Understanding Hypertension: Causes, Symptoms, Treatment, and Prevention
Introduction to Hypertension
Hypertension, commonly known as high blood pressure, is a significant health concern worldwide. It is a condition in which the force of the blood against the artery walls is consistently too high. Over time, this can lead to serious health problems, including heart disease, stroke, and kidney failure. Despite its prevalence and potential severity, hypertension often goes undetected and untreated, making it essential to raise awareness about its causes, symptoms, treatment options, and prevention strategies.
Understanding Blood Pressure
To understand hypertension, it's crucial to grasp the concept of blood pressure. Blood pressure is the force exerted by the blood against the walls of the blood vessels as it flows through them. It is typically measured in millimeters of mercury (mmHg) and consists of two numbers: systolic pressure (the top number) and diastolic pressure (the bottom number).
Systolic pressure measures the pressure in the arteries when the heart beats, pumping blood out, while diastolic pressure measures the pressure in the arteries when the heart is at rest between beats. Normal blood pressure is usually considered to be around 120/80 mmHg, with slight variations depending on factors such as age and overall health.
Understanding Hypertension Levels
Hypertension is classified into different stages based on blood pressure readings:
1. Normal: Systolic less than 120 mmHg and diastolic less than 80 mmHg.
2. Elevated: Systolic between 120-129 mmHg and diastolic less than 80 mmHg.
3. Stage 1 Hypertension: Systolic between 130-139 mmHg or diastolic between 80-89 mmHg.
4. Stage 2 Hypertension: Systolic 140 mmHg or higher or diastolic 90 mmHg or higher.
Causes of Hypertension
Hypertension can be caused by various factors, including:
1. Unhealthy lifestyle habits: Poor diet, lack of physical activity, excessive alcohol consumption, and smoking can contribute to high blood pressure.
2. Genetics: Family history of hypertension increases the risk of developing the condition.
3. Age: Blood pressure tends to increase with age as arteries become less flexible.
4. Obesity: Being overweight or obese puts extra strain on the heart and increases blood pressure.
5. Chronic conditions: Certain medical conditions, such as diabetes, kidney disease, and sleep apnea, can raise blood pressure.
6. Stress: Chronic stress can temporarily elevate blood pressure and, over time, contribute to hypertension.
Symptoms of Hypertension
Hypertension is often referred to as a "silent killer" because it typically doesn't cause noticeable symptoms until it reaches a severe stage or leads to complications. However, some people may experience symptoms such as:
1. Headaches
2. Shortness of breath
3. Dizziness
4. Chest pain
5. Visual changes
6. Fatigue
7. Nausea
It's essential to monitor blood pressure regularly, especially for individuals with risk factors for hypertension, even if they don't experience symptoms.
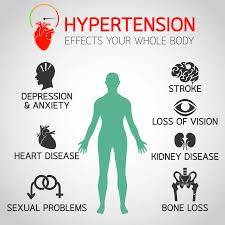
Complications of Hypertension
If left untreated, hypertension can lead to various serious health complications, including:
1. Heart disease: High blood pressure can damage the arteries and increase the risk of coronary artery disease, heart attack, and heart failure.
2. Stroke: Hypertension can cause blood vessels in the brain to narrow or rupture, leading to a stroke.
3. Kidney damage: Chronic high blood pressure can damage the kidneys' blood vessels and impair their function, leading to kidney failure.
4. Vision loss: Hypertension can damage the blood vessels in the eyes, leading to vision problems or even blindness.
5. Peripheral artery disease: Narrowing of the arteries due to hypertension can reduce blood flow to the limbs, leading to pain and tissue damage.
Treatment Options for Hypertension
Managing hypertension typically involves a combination of lifestyle changes and medication. Treatment goals aim to lower blood pressure and reduce the risk of complications. Treatment options include:
1. Lifestyle modifications:
- Healthy diet: Emphasize fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins while limiting sodium, saturated fats, and added sugars.
- Regular exercise: Aim for at least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity aerobic activity or 75 minutes of vigorous-intensity activity per week.
- Weight management: Losing weight can help lower blood pressure, especially for individuals who are overweight or obese.
- Limit alcohol intake: Men should limit alcohol to two drinks per day, while women should limit it to one drink per day.
- Quit smoking: Smoking increases blood pressure and damages blood vessels, so quitting is essential for overall cardiovascular health.
- Stress management: Techniques such as deep breathing, meditation, and yoga can help reduce stress levels.
2. Medications:
- Diuretics: Help the kidneys eliminate excess sodium and water from the body, reducing blood volume and lowering blood pressure.
- ACE inhibitors: Relax blood vessels, making it easier for blood to flow and lowering blood pressure.
- Calcium channel blockers: Prevent calcium from entering the heart and blood vessel cells, leading to relaxation of blood vessels and lower blood pressure.
- Beta-blockers: Reduce the heart rate and decrease the force of contraction, lowering blood pressure.
- Angiotensin II receptor blockers (ARBs): Block the action of angiotensin II, a hormone that narrows blood vessels, leading to lower blood pressure.
It's essential for individuals with hypertension to work closely with their healthcare providers to develop a personalized treatment plan based on their specific needs and medical history.
Prevention Strategies for Hypertension
While some risk factors for hypertension, such as age and genetics, are beyond our control, there are steps we can take to reduce the risk and prevent the condition:
1. Adopt a healthy lifestyle: Follow a balanced diet, engage in regular physical activity, maintain a healthy weight, limit alcohol consumption, and avoid smoking.
2. Monitor blood pressure: Regularly check blood pressure levels, especially if you have risk factors for hypertension or a family history of the condition.
3. Manage stress: Find healthy ways to cope with stress, such as relaxation techniques, exercise, hobbies, or social support.
4. Get regular check-ups: Visit your healthcare provider regularly for preventive care and screenings to detect and manage hypertension and other health conditions early.
5. Follow medical advice: If diagnosed with hypertension, follow your healthcare provider's recommendations for treatment and lifestyle modifications to keep blood pressure under control.
Conclusion
Hypertension is a common and serious health condition that affects millions of people worldwide. While it often doesn't cause symptoms, untreated hypertension can lead to severe complications such as heart disease, stroke, and kidney failure. Fortunately, hypertension can be effectively managed with lifestyle changes, medication, and regular monitoring. By adopting a healthy lifestyle, managing stress, and following medical advice, individuals can reduce their risk of developing hypertension and improve their overall cardiovascular health. Awareness, education, and proactive management are essential in the fight against hypertension and its associated complications.



No comments yet
Be the first to share your thoughts!