Seborrheic Dermatitis
Seborrheic dermatitis is a chronic skin condition that affects areas of the body with a high concentration of oil glands, particularly the scalp, face, and upper chest. It causes red, scaly, and itchy skin, often accompanied by dandruff.
---
Causes
The exact cause of seborrheic dermatitis is not fully understood, but several factors are believed to contribute:
1. Malassezia Yeast Overgrowth:
An overgrowth of Malassezia yeast, which naturally occurs on the skin, can irritate and inflame the skin, leading to symptoms.
2. Excess Oil Production:
Overactive sebaceous (oil) glands can create an environment conducive to yeast overgrowth and inflammation.
3. Immune System Response:
An abnormal immune response to the yeast or other triggers may exacerbate the condition.
4. Genetic Predisposition:
A family history of seborrheic dermatitis or related conditions like psoriasis may increase susceptibility.
5. Triggers:
Stress and Fatigue: Emotional stress and lack of sleep can worsen symptoms.
Weather: Cold, dry weather or hot, humid conditions can exacerbate the condition.
Hormonal Changes: Hormonal fluctuations may contribute to flare-ups.
6. Underlying Conditions:
More common in individuals with certain conditions such as Parkinson's disease, HIV/AIDS, or depression.
---
Signs and Symptoms
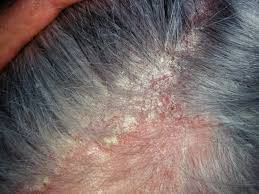
1. Scaly Patches:
White or yellowish, greasy scales on the scalp, eyebrows, eyelids, ears, or other areas rich in oil glands.
2. Dandruff:
Flaking skin on the scalp, which can range from mild to severe.
3. Redness:
Inflamed, red patches of skin, especially on the face, hairline, or chest.
4. Itching and Irritation:
Persistent itching that can worsen with scratching.
5. Crusting or Oozing:
In severe cases, the affected areas may develop crusts or ooze.
6. Hair Loss:
Repeated scratching or inflammation may lead to temporary hair loss.
---
Effects
1. Physical Discomfort:
Persistent itching and irritation can interfere with daily activities and sleep.
2. Emotional Distress:
Visible symptoms like dandruff or facial redness may lead to embarrassment, anxiety, or reduced self-esteem.
3. Chronic Flare-Ups:
Seborrheic dermatitis is a recurring condition that may require long-term management.
4. Secondary Infections:
Scratching can introduce bacteria, leading to infections in affected areas.
---
Solutions and Treatments
Over-the-Counter Treatments
1. Medicated Shampoos:
Anti-dandruff shampoos containing active ingredients like:
Ketoconazole: Reduces fungal overgrowth.
Selenium sulfide: Slows down skin cell turnover and reduces flaking.
Zinc pyrithione: Antifungal and antibacterial properties.
Coal tar: Slows skin cell production and reduces scaling.
Use these shampoos regularly for maintenance.
2. Topical Creams and Ointments:
Hydrocortisone cream: Reduces inflammation and redness (short-term use only).
Antifungal creams: Treat yeast overgrowth (e.g., ketoconazole or clotrimazole).
Prescription Treatments
1. Stronger Topical Corticosteroids:
For severe inflammation, a dermatologist may prescribe potent steroids for short-term use.
2. Topical Calcineurin Inhibitors:
Non-steroidal creams like tacrolimus or pimecrolimus can reduce inflammation without steroid-related side effects.
3. Oral Antifungal Medications:
In cases of widespread or resistant seborrheic dermatitis, oral antifungal medications like itraconazole may be prescribed.
4. Oral Steroids or Immunosuppressants:
Rarely used for severe cases that don't respond to other treatments.
Lifestyle and Home Remedies
1. Maintain Good Hygiene:
Wash the affected areas regularly with gentle cleansers to remove excess oil and flakes.
2. Moisturize:
Use non-comedogenic moisturizers to prevent dryness and irritation.
3. Avoid Triggers:
Manage stress, get adequate sleep, and avoid harsh chemicals or hair products.
4. Use Natural Remedies:
Tea Tree Oil: Diluted tea tree oil may have antifungal and soothing properties.
Aloe Vera: Can reduce inflammation and moisturize the skin.
Preventive Measures
1. Regular Hair Washing:
Use mild shampoos or medicated options to keep the scalp clean.
2. Stress Management:
Practice relaxation techniques like yoga, meditation, or exercise to reduce stress-related flare-ups.
3. Healthy Diet:
Eat a balanced diet rich in vitamins (e.g., biotin, zinc) to support skin health.
4. Avoid Scratching:
Scratching can worsen symptoms and lead to infections; keep nails short to minimize damage.
---
When to See a Doctor
Seek medical advice if:
Symptoms are severe, widespread, or persistent.
Over-the-counter treatments do not provide relief.
Secondary infections develop (e.g., oozing, crusting, or increased pain).
With proper management, seborrheic dermatitis can be controlled effectively, though it may require ongoing care to prevent flare-ups.



No comments yet
Be the first to share your thoughts!