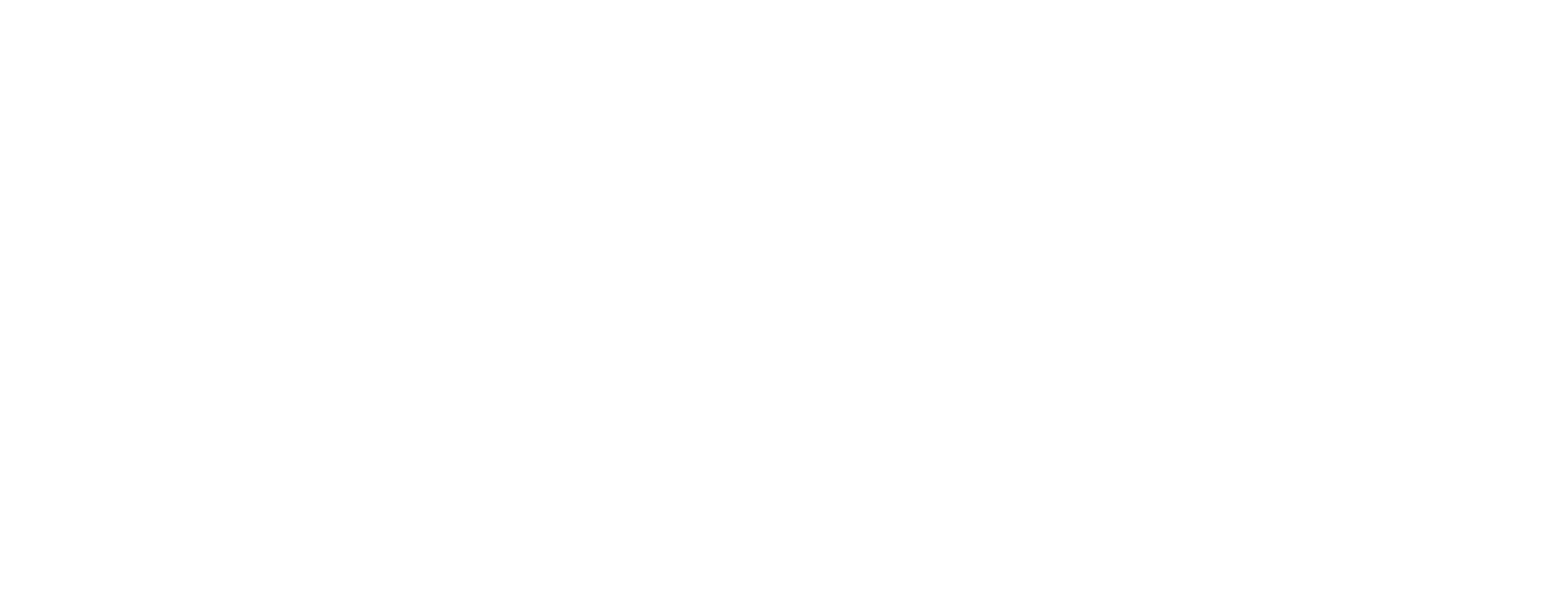
Epididymitis

Causes
Epididymitis is the inflammation of the epididymis, the coiled tube at the back of the testicle that stores and carries sperm. Common causes include:
1. Infections:
Sexually Transmitted Infections (STIs): Chlamydia and gonorrhea are frequent causes in sexually active men.
Urinary Tract Infections (UTIs): Bacterial infections can spread from the urinary tract to the epididymis.
Prostatitis: Infection of the prostate gland can lead to epididymitis.

2. Non-Infectious Causes:
Trauma or injury to the scrotum.
Retrograde flow of urine into the epididymis due to heavy lifting or straining.
Use of urinary catheters.
3. Other Risk Factors:
Unprotected sexual activity.
Anatomical abnormalities.
Recent surgery involving the urinary tract.
 ---
---
Signs and Symptoms
1. Pain: Gradual onset of pain in the scrotum, typically on one side.
2. Swelling: Enlargement and tenderness of the affected epididymis and testicle.
3. Redness and Warmth: The skin of the scrotum may appear red and feel warm.
4. Painful Urination: Dysuria or burning sensation during urination.
5. Discharge: Possible penile discharge, especially if caused by STIs.
6. Fever and Chills: Indicating a systemic infection.
7. Pain During Intercourse or Ejaculation.
8. Lump in the Testicle: A firm mass may be felt in severe cases.
---
Effects
If left untreated, epididymitis can lead to:
1. Chronic Epididymitis: Long-lasting pain and inflammation.
2. Abscess Formation: Pockets of pus may develop in the epididymis.
3. Infertility: Damage to the epididymis can impair sperm transport.
4. Testicular Involvement (Epididymo-Orchitis): Inflammation may spread to the testicle.
5. Systemic Infection: Severe cases can lead to sepsis.
---
Solutions
1. Medications:
Antibiotics: Prescribed based on the underlying cause (e.g., doxycycline or ceftriaxone for STIs, fluoroquinolones for UTIs).
Pain Relievers: NSAIDs like ibuprofen to reduce pain and swelling.
2. Supportive Care:
Rest and scrotal elevation to reduce swelling.
Ice packs applied intermittently for pain relief.
Avoidance of sexual activity during treatment.
3. Surgery (Rare cases):
Abscess drainage if present.
Epididymectomy (removal of the epididymis) in recurrent or chronic cases.
4. Prevention:
Practice safe sex (use condoms).
Treat urinary tract infections promptly.
Avoid trauma to the groin area.
If you experience symptoms of epididymitis, consult a healthcare provider immediately to avoid complications. Early treatment is key to recovery.
 blogpay
blogpay

























Total Comments: 0