How to Prevent Coronary Artery Disease
Introduction
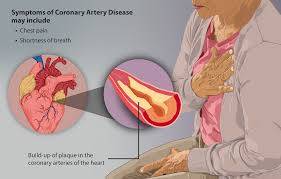
Coronary Artery Disease (CAD) is a prevalent and potentially life-threatening condition that affects millions of people worldwide. It occurs when the blood vessels that supply oxygen and nutrients to the heart become narrowed or blocked by a buildup of plaque, leading to reduced blood flow to the heart muscle. CAD can result in various complications, including heart attack, heart failure, and even sudden cardiac death. However, the good news is that many of the risk factors for CAD are modifiable, meaning there are steps individuals can take to reduce their risk and prevent the development of this disease.
In this comprehensive guide, we will delve into the various strategies and lifestyle modifications that can help prevent Coronary Artery Disease. From dietary changes to regular exercise and stress management techniques, we will explore evidence-based recommendations to promote heart health and reduce the risk of CAD.
Understanding Coronary Artery Disease
Before we dive into prevention strategies, it's essential to understand the underlying mechanisms and risk factors associated with Coronary Artery Disease. CAD typically develops over time due to a combination of factors, including:
1. **Atherosclerosis:** The primary cause of CAD is atherosclerosis, a condition characterized by the buildup of plaque (a mixture of cholesterol, fat, calcium, and other substances) in the walls of the coronary arteries. This buildup narrows the arteries, restricting blood flow to the heart.
2. **Risk Factors:** Several risk factors increase the likelihood of developing CAD. These include:
- **High blood pressure (hypertension)**
- **High cholesterol levels (hyperlipidemia)**
- **Diabetes mellitus**
- **Obesity**
- **Smoking**
- **Sedentary lifestyle**
- **Unhealthy diet**
- **Family history of heart disease**
3. **Symptoms:** CAD often progresses silently, with many individuals unaware of the condition until they experience symptoms such as chest pain (angina), shortness of breath, fatigue, or even a heart attack.
Given the complex interplay of these factors, preventing CAD requires a multifaceted approach targeting various aspects of lifestyle and health.
Preventive Strategies for Coronary Artery Disease
1. **Adopting a Heart-Healthy Diet:**
- **Emphasize Fruits and Vegetables:** Incorporate plenty of fruits and vegetables into your diet, as they are rich in antioxidants, vitamins, and minerals that support heart health.
- **Choose Whole Grains:** Opt for whole grains such as brown rice, quinoa, and whole wheat bread over refined grains to increase fiber intake and reduce the risk of CAD.
- **Limit Saturated and Trans Fats:** Reduce consumption of saturated and trans fats found in fried foods, processed snacks, and high-fat dairy products, as they can raise cholesterol levels and contribute to atherosclerosis.
- **Include Healthy Fats:** Incorporate sources of healthy fats, such as fatty fish (salmon, mackerel), nuts, seeds, and olive oil, which contain omega-3 fatty acids and can help lower cholesterol and reduce inflammation.
- **Moderate Alcohol Consumption:** If you choose to drink alcohol, do so in moderation. Excessive alcohol consumption can increase blood pressure and triglyceride levels, raising the risk of CAD.
2. **Maintaining a Healthy Weight:**
- **Calculate Your Body Mass Index (BMI):** Determine your BMI to assess whether you are within a healthy weight range. Aim for a BMI between 18.5 and 24.9.
- **Engage in Regular Physical Activity:** Incorporate at least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity aerobic exercise or 75 minutes of vigorous-intensity exercise per week, along with muscle-strengthening activities on two or more days a week. Exercise helps control weight, lower blood pressure, and improve cholesterol levels.
3. **Managing Blood Pressure and Cholesterol:**
- **Monitor Blood Pressure:** Keep track of your blood pressure regularly and take steps to keep it within a healthy range (less than 120/80 mm Hg).
- **Control Cholesterol Levels:** Get regular cholesterol screenings and work with your healthcare provider to manage cholesterol levels through lifestyle changes and, if necessary, medication.
4. **Quitting Smoking:**
- **Seek Support:** If you smoke, quit as soon as possible. Seek support from healthcare professionals, smoking cessation programs, or support groups to help you quit successfully.
- **Avoid Secondhand Smoke:** Minimize exposure to secondhand smoke, as it can also increase the risk of CAD and other cardiovascular diseases.
5. **Managing Diabetes:**
- **Monitor Blood Sugar Levels:** Keep blood sugar levels within the target range recommended by your healthcare provider through diet, exercise, medication, and regular monitoring.
- **Follow a Diabetic-Friendly Diet:** Choose foods low in added sugars and carbohydrates, focus on fiber-rich foods, and spread carbohydrate intake throughout the day to prevent spikes in blood sugar levels.
6. **Reducing Stress:**
- **Practice Stress-Relief Techniques:** Incorporate stress-reduction techniques such as mindfulness meditation, deep breathing exercises, yoga, or hobbies that promote relaxation and enjoyment.
- **Prioritize Self-Care:** Make time for activities that bring you joy and relaxation, such as spending time with loved ones, pursuing hobbies, or engaging in leisure activities.
7. **Getting Quality Sleep:**
- **Establish a Sleep Routine:** Aim for 7-9 hours of quality sleep each night by establishing a consistent sleep schedule and creating a relaxing bedtime routine.
- **Create a Sleep-Conducive Environment:** Make your bedroom conducive to sleep by keeping it dark, quiet, and cool, and avoiding screens and stimulating activities before bedtime.
Conclusion
Preventing Coronary Artery Disease requires a proactive approach that addresses various risk factors and promotes heart-healthy habits. By adopting a nutritious diet, maintaining a healthy weight, engaging in regular physical activity, managing blood pressure and cholesterol levels, quitting smoking, controlling diabetes, reducing stress, and prioritizing quality sleep, individuals can significantly reduce their risk of developing CAD and other cardiovascular diseases. Additionally, regular check-ups with healthcare providers and adherence to medical recommendations are essential for early detection and management of risk factors. By taking these steps, individuals can empower themselves to lead healthier lives and protect their heart health for years to come.



No comments yet
Be the first to share your thoughts!