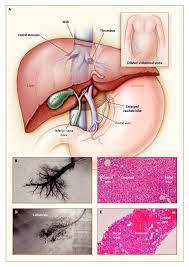
Budd-Chiari syndrome is a rare condition that occurs when the blood flow from the liver is partially or completely blocked. Here are 20 potential factors related to Budd-Chiari syndrome, along with signs and symptoms, effects, and solutions:
**Causes:**
1. Blood clot in the hepatic veins.
2. Myeloproliferative disorders (e.g., polycythemia vera).
3. Genetic mutations related to clotting disorders.
4. Pregnancy and postpartum state (related to clotting risk).
5. Use of oral contraceptives or hormone replacement therapy.
6. Inflammatory conditions (e.g., Behçet's disease).
7. Liver tumors or masses compressing veins.
8. Trauma or injury to the liver.
9. Infections (rarely associated).
10. Autoimmune diseases (e.g., systemic lupus erythematosus).
11. Thrombophilia (increased clotting tendency).
12. High clotting factors in the blood (hypercoagulable states).
13. Liver surgery or transplantation (rarely).
14. Chronic inflammatory conditions (e.g., inflammatory bowel disease).
15. Use of certain medications (e.g., azathioprine).
16. Hematological disorders (e.g., paroxysmal nocturnal hemoglobinuria).
17. Exposure to environmental toxins.
18. Dehydration.
19. Hyperhomocysteinemia (elevated homocysteine levels).
20. Rare hereditary factors.
**Signs and Symptoms:**
1. Abdominal pain and discomfort (upper right quadrant).
2. Enlargement of the liver.
3. Ascites (fluid buildup in the abdomen).
4. Jaundice (yellowing of the skin and eyes).
5. Hepatomegaly (enlarged liver).
6. Splenomegaly (enlarged spleen).
7. Fatigue and weakness.
8. Anorexia (loss of appetite).
9. Nausea and vomiting.
10. Abdominal fullness.
11. Spider-like blood vessels on the skin (spider angiomas).
12. Liver tenderness.
13. Liver tenderness.
14. Swelling of the legs and ankles (edema).
15. Gastrointestinal bleeding.
16. Cognitive changes (hepatic encephalopathy).
17. Renal dysfunction.
18. Venous collaterals (engorged blood vessels).
19. Heart and lung complications (e.g., pulmonary embolism).
20. Weight loss.
**Effects:**
1. Liver damage and cirrhosis.
2. Impairment of liver function.
3. Impaired blood flow from the liver.
4. Accumulation of toxins in the blood.
5. Hepatic encephalopathy (cognitive changes).
6. Portal hypertension (high blood pressure in the liver's blood vessels).
7. Increased risk of liver cancer.
8. Abdominal fluid buildup (ascites).
9. Kidney problems.
10. Gastrointestinal bleeding.
11. Impairment of quality of life.
12. Malnutrition and weight loss.
13. Cardiovascular issues.
14. Thromboembolic complications.
15. Risk of complications during surgery.
16. Psychological and cognitive issues.
17. Renal dysfunction.
18. Enlargement of the liver and spleen.
19. Swelling in the legs and ankles (edema).
20. Increased healthcare costs.
**Solutions:**
1. Diagnosis through imaging and blood tests.
2. Management of the underlying cause (e.g., anticoagulation for clotting disorders).
3. Liver transplant evaluation in severe cases.
4. Medications to reduce blood clotting



No comments yet
Be the first to share your thoughts!