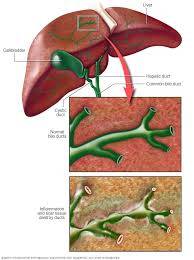
Primary biliary cirrhosis, now known as primary biliary cholangitis (PBC), is a chronic liver disease characterized by the inflammation and destruction of the bile ducts. Here are 20 potential factors related to PBC, along with signs and symptoms, effects, and solutions:
**Causes:**
1. Autoimmune disorder.
2. Genetic predisposition.
3. Environmental factors.
4. Hormonal factors (more common in women).
5. Family history of autoimmune diseases.
6. Viral infections.
7. Hormonal changes during menopause.
8. Bacterial infections.
9. Toxic chemical exposure.
10. Medications (e.g., certain antibiotics).
11. Hormone replacement therapy.
12. Cigarette smoking.
13. Certain chemicals and toxins.
14. Immunological factors.
15. Radiation exposure.
16. Microbial factors.
17. Hormonal contraceptives.
18. Ethnic and geographic factors.
19. Seasonal variation in disease onset.
20. Stress and emotional factors.
**Signs and Symptoms:**
1. Fatigue.
2. Itchy skin (pruritus).
3. Jaundice (yellowing of the skin and eyes).
4. Abdominal pain and discomfort.
5. Unexplained weight loss.
6. Dry eyes and mouth (sicca syndrome).
7. Cognitive changes.
8. Bone and joint pain.
9. Enlargement of the liver and spleen.
10. Elevated levels of liver enzymes.
11. Hyperlipidemia (elevated blood lipids).
12. Xanthelasma (yellowish cholesterol deposits in skin).
13. Osteoporosis.
14. Thyroid disorders.
15. Kidney problems.
16. High cholesterol levels.
17. Increased susceptibility to infections.
18. Hematological abnormalities.
19. Impaired fat-soluble vitamin absorption.
20. Gastrointestinal disturbances (e.g., diarrhea).
**Effects:**
1. Bile duct damage and inflammation.
2. Liver damage and cirrhosis.
3. Impairment of liver function.
4. Malabsorption of fat-soluble vitamins (A, D, E, K).
5. Metabolic complications.
6. Osteoporosis and bone fractures.
7. Increased risk of infections.
8. Cardiovascular issues.
9. Cognitive and mood changes.
10. Sicca syndrome.
11. Increased risk of gastrointestinal cancers.
12. Impaired quality of life.
13. Impairment of kidney function.
14. Increased healthcare costs.
15. Reduced life expectancy.
16. Increased risk of complications during surgery.
17. Social and relationship issues.
18. Impaired bone health.
19. Impaired fat metabolism.
20. Hematological and thyroid issues.
**Solutions:**
1. Early diagnosis and medical evaluation.
2. Medications to manage symptoms and slow disease progression (e.g., ursodeoxycholic acid).
3. Supportive care for managing complications.
4. Management of bone health (calcium and vitamin D supplements).
5. Lifestyle changes, including a healthy diet and exercise.
6. Support from healthcare professionals.
7. Psychological support and counseling.
8. Support from family and friends.
9. Support groups for PBC patients.
10. Regular medical monitoring.
11. Vaccinations to prevent infections.
12. Managing cardiovascular risk factors (e.g., cholesterol levels).
13. Monitoring for cancer and managing cancer risk.
14. Hepatitis A and B vaccinations.
15. Educational programs for healthcare professionals.
16. Public health initiatives to promote awareness.
17. Legal regulations and policies to reduce toxin exposure.
18. Avoiding alcohol and certain medications.
19. Smoking cessation.
20. Stress management techniques.
Early intervention, proper management, and lifestyle adjustments are crucial in the care of individuals with primary biliary cholangitis. If you suspect you have PBC or are at risk, consult a healthcare professional for evaluation and guidance.


No comments yet
Be the first to share your thoughts!