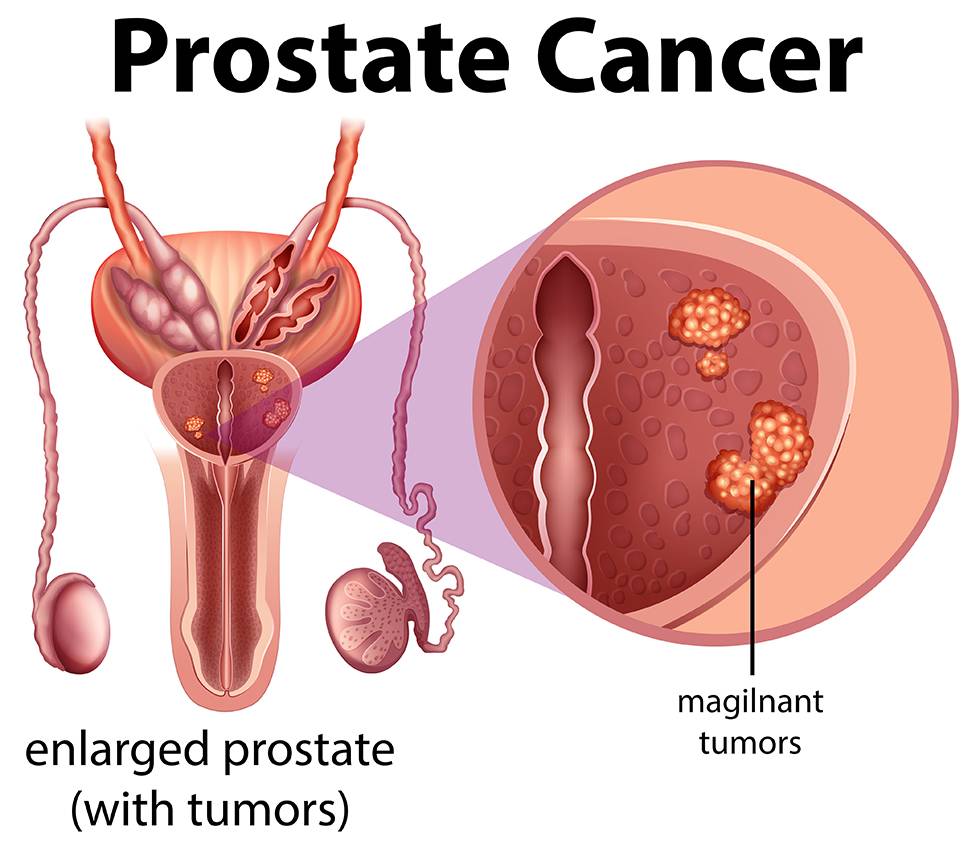
Prostate cancer is a prevalent and potentially life-threatening condition that affects the prostate gland, a small walnut-shaped organ in men that produces seminal fluid. As we delve into the nuances of this disease, it's essential to understand its prevalence, risk factors, symptoms, diagnosis, treatment options, and the importance of early detection.
Prevalence and Risk Factors:
Prostate cancer is one of the most common cancers among men globally. According to the World Health Organization (WHO), it accounts for a significant percentage of cancer diagnoses. Age is a primary risk factor, with the likelihood of developing prostate cancer increasing with age. Family history, race, and genetics also play roles, as men with close relatives who have had prostate cancer are at a higher risk.
Symptoms and Early Detection:
Prostate cancer often exhibits no symptoms in its early stages. However, as the disease progresses, symptoms may include difficulty urinating, blood in the urine or semen, discomfort in the pelvic area, and bone pain. Early detection is crucial for effective treatment, making regular screenings, such as the prostate-specific antigen (PSA) blood test and digital rectal exam (DRE), vital components of men's healthcare routines.
Diagnosis and Staging:
If prostate cancer is suspected, a series of diagnostic tests are employed. These may include a biopsy, imaging tests like MRI or CT scans, and bone scans to determine the extent of the cancer. Staging is crucial in determining the appropriate treatment plan. The stages range from localized cancer within the prostate to advanced cases that have spread to distant organs.
Treatment Options:
Treatment strategies for prostate cancer vary based on the cancer's stage, grade, and the patient's overall health. Common treatments include surgery, radiation therapy, hormone therapy, chemotherapy, and immunotherapy. In some cases, a combination of these approaches may be recommended. The choice of treatment is a collaborative decision between the patient and their healthcare team.
Surgery:
Surgical options for prostate cancer include radical prostatectomy, where the entire prostate gland is removed, and transurethral resection, a procedure to relieve symptoms by removing obstructive prostate tissue.
Radiation Therapy:
Radiation therapy utilizes high-energy rays to target and destroy cancer cells. It can be delivered externally or through implants within the prostate. This treatment is often used in conjunction with surgery or as a primary treatment for localized cancer.
Hormone Therapy:
Hormone therapy aims to reduce the levels of male hormones (androgens) in the body, as these hormones can stimulate the growth of prostate cancer cells. This approach is particularly effective in treating cancers that have spread beyond the prostate.
Chemotherapy:
Chemotherapy involves the use of drugs to kill or slow the growth of cancer cells. While not the primary treatment for early-stage prostate cancer, it may be recommended for advanced cases.
Immunotherapy:
Immunotherapy enhances the body's immune system to target and destroy cancer cells. This innovative approach is being researched for its potential in treating prostate cancer.
Supportive Care:
Prostate cancer and its treatments can have physical and emotional side effects. Supportive care, including counseling, support groups, and medications to manage side effects, plays a crucial role in enhancing the quality of life for individuals facing prostate cancer.
Preventive Measures:
While the exact cause of prostate cancer remains unclear, adopting a healthy lifestyle can contribute to prevention. This includes maintaining a balanced diet, regular exercise, avoiding tobacco, and moderating alcohol consumption. Additionally, early detection through routine screenings significantly improves the prognosis.
Conclusion:
Prostate cancer is a complex and multifaceted disease that requires a comprehensive approach to diagnosis, treatment, and support. As we celebrate advancements in medical science that have improved the prognosis for many individuals, ongoing research and awareness efforts remain paramount. Regular health check-ups, open communication with healthcare providers, and a commitment to a healthy lifestyle are essential in the collective effort to combat prostate cancer and improve men's health worldwide.q



No comments yet
Be the first to share your thoughts!