Verb Types
Verbs are one of the essential parts of speech in English and play a crucial role in sentence construction. They express actions, states, events, or conditions. Here are some common types of verbs:
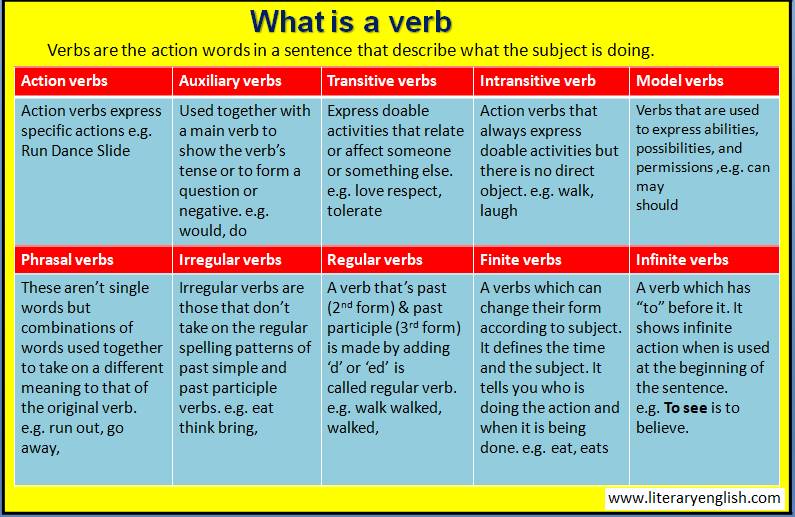
Action Verbs: These verbs describe physical or mental actions. Examples include "run," "jump," "write," "think," and "read."
Linking Verbs: Linking verbs connect the subject of a sentence with a noun, pronoun, or adjective that describes or renames it. They do not express action but instead show a relationship between the subject and the complement. Examples include "be," "appear," "seem," "become," and "feel." For instance, in the sentence "She is a doctor," the verb "is" links the subject "She" to the complement "doctor."
Auxiliary Verbs: Also known as "helping verbs," auxiliary verbs are used in combination with main verbs to express various tenses, moods, voices, and conditions. Examples include "be," "have," "do," "will," "shall," "can," "may," "must," and "should." For instance, in the sentence "They have finished their homework," the auxiliary verb "have" helps to form the present perfect tense.
Modal Verbs: Modal verbs indicate attitudes, possibilities, permissions, obligations, and abilities. They are used with a base verb to modify its meaning. Common modal verbs include "can," "could," "may," "might," "will," "would," "shall," "should," "must," "ought to," and "need to." For example, in the sentence "I can swim," the modal verb "can" expresses the ability to swim.
Transitive Verbs: Transitive verbs are action verbs that require a direct object to complete their meaning. They transfer the action from the subject to the object. For example, in the sentence "She wrote a letter," the verb "wrote" requires a direct object "a letter" to make sense.
Intransitive Verbs: Intransitive verbs do not require a direct object to complete their meaning. They express action or a state without transferring it to an object. Examples include "arrive," "run," "laugh," and "sleep." In the sentence "He laughed," the verb "laughed" does not need a direct object.
Regular Verbs: Regular verbs form their past tense and past participle by adding "-ed" to the base form. For example, "talk" becomes "talked" (past tense) and "talked" (past participle).
Irregular Verbs: Irregular verbs do not follow the regular pattern of forming the past tense and past participle. They have unique forms for these tense forms. Examples include "go" (went, gone), "see" (saw, seen), and "eat" (ate, eaten).
These are just a few examples of the different kinds of verbs in English. Verbs are diverse and versatile, allowing for a range of expressions and meanings in sentences.



No comments yet
Be the first to share your thoughts!