Home
Politics, Law & Government
World Leaders
Presidents & Heads of States
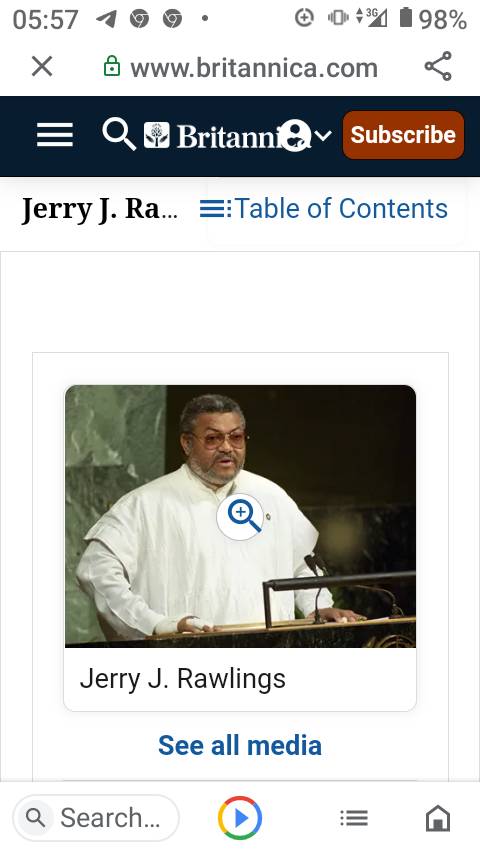
Jerry J. Rawlings
head of state, Ghana
Also known as: Jerry John Rawlings
Written and fact-checked by
Last Updated: Article History
Jerry J. Rawlings, in full Jerry John Rawlings also called J.J. Rawlings, (born June 22, 1947, Accra, Ghana—died November 12, 2020, Accra), military and political leader in Ghana who twice (1979, 1981) overthrew the government and seized power. His second period of rule (1981–2001) afforded Ghana political stability and competent economic management.
Jerry J. Rawlings
Jerry J. Rawlings
See all media
Born: June 22, 1947 Accra Ghana
Died: November 12, 2020 (aged 73) Accra Ghana
Title / Office: president (1992-2001), Ghana
Rawlings was the son of a Scottish father and a Ghanaian mother. He was educated at Achimota College and the military academy at Teshie. He was commissioned a second lieutenant in the Ghanaian air force in 1969 and became a flight lieutenant and expert pilot, skilled in aerobatics. In June 1979 Rawlings and other junior officers led a successful military coup with the purported aim of purging the military and public life of widespread corruption. He and his Armed Forces Revolutionary Council ruled for 112 days, during which time the former heads of state, Gen. Ignatius Kutu Acheampong and Lieut. Gen. Frederick W.K. Akuffo, were tried and executed. Rawlings then yielded power to a freely elected civilian president, Hilla Limann, who promptly retired Rawlings from the air force.
Undated photograph of Julius Nyerere, the first prime minister of Tanganyika, which eventually became Tanzania.
Britannica Quiz
African Leaders: Part One
Rawlings continued to be a popular figure, however, and on December 31, 1981, after two years of weak civilian rule during which Ghana’s economy continued to deteriorate, Rawlings overthrew Limann’s government, accusing it of leading the nation “down to total economic ruin.” Rawlings established a Provisional National Defense Council as the new government and imprisoned Limann and some 200 other politicians. “Peoples’ Defense Committees” were set up in neighbourhoods, as were workers’ councils to monitor production in factories. When the failure of these and other populist measures had become clear by 1983, Rawlings reversed course and adopted conservative economic policies, including dropping subsidies and price controls in order to reduce inflation, privatizing many state-owned companies, and devaluing the currency in order to stimulate exports. These free-market measures sharply revived Ghana’s economy, which by the early 1990s had one of the highest growth rates in Africa. In 1992, in the first presidential elections held in Ghana since 1979, Rawlings was chosen as president. He was reelected in 1996 and stepped down from the presidency in early 2001.
The Editors of Encyclopaedia Britannica
This article was most recently revised and updated by Amy McKenna.
Home
Politics, Law & Government
Military
air force
Also known as: airforce
Written and fact-checked by
Last Updated: Jun 11, 2023 • Article History
Recent News
Jun. 11, 2023, 5:43 PM ET (AP)
Join the military, become a US citizen: Uncle Sam wants you and vous and tu
The U.S. military has struggled to overcome recruiting shortfalls and as a way to try to address that problem, it's stepping up efforts to sign up immigrants
Jun. 7, 2023, 1:18 PM ET (AP)
Home to Glenn, Armstrong and Wrights perfect spot for Space Command HQ, Ohio lawmakers tell Biden
Ohio's rich history of aviation innovation makes it an ideally suited location for the Air Force's new U.S. Space Command headquarters or Space Force units, a group of the state's congressional delegates told Democratic President Joe Biden in a letter Wednesday
air force, military organization of a nation that is primarily responsible for the conduct of air warfare. The air force has the missions of gaining control of the air, supporting surface forces (as by bombing and strafing), and accomplishing strategic-bombing objectives. The basic weapon systems of air forces are such military airplanes as fighters, bombers, fighter-bombers, attack aircraft, reconnaissance craft, and training craft. Since the mid-20th century, the air forces of some of the world’s major powers have also operated those nations’ contingents of land-based intercontinental ballistic missiles, as well as of nuclear-armed long-range bombers. The army and naval branches of a nation’s armed forces may also operate aircraft, but the air force usually remains the prime instrument of a nation’s air power. The organization, command structure, and personnel grades within air forces vary from country to country. (See also military aircraft; air warfare.)
Key People: Hermann Göring Hosni Mubarak William Mitchell William Barker Barry Sadler
Related Topics: air group air staff wing air division airman
Original text
Rate this translation
Your feedback will be used to help improve Google Translate