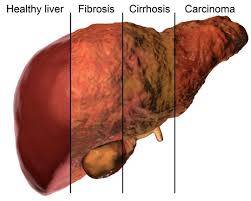
Liver fibrosis is the scarring of the liver tissue. It often occurs as a response to liver injury. Here are 20 causes, signs and symptoms, effects, and solutions related to liver fibrosis:
**Causes:**
1. Chronic alcohol abuse.
2. Chronic viral hepatitis (e.g., hepatitis B or C).
3. Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD).
4. Non-alcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH).
5. Hemochromatosis (iron overload disorder).
6. Wilson's disease (copper buildup).
7. Autoimmune hepatitis.
8. Biliary atresia (congenital condition).
9. Cystic fibrosis-related liver disease.
10. Alpha-1 antitrypsin deficiency.
11. Schistosomiasis (parasitic infection).
12. Medications and toxins.
13. Metabolic syndrome.
14. Obesity.
15. Genetic predisposition.
16. Viral infections other than hepatitis (e.g., Epstein-Barr virus).
17. Excessive intake of alcohol in short periods (binge drinking).
18. High intake of trans fats and saturated fats.
19. Environmental toxins and pollutants.
20. Certain rare genetic diseases.
**Signs and Symptoms:**
1. Fatigue and weakness.
2. Enlargement of the liver and spleen.
3. Abdominal pain and discomfort.
4. Jaundice (yellowing of the skin and eyes).
5. Unexplained weight loss.
6. Dark urine.
7. Pale-colored stools.
8. Itchy skin (pruritus).
9. Loss of appetite.
10. Nausea and vomiting.
11. Swelling in the abdomen (ascites).
12. Spider-like blood vessels on the skin (spider angiomas).
13. Muscle wasting.
14. Cognitive changes (hepatic encephalopathy).
15. Easy bruising and bleeding.
16. Coagulation problems.
17. Hormonal imbalances.
18. Enlarged breasts in men (gynecomastia).
19. Increased susceptibility to infections.
20. Fluid retention in the ankles.
**Effects:**
1. Progression to cirrhosis.
2. Portal hypertension (high blood pressure in the liver's blood vessels).
3. Increased risk of liver cancer (hepatocellular carcinoma).
4. Liver function impairment.
5. Metabolic complications, including diabetes.
6. Cardiovascular disease.
7. Pancreatitis (inflammation of the pancreas).
8. High blood pressure.
9. Kidney disease.
10. Sleep disturbances and sleep disorders.
11. Gastrointestinal problems.
12. Hormonal imbalances.
13. Reduced quality of life.
14. Psychological and cognitive issues.
15. Increased healthcare costs.
16. Social and relationship problems.
17. Increased risk of accidents and injuries.
18. Fluid retention and ascites.
19. Bone health problems.
20. Risk of complications during surgery or invasive procedures.
**Solutions:**
1. Treatment of the underlying cause (e.g., alcohol cessation or hepatitis management).
2. Lifestyle changes, including a healthy diet and exercise.
3. Weight loss for NAFLD/NASH.
4. Medications to manage symptoms and complications.
5. Avoiding alcohol and certain medications.
6. Hepatitis vaccination and treatment.
7. Treating co-occurring conditions (e.g., diabetes, high blood pressure).
8. Regular medical monitoring and follow-up.
9. Liver transplantation in severe cases.
10. Nutritional support.
11. Support from healthcare professionals.
12. Managing coagulation problems.
13. Managing bone health.
14. Support from family and friends.
15. Psychological support and counseling.
16. Support groups for liver disease patients.
17. Public health initiatives to promote awareness and prevention.
18. Legal regulations and policies to reduce exposure to environmental toxins.
19. Educational programs on liver health.
20. Early intervention and disease management.
Early diagnosis and appropriate management of liver fibrosis can prevent or slow down its progression to cirrhosis. If you suspect you have liver fibrosis or are at risk, consult a healthcare professional for evaluation and guidance.


No comments yet
Be the first to share your thoughts!