Testicular tuberculosis is a rare form of extrapulmonary tuberculosis that affects the testicles. It occurs when the bacteria responsible for tuberculosis, Mycobacterium tuberculosis, infect the testicular tissue. Here are some key points regarding its causes, symptoms, and treatment:
Tuberculosis can affect many organs in the genitourinary region. It affects the testicles at a rate of 0.5% among the genitourinary organs. It is one of the rare forms of extra-pulmonary involvement
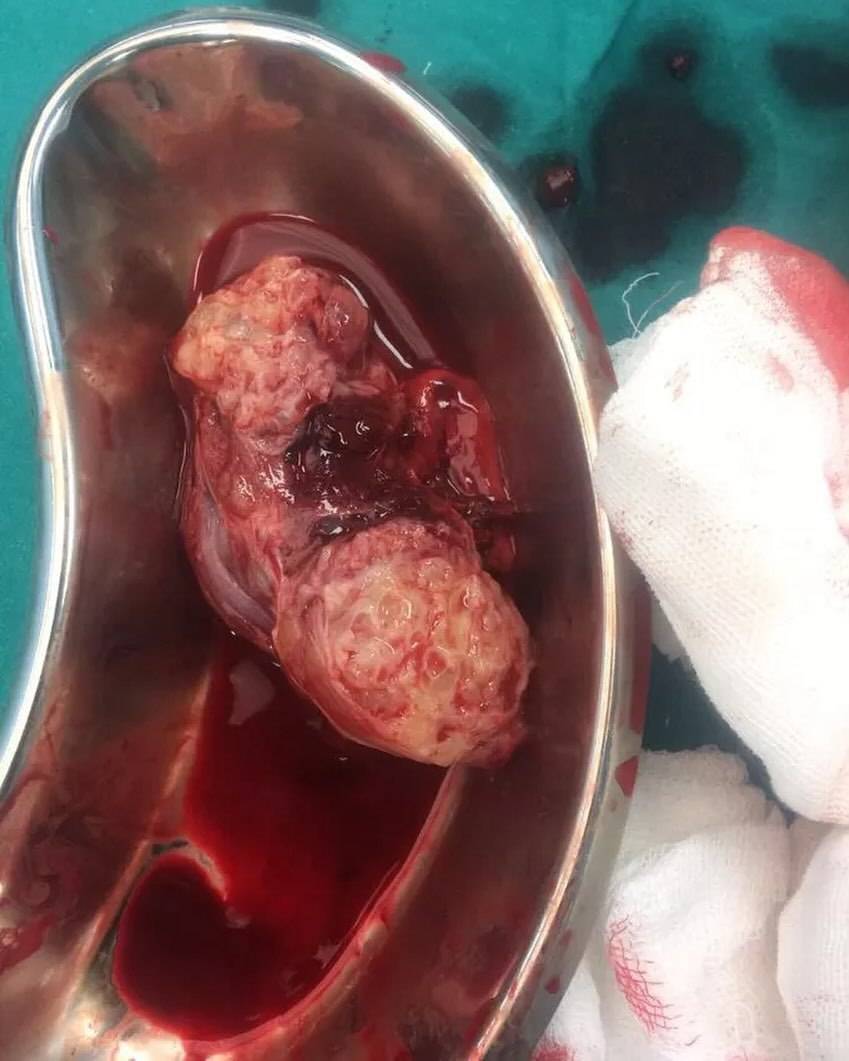
Tuberculosis orchitis usually occurs as a result of contiguous extension from the epididymis. It is considered to reflect a later stage of the disease process. Isolated tuberculosis orchitis from hematogenous spread without epididymal involvement is rare.
Causes:
1. Infection Spread: Testicular tuberculosis usually results from the spread of tuberculosis from other parts of the body, such as the lungs.
2. Blood or Lymphatic Spread: The bacteria can reach the testicles through the bloodstream or lymphatic system.
Symptoms:
1. Pain and Swelling: Affected individuals may experience pain and swelling in one or both testicles.
2. Scrotal Mass: A painless, firm mass or lump within the testicle can be a symptom.
3. Epididymal Involvement: The epididymis, a structure adjacent to the testicle, may also be affected, leading to epididymitis.
4. Systemic Symptoms: In some cases, systemic symptoms like fever, weight loss, and night sweats may occur.
Treatment:
1. Anti-Tuberculosis Medications: Testicular tuberculosis is treated with standard anti-tuberculosis drugs, such as isoniazid, rifampicin, pyrazinamide, and ethambutol. Treatment typically lasts for several months.
2. Surgery: Surgical intervention may be necessary in cases of abscess formation, extensive tissue damage, or when the infection does not respond to medications.
3. Pain Management: Pain and discomfort can be managed with analgesics and anti-inflammatory medications.
4. Follow-Up: Regular follow-up with a healthcare provider is essential to monitor treatment progress and ensure complete recovery.
It's crucial for individuals with suspected testicular tuberculosis to consult a healthcare professional for a proper diagnosis and tailored treatment plan.



No comments yet
Be the first to share your thoughts!