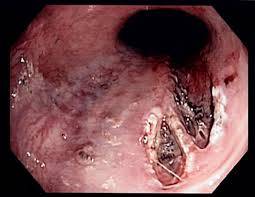
A Mallory-Weiss tear is a laceration in the mucous membrane at the junction of the esophagus and stomach, typically caused by severe or forceful vomiting. Here are 20 signs and symptoms, 20 potential causes, 20 effects, and solutions related to Mallory-Weiss tears:
**Signs and Symptoms:**
1. Hematemesis: Vomiting bright red or coffee-ground-like blood.
2. Epigastric Pain: Pain in the upper abdomen.
3. Nausea: Feeling sick to the stomach.
4. Vomiting: Forceful and recurrent vomiting.
5. Melena: Dark, tarry stools due to swallowed blood.
6. Hematochezia: Passing fresh blood in bowel movements.
7. Dizziness: Feeling lightheaded or faint.
8. Rapid Heartbeat: Tachycardia due to blood loss.
9. Low Blood Pressure: Hypotension from significant blood loss.
10. Pallor: Paleness of the skin.
11. Weakness: Feeling weak or fatigued.
12. Abdominal Tenderness: Sensitivity in the upper abdomen.
13. Anemia: Low red blood cell count from blood loss.
14. Hemodynamic Instability: Unstable vital signs due to bleeding.
15. Syncope: Fainting episodes.
16. Shortness of Breath: Difficulty breathing due to blood loss.
17. Dehydration: Reduced fluid levels from vomiting and blood loss.
18. Chest Pain: May mimic heart-related pain.
19. Fever: Infection may occur if the tear becomes contaminated.
20. Gastrointestinal Bleeding: Continuous or recurrent bleeding.
**Causes:**
1. Forceful Vomiting: Violent or persistent vomiting.
2. Alcohol Binge Drinking: Excessive alcohol consumption.
3. Overeating: Consuming large amounts of food.
4. Coughing: Severe, persistent coughing fits.
5. Pregnancy: Morning sickness and increased abdominal pressure.
6. Eating Disorders: Frequent vomiting in individuals with bulimia.
7. Weightlifting: Intense straining during weightlifting.
8. Medications: Some drugs can cause vomiting.
9. Infections: Severe gastroenteritis with vomiting.
10. Hiatal Hernia: Increased pressure on the stomach.
11. Esophageal Disorders: Conditions affecting the esophagus.
12. Eating Spicy or Irritating Foods: Can lead to vomiting.
13. Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease (GERD): Chronic acid reflux.
14. Sudden Shock or Trauma: Severe emotional or physical stress.
15. Chemotherapy: Certain cancer treatments.
16. Intestinal Obstruction: Increased abdominal pressure.
17. Retching: Repeated attempts to vomit.
18. Swallowed Toxins: Ingestion of harmful substances.
19. Bulimia Nervosa: An eating disorder characterized by binge eating and purging.
20. Gastrointestinal Surgeries: Surgical procedures involving the upper digestive tract.
**Effects:**
1. Blood Loss: Hemorrhage from the tear.
2. Anemia: Low red blood cell count due to blood loss.
3. Shock: Potentially life-threatening condition from severe blood loss.
4. Hypotension: Low blood pressure due to bleeding.
5. Tachycardia: Rapid heart rate in response to blood loss.
6. Hypoxia: Reduced oxygen levels in the blood.
7. Aspiration Pneumonia: Inhalation of stomach contents into the lungs.
8. Syncope: Fainting episodes.
9. Organ Dysfunction: Impaired organ function due to hypovolemia.
10. Infection: Infection risk if the tear becomes contaminated.
11. Scarring: Formation of scars at the tear site.
12. Persistent Symptoms: Ongoing pain or discomfort.
13. Fear of Vomiting: Psychological distress related to vomiting.
14. Esophageal Strictures: Narrowing of the esophagus from scarring.
15. Anxiety and Stress: Emotional impact of the tear and bleeding.
16. Gastrointestinal Symptoms: Ongoing gastrointestinal issues.
17. Dental Problems: Acid exposure can harm tooth enamel.
18. Reduced Quality of Life: Due to symptoms and psychological impact.
19. Weight Loss: Unintended weight loss.
20. Need for Medical Intervention: Ongoing monitoring and treatment.
**Solutions:**
1. Supportive Care: Intravenous fluids and blood transfusions if needed.
2. Endoscopy: To visualize and possibly treat the tear.
3. Proton Pump Inhibitors (PPIs): Medications to reduce stomach acid.
4. Antiemetics: Medications to control nausea and vomiting.
5. Blood Pressure Support: Medications to stabilize blood pressure.
6. Oxygen Therapy: Supplemental oxygen if hypoxia is present.
7. Esophageal Stent: Placement of a stent to support healing.
8. Hemostasis Procedures: Techniques to stop active bleeding.
9. Antibiotics: If there is a risk of infection.
10. Surgery: In rare cases, surgical repair may be necessary.
11. Counseling: Psychological support for emotional distress.
12. Lifestyle Changes: Avoiding triggers like alcohol or overeating.
13. Nutritional Support: Ensuring proper nutrition during recovery.
14. Esophageal Dilation: In cases of stricture formation.
15. Weight Management: Achieving and maintaining a healthy weight.
16. Follow-Up Care: Regular monitoring for complications.
17. Dental Care: Regular dental checkups and oral hygiene.
18. Stress Reduction: Techniques to manage stress and anxiety.
19. Avoiding Irritants: Identifying and avoiding potential triggers.
20. Education: Understanding the condition and preventive measures.
Treatment of Mallory-Weiss tears depends on the severity of symptoms and underlying causes, and consulting a healthcare professional is essential for proper diagnosis and management.


No comments yet
Be the first to share your thoughts!