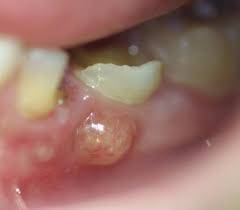
A tooth abscess is a pocket of pus caused by a bacterial infection in the tooth or gums. Abscesses are painful and can lead to serious complications if untreated. They are usually categorized into three types: periapical (at the tip of the tooth root), periodontal (in the gums next to the tooth root), and gingival (in the gum tissue).
---
Causes of a Tooth Abscess
1. Untreated Tooth Decay: Cavities that penetrate deep into the tooth can allow bacteria to reach the pulp (the inner part of the tooth), leading to infection.
2. Gum Disease (Periodontitis): Severe gum disease can create pockets around the teeth where bacteria can accumulate, leading to infection.
3. Tooth Trauma or Injury: A crack or chip in the tooth can expose the inner layers to bacteria, which can result in an infection.
4. Poor Oral Hygiene: Not brushing or flossing regularly can lead to plaque buildup, increasing the risk of tooth decay and gum disease.
5. Weakened Immune System: Conditions such as diabetes or autoimmune diseases can make it harder for the body to fight infections.
6. Previous Dental Work: In some cases, dental work that didn’t fully remove bacteria from a cavity or root canal can lead to an abscess later.
---
Signs and Symptoms of a Tooth Abscess
1. Severe Toothache: A persistent, throbbing pain that can radiate to the jaw, neck, or ear.
2. Sensitivity to Hot and Cold: Increased sensitivity to temperature changes or sweet foods.
3. Swelling: Swelling in the gums, face, or jaw near the affected area.
4. Bad Taste or Smell: A foul taste or odor in the mouth, often from pus drainage.
5. Fever: A sign that the body is fighting off an infection, especially in severe cases.
6. Swollen Lymph Nodes: Swelling in the lymph nodes under the jaw or in the neck.
7. Difficulty Chewing or Biting: Pain when applying pressure to the affected tooth.
8. Redness and Inflammation: The gums around the affected area may appear red and inflamed.
---
Effects of a Tooth Abscess
1. Spread of Infection: If untreated, the infection can spread to nearby areas, such as the jawbone, neck, and even other parts of the body.
2. Bone Loss: The infection can damage the jawbone around the affected tooth, potentially leading to bone loss.
3. Tooth Loss: Severe infection can cause damage to the tooth and its supporting structures, leading to tooth loss.
4. Sinus Infection: Upper tooth abscesses can spread into the sinus cavities, causing sinus infections.
5. Sepsis: In rare cases, the infection can enter the bloodstream, leading to sepsis, a life-threatening condition.
6. Swelling and Difficulty Breathing or Swallowing: In extreme cases, the swelling from an abscess can interfere with breathing or swallowing.
---
Solutions and Treatments for a Tooth Abscess
1. Antibiotic Therapy:
Antibiotics: Dentists may prescribe antibiotics to help eliminate the infection and prevent it from spreading, especially if the abscess is accompanied by swelling or fever.
2. Drainage of the Abscess:
Incision and Drainage: In some cases, the dentist may need to make a small incision in the gum to drain the abscess and clear the pus, providing immediate relief.
3. Root Canal Therapy:
Root Canal: For abscesses that originate from within the tooth, a root canal can be performed to remove the infected tissue from the tooth’s pulp and root canals. After cleaning and sealing, the tooth may be restored with a crown.
4. Tooth Extraction:
Extraction: If the tooth is severely damaged or cannot be saved, the dentist may recommend extracting it to prevent further infection.
5. Pain Management:
Over-the-Counter Pain Relievers: Medications like ibuprofen or acetaminophen can help manage pain and inflammation while awaiting treatment.
Cold Compress: Applying a cold compress to the face near the abscessed area can help reduce pain and swelling.
6. Saltwater Rinse:
Rinse with Warm Saltwater: A saltwater rinse can help cleanse the mouth and temporarily soothe the gums. Mix a teaspoon of salt in a glass of warm water and rinse several times a day.
7. Lifestyle and Dietary Changes:
Avoid Sugary and Acidic Foods: Foods that increase acidity in the mouth can worsen infection and decay.
Stay Hydrated: Drinking water helps rinse away food particles and bacteria.
8. Regular Dental Checkups:
Frequent Monitoring: Regular dental visits can help identify issues early and prevent infections from becoming severe.
9. Good Oral Hygiene:
Brushing and Flossing: Practicing good oral hygiene habits can help prevent future abscesses by removing plaque and food particles from the teeth and gums.
---
Tooth abscesses require prompt dental attention to prevent complications. Early intervention and treatment can resolve the infection and prevent further spread, while good oral hygiene and regular dental visits can help reduce the risk of abscesses in the future.