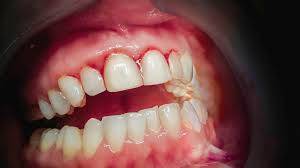
Gingivitis is a common and mild form of gum disease (periodontal disease) that causes irritation, redness, and swelling (inflammation) of your gingiva, the part of your gum around the base of your teeth.
**Causes of Gingivitis:**
1. Poor Oral Hygiene
2. Plaque Buildup
3. Smoking and Tobacco Use
4. Poor Nutrition
5. Dry Mouth (xerostomia)
6. Certain Medications
7. Ill-Fitting Dental Appliances
8. Hormonal Changes (e.g., pregnancy)
9. Medical Conditions (e.g., diabetes)
10. Genetic Predisposition
11. Certain Infections (e.g., viral)
12. Stress
13. Teeth Grinding (Bruxism)
14. Crooked Teeth
15. Dental Restorations with Poor Margins
16. Substance Abuse
17. Poor-Fitting Dental Bridges or Crowns
18. Nutritional Deficiencies
19. Immunodeficiency
20. Age (increased susceptibility)
**Signs of Gingivitis:**
1. Redness and Swelling of Gums
2. Bleeding Gums, Especially When Brushing or Flossing
3. Bad Breath (Halitosis)
4. Receding Gums
5. Tender Gums
6. Pus Between Teeth and Gums
7. Changes in Gum Color (from pink to dusky red)
8. Shiny Appearance of Gums
9. Soft Gums
10. Gum Pain or Discomfort
11. Loose Teeth
12. Gums That Easily Bleed Upon Touch
13. Persistent Metallic Taste
14. Formation of Gum Pockets
15. Gum Ulcers
16. Gum Boils or Abscesses
17. Gum Tenderness
18. Gums That Itch
19. Tooth Sensitivity
20. Gum Tissue Overgrowth
**Effects of Gingivitis:**
1. Progression to Periodontitis (advanced gum disease)
2. Tooth Decay
3. Tooth Loss
4. Tooth Mobility
5. Gum Recession
6. Abscess Formation
7. Halitosis (Bad Breath)
8. Painful Chewing
9. Compromised Nutrition
10. Reduced Quality of Life
11. Psychological Impact (self-esteem)
12. Spread of Infection
13. Dental Expenses
14. Difficulty Speaking
15. Increased Risk of Systemic Diseases (e.g., heart disease)
16. Prolonged or Chronic Inflammation
17. Bone Loss Around Teeth
18. Gum Tissue Damage
19. Tooth Sensitivity
20. Social Confidence Impact
**Solutions and Prevention for Gingivitis:**
1. Proper Oral Hygiene (Brushing and Flossing)
2. Regular Dental Check-ups and Cleanings
3. Antiseptic Mouthwashes
4. Dental Scaling and Root Planing
5. Professional Dental Care
6. Nutritious Diet
7. Drinking Water
8. Avoiding Tobacco Use
9. Stress Management Techniques
10. Proper Medication Use (if contributing)
11. Dental Appliances Adjusted or Replaced (if needed)
12. Gum Tissue Grafting (for recession)
13. Orthodontic Treatment (if misalignment is a factor)
14. Dental Restoration Reevaluation (e.g., crowns)
15. Scaling and Polishing Procedures
16. Eliminating Gum Irritation Sources
17. Diabetes Management (if relevant)
18. Regular Physical Activity
19. Addressing Dry Mouth
20. Education on Oral Health
Early detection and proper management of gingivitis can help prevent its progression to more severe periodontal disease and its associated complications.



No comments yet
Be the first to share your thoughts!