Alagille syndrome is a rare genetic disorder that primarily affects the liver and can involve other organs. Here are 20 factors related to Alagille syndrome, along with signs and symptoms, effects, and solutions:
**Causes:**
1. Genetic mutations in the JAG1 or NOTCH2 genes.
2. Autosomal dominant inheritance.
3. De novo mutations (new genetic mutations).
4. Family history of Alagille syndrome.
5. Mutations that affect bile duct formation.
6. Variable expressivity of genetic mutations.
7. Environmental factors (possibly involved).
8. Rare mutations in other genes.
9. Interactions with genetic modifiers.
10. Genetic counseling and testing.
11. Ethnic and geographic factors.
12. Gender-neutral disorder.
13. Hormonal factors.
14. Family size (more children may carry the mutation).
15. Advanced parental age.
16. Consanguinity (marriages between close relatives).
17. Environmental toxins (possible influence).
18. Pregnancy factors (may affect severity).
19. Risk of mosaicism (mutations in some cells).
20. Microbial factors.
**Signs and Symptoms:**
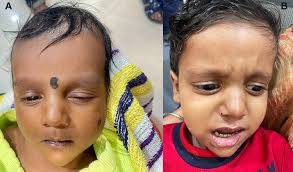
1. Jaundice (yellowing of the skin and eyes).
2. Pruritus (itchy skin).
3. Cholestasis (impaired bile flow).
4. Poor weight gain and growth (in children).
5. Abnormal facial features (butterfly vertebrae, pointed chin).
6. Enlargement of the liver and spleen.
7. Xanthomas (yellow cholesterol deposits).
8. Cardiac abnormalities (e.g., heart murmur).
9. Butterfly vertebrae (vertebral abnormalities).
10. Eye problems (e.g., posterior embryotoxon).
11. Renal abnormalities.
12. Vascular abnormalities.
13. Cognitive and developmental issues.
14. Bone and joint abnormalities.
15. Dental problems.
16. Hyperlipidemia (elevated blood lipids).
17. Short stature.
18. Thyroid disorders.
19. Coagulation problems.
20. Hearing loss.
**Effects:**
1. Impaired bile duct formation and function.
2. Cholestasis and liver damage.
3. Impairment of liver function.
4. Reduced ability to absorb fat-soluble vitamins.
5. Growth and developmental delays (in children).
6. Bone and vertebral abnormalities.
7. Cognitive and developmental challenges.
8. Impaired quality of life.
9. Increased healthcare costs.
10. Risk of complications during surgery.
11. Risk of bleeding disorders.
12. Dental issues.
13. Cardiovascular issues.
14. Hyperlipidemia.
15. Renal problems.
16. Impaired bone health.
17. Impaired thyroid function.
18. Hearing loss.
19. Cognitive and behavioral challenges.
20. Increased susceptibility to infections.
**Solutions:**
1. Genetic testing and counseling for at-risk individuals.
2. Multidisciplinary medical care to manage symptoms.
3. Medications and treatments to address specific issues.
4. Nutritional support, including fat-soluble vitamin supplementation.
5. Lifestyle changes, including a healthy diet and exercise.
6. Support from healthcare professionals.
7. Psychological support and counseling.
8. Support from family and friends.
9. Support groups for Alagille syndrome patients.
10. Regular medical monitoring and management of complications.
11. Hearing evaluations and hearing aids when needed.
12. Educational programs for healthcare professionals.
13. Public health initiatives to promote awareness.
14. Legal regulations and policies to reduce toxin exposure.
15. Avoiding alcohol and certain medications.
16. Smoking cessation.
17. Stress management techniques.
18. Genetic counseling and testing for family members.
19. Growth hormone therapy for growth delays (in children).
20. Liver transplant evaluation in severe cases.
Managing Alagille syndrome often involves ongoing medical care and a multidisciplinary approach to address the wide range of potential symptoms and complications. If you suspect you or someone you know has Alagille syndrome, consult a healthcare professional for evaluation and guidance.



No comments yet
Be the first to share your thoughts!