Title: Tracking the Global AIDS Rate in 2023: Progress, Challenges, and a Path Forward
Introduction:
As the world evolves, so does our battle against the human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) and acquired immunodeficiency syndrome (AIDS). In 2023, it is crucial to analyze the global trends in AIDS rates, understand the progress achieved, acknowledge the challenges that remain, and outline strategies moving forward to combat this persistent global health issue.
Progress Made in AIDS Prevention and Treatment:
Over the past few decades, remarkable strides have been made in HIV prevention, education, and treatment. Access to antiretroviral therapy (ART) has expanded, helping individuals living with HIV lead healthy and productive lives. Global efforts to prevent mother-to-child transmission have seen remarkable success, resulting in fewer infants being born with HIV. Additionally, the availability of pre-exposure prophylaxis (PrEP) has contributed to reducing new infections among high-risk populations.
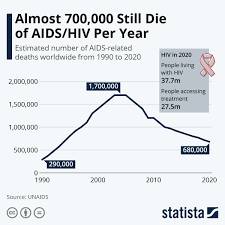
Global AIDS Rate in 2023:
Although significant progress has been made, the global AIDS rate remains a pressing concern. According to UNAIDS, approximately 38 million people were living with HIV worldwide in 2020. Out of these, around 1.5 million were children under the age of 15. The prevalence varied across regions, with sub-Saharan Africa being the most affected. However, the epidemic is not limited to this region, as many other parts of the world continue to face challenges in the fight against AIDS.
Challenges to Overcome in Combating AIDS:
1. Stigma and Discrimination: Despite increased awareness and education campaigns, stigma and discrimination towards people living with HIV remain prevalent. This hinders testing, treatment adherence, and social support systems, making it harder to control the spread of the disease.
2. Access to Healthcare: Unequal access to healthcare services, particularly in low-income and marginalized communities, continues to pose a significant challenge. Lack of resources, healthcare infrastructure, and trained personnel hinder early detection, treatment initiation, and retention in care.
3. Inadequate Prevention Efforts: Despite effective prevention methods available, such as the use of condoms, needle exchange programs, and education, the implementation and accessibility of these interventions remain inconsistent globally. This leads to ongoing transmission of the virus, especially among vulnerable populations like sex workers, men who have sex with men, and intravenous drug users.
4. Disruptions Caused by COVID-19: The COVID-19 pandemic has had unintended consequences on global HIV/AIDS efforts. Restrictions, interruptions in healthcare services, and diverted resources have affected HIV testing, treatment availability, and community support. This underscores the need to strengthen healthcare systems and ensure pandemics do not hamper progress against other health challenges.
The Way Forward:
1. Continued Funding: Sustained financial commitments from governments, international organizations, and private donors are crucial to strengthen healthcare systems, expand access to HIV testing and treatment, and support research for a potential cure and more effective prevention methods.
2. Education and Awareness: Promoting accurate knowledge about HIV transmission, prevention, and detection is vital to combat stigma and discrimination, encourage testing, and ensure early treatment initiation.
3. Improved Access: Enhancing access to affordable and culturally sensitive healthcare services and medications, especially in underserved communities, can contribute significantly to reducing AIDS rates.
4. Collaboration and Partnerships: Collaboration among governments, civil society organizations, researchers, and affected communities is essential to exchange knowledge, share best practices, and work together towards a comprehensive response.
Conclusion:
As we move through 2023, the global AIDS rate remains a complex challenge. Despite progress in prevention, treatment, and education, further efforts are necessary to address the remaining barriers. By tackling stigma and discrimination, improving access to healthcare, bolstering prevention efforts, and prioritizing research and funding, we can collectively strive towards an AIDS-free future. It is through unity, determination, and shared responsibility that we can amplify our impact and make global progress against this devastating pandemic.



No comments yet
Be the first to share your thoughts!