A new study has found higher rates of brain bleeds among those who took daily low-dose aspirin as a preventive drug with no significant protection against risk. Of course, anybody who has had a heart attack or intervention must have it life-long. Always go by the advice of your medical practitioner before picking up aspirin over the counter, says Dr Nishith Chandra, Principal Director, Interventional Cardiology, Fortis Escorts Heart Institute, Delhi
Aspirin
Low-dose aspirin, popularly known as baby aspirin, slows down the clotting action of platelets, thinning the blood, which can cause problems during injuries. (Source: Freepik)
For a long time, aspirin has been seen as a preventive pill which could protect healthy patients against a future heart attack or stroke. But as recent studies have shown — while the drug is indispensable for those who have already had a cardiac event or an intervention, like stenting or bypass — it has limited protective power in people who have not had a heart episode or atherosclerosis (plaque deposits). In fact, its preventive use comes at a cost of dangerous side effects like bleeding. That’s why you shouldn’t have it as a preventive, considering it is an over-the-counter drug.
Data from a large clinical trial of healthy older adults, the results of which were published in JAMA Network, found higher rates of brain bleeds among those who took daily low-dose aspirin and no significant protection against stroke. Low-dose aspirin, popularly known as baby aspirin, slows down the clotting action of platelets, thinning the blood, which can cause problems during injuries. Older people, who do not have a history of heart conditions or demonstrate any worrisome signs or symptoms of stroke, should be particularly cautious about taking aspirin, the study says as they are anyway more prone to falls and bleeding, which could be aggravated if they are on the drug. That’s too much of a cost compared to the benefits among the 60 plus group.
The new analysis used data from a study called “Aspirin in Reducing Events in the Elderly” or ASPREE, a randomised control trial of daily low-dose aspirin among people living in Australia and the US. The 19,114 participants were adults over 70, who were free of any symptomatic cardiovascular disease. (Any person with a history of stroke or heart attack was excluded from the study.) While aspirin did not show any significant effect on reducing the risk of stroke or clotting, it did raise the risk of intracranial bleeding by 38 per cent.
That’s why the US task force has said that anybody older than 60 and without a pre-existing heart disease and stroke should not be given aspirin as a preventive measure.
WHAT IS BABY ASPIRIN AND WHY DO WE ADMINISTER IT?
Aspirin
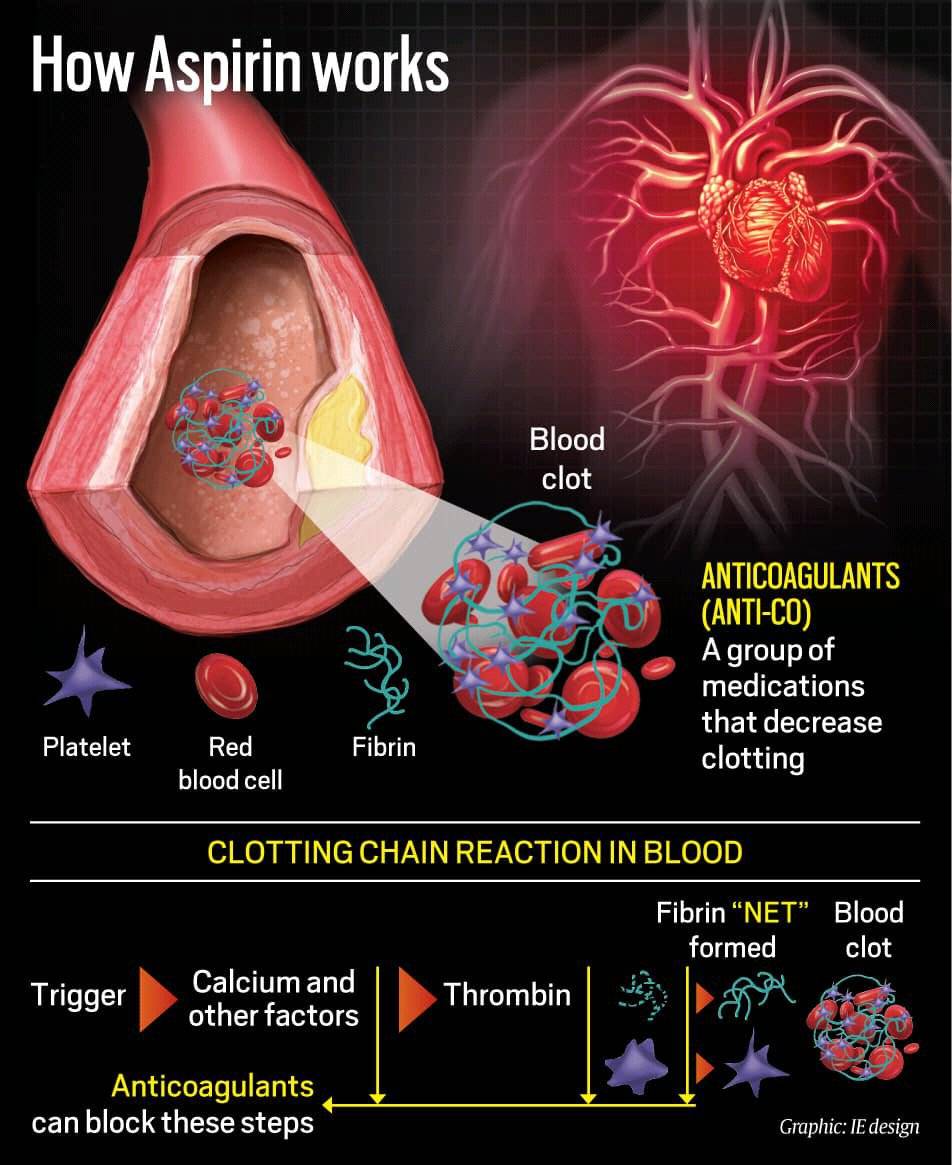
How aspirin works. (Designer by Abhishek Mitra)
