---
Signs and Symptoms
Severe Scrotal Pain: Persistent and worsening over time.
Swelling and Redness: Enlargement of the affected side of the scrotum.
Fever and Chills: Often indicative of systemic infection.
Scrotal Skin Changes: Warmth and tenderness over the area.
Pus Drainage: In advanced cases, the abscess may rupture, causing pus to drain through the skin.
Difficulty Urinating: If associated with a urinary tract infection.
---
Effects
1. Testicular Damage:
Destruction of testicular tissue, potentially leading to infertility.
2. Chronic Pain:
Persistent discomfort due to scar tissue or nerve damage.
3. Sepsis:
The infection can spread to the bloodstream, becoming life-threatening.
4. Testicular Atrophy:
Shrinkage of the affected testicle due to tissue damage.
5. Necrosis:
If untreated, parts of the testicle may die, requiring removal.
---
Solutions
1. Diagnosis:
Physical Examination: Assess for swelling, tenderness, and signs of infection.
Ultrasound: Confirms the presence of an abscess and evaluates blood flow to the testicle.
Laboratory Tests:
Blood tests to check for elevated white blood cells (infection).
Urinalysis and culture to identify underlying infections.
2. Treatment:
Antibiotic Therapy:
Broad-spectrum antibiotics are started immediately to treat the infection. Specific antibiotics may be used after identifying the causative organism.
Abscess Drainage:
Small abscesses can sometimes be drained using ultrasound-guided aspiration.
Larger or severe abscesses require surgical drainage.
Orchiectomy (Testicle Removal):
In extreme cases, if the testicle is severely damaged or necrotic, surgical removal may be necessary.
3. Supportive Care:
Rest and elevation of the scrotum.
Pain management with analgesics.
Warm or cold compresses to reduce pain and swelling.
4. Prevention:
Timely Treatment of Infections:
Treat epididymo-orchitis, urinary tract infections, or sexually transmitted infections promptly to prevent complications.
Safe Sexual Practices:
Use condoms and get regular STI screenings.
Good Hygiene:
Maintain proper genital hygiene to reduce infection risks.
5. Follow-Up Care:
Regular monitoring to ensure complete resolution of the abscess and prevention of recurrence.
---
Prognosis
With early diagnosis and treatment, most testicular abscesses resolve without long-term complications. Delayed treatment increases the risk of severe outcomes like infertility or systemic infection. Regular health check-ups and prompt management of infections are essential to avoid this condition.



No comments yet
Be the first to share your thoughts!