In the early days, aspirin would be available as 350 mg to 600 mg tablets to prevent clumping of platelets in the blood that form clots in the blood vessels. Blood clots are the leading cause of heart attacks and strokes and form when plaque (deposits of cholesterol and other substances on artery walls) ruptures and your body tries to contain the tear by creating a blood clot as a plug. When arteries are already narrowed by plaque, a clot can block a blood vessel further and stop the flow of blood to the brain or heart. A regular dose of aspirin then becomes necessary to diminish the ability of your blood to cluster together and solidify.
Subsequently, the protocol was revised to administer anything between 81 to 100 mg. This is called a baby aspirin. For context, let me give you an example. Disprin has a higher aspirin content, between 300 mg and 600 mg. Which is why we always say it can be dangerous when bought over the counter and used indiscriminately as a painkiller. Ecosprin 75 is a baby aspirin.
WHAT ARE THE SIDE-EFFECTS OF ASPIRIN?
It can make your stomach lining sensitive and trigger gastric irritability, ulcers and bleeding. The risk of bleeding is what has made researchers relook at the preventive use of baby aspirin over a long time. Besides, a user would have to be particular about using any other medication that thins the blood too.
That’s why previous guidelines from the US Preventive Services Task Force warned against taking aspirin for primary prevention of heart disease unless you were at a heightened risk of heart attack or stroke. It advised it only for potential high risk stroke cases between the ages of 50 and 69 years old, particularly those who had a 10 per cent or greater chance of having a heart attack or stroke within the next 10 years. Some researchers had also tracked long term preventive baby aspirin use among women and found that it didn’t reduce their risk of heart attacks but increased their risk of bleeding. Some benefit was seen for women over the age of 65.
HOW IS ASPIRIN TO BE ADMINISTERED?
Always remember that once you have had a heart attack/stroke or a procedure like stenting and bypass, you will be given high dose aspirin to reduce blockages immediately after intervention. The dose is reduced later in a phased manner and has to be taken for a lifetime. All this means your cardiologist should be taking the call depending on your organ functionality.
Don’t self-medicate with aspirin in the hope of that becoming a preventive if you have not had any episode so far. Instead, take care of your co-morbidities in earnest. Sometimes cardiologists take a call on selective baby aspirin use among those who are at a very high risk like having significant plaque deposits in their arteries, having a 10 per cent higher risk of experiencing a heart episode in 10 years than others or have multiple co-morbidities like diabetes and hypertension as triggers. But for those with a lower risk, the disadvantages of the preventive use of aspirin outweigh the benefits. Statins, medication for blood pressure control and controlling blood sugar should work to lower risks.



No comments yet
Be the first to share your thoughts!