Arrhythmias: Causes, Types, Symptoms, and Treatments
**Introduction**
Arrhythmias are disruptions in the rhythm or rate of the heartbeat. They occur when the electrical impulses that coordinate heartbeats don't work properly, causing the heart to beat too fast, too slow, or irregularly. Arrhythmias can range from harmless to life-threatening and can affect people of all ages. Understanding the causes, types, symptoms, and treatments of arrhythmias is essential for proper management and prevention of complications.
**Causes of Arrhythmias**
1. **Heart Conditions**: Various heart conditions can predispose individuals to arrhythmias. These include coronary artery disease, heart valve disorders, heart failure, congenital heart defects, and cardiomyopathy.
2. **Electrolyte Imbalances**: Imbalances in essential minerals like potassium, sodium, calcium, and magnesium can disrupt the heart's electrical activity, leading to arrhythmias.
3. **Medications**: Certain medications, especially those used to treat high blood pressure, asthma, depression, and other conditions, can trigger arrhythmias as a side effect.
4. **Substance Abuse**: Excessive consumption of caffeine, nicotine, alcohol, and illicit drugs like cocaine or amphetamines can induce arrhythmias.
5. **Stress and Anxiety**: Intense emotional or physical stress can stimulate the release of stress hormones, which may affect heart rhythm.
6. **Genetic Factors**: Some arrhythmias have a genetic component, meaning they can run in families.
7. **Age**: The risk of developing arrhythmias increases with age, as the heart's electrical system may become less efficient over time.
**Types of Arrhythmias**
1. **Atrial Fibrillation (AFib)**: AFib is the most common type of arrhythmia, characterized by rapid and irregular heartbeat originating in the heart's upper chambers (atria). It increases the risk of stroke and heart failure.
2. **Atrial Flutter**: Similar to AFib, atrial flutter involves rapid but regular contractions of the atria. It can also increase the risk of stroke and heart failure.
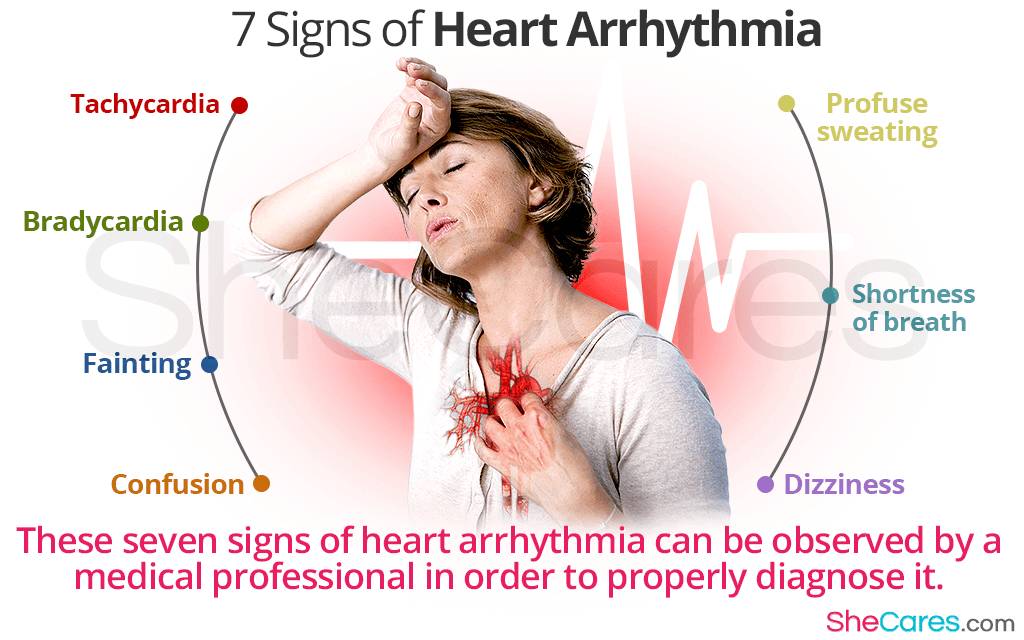
3. **Bradycardia**: Bradycardia is a slow heartbeat, usually defined as fewer than 60 beats per minute. It can result from aging, heart damage, or certain medications.
4. **Tachycardia**: Tachycardia is a fast heartbeat, typically exceeding 100 beats per minute. It can occur in the atria (supraventricular tachycardia) or ventricles (ventricular tachycardia).
5. **Premature Contractions**: Premature atrial contractions (PACs) and premature ventricular contractions (PVCs) are extra, abnormal heartbeats that occur before the next normal heartbeat. They are usually harmless but can cause discomfort.
6. **Ventricular Fibrillation**: Ventricular fibrillation is a life-threatening arrhythmia characterized by rapid, chaotic contractions of the heart's ventricles. It can lead to sudden cardiac arrest and requires immediate medical intervention.
**Symptoms of Arrhythmias**
The symptoms of arrhythmias can vary depending on the type and severity of the condition. Some common symptoms include:
1. **Palpitations**: Sensations of rapid, fluttering, or pounding heartbeat.
2. **Fatigue**: Feeling unusually tired or weak, even with normal activity.
3. **Dizziness or lightheadedness**: Feeling faint or dizzy, especially when standing up quickly.
4. **Shortness of breath**: Difficulty breathing or catching your breath, even at rest.
5. **Chest pain or discomfort**: Pressure, tightness, or pain in the chest, which may resemble a heart attack.
6. **Syncope**: Fainting or loss of consciousness, particularly in severe cases of arrhythmia.
It's important to note that some arrhythmias may not cause any noticeable symptoms and may only be detected during routine medical exams or diagnostic tests.
**Diagnosis of Arrhythmias**
Diagnosing arrhythmias typically involves a combination of medical history review, physical examination, and diagnostic tests. These may include:
1. **Electrocardiogram (ECG or EKG)**: This non-invasive test records the heart's electrical activity and can detect abnormal rhythms.
2. **Holter Monitor**: A portable device worn for 24 to 48 hours to continuously record the heart's activity, allowing for the detection of intermittent arrhythmias.
3. **Event Monitor**: Similar to a Holter monitor, but worn for a longer period and activated by the patient when they experience symptoms.
4. **Echocardiogram**: This imaging test uses sound waves to create a moving picture of the heart, helping to evaluate its structure and function.
5. **Stress Test**: During a stress test, the heart's activity is monitored while the patient exercises on a treadmill or stationary bike, providing information about how the heart responds to physical exertion.
6. **Electrophysiological (EP) Study**: In this invasive procedure, catheters are threaded through blood vessels to the heart, where they measure the heart's electrical activity and help identify the source of arrhythmias.
**Treatment Options for Arrhythmias**
1. **Lifestyle Changes**: Making healthy lifestyle choices can often help manage arrhythmias. This includes maintaining a balanced diet, exercising regularly, avoiding excessive alcohol and caffeine consumption, managing stress, and quitting smoking.
2. **Medications**: Various medications may be prescribed to control heart rhythm and rate, regulate blood pressure, prevent blood clots, and manage underlying heart conditions.
3. **Cardioversion**: Cardioversion is a procedure that uses electrical shocks or medications to restore normal heart rhythm in individuals with certain types of arrhythmias, such as AFib.
4. **Catheter Ablation**: During catheter ablation, thin, flexible wires (catheters) are inserted into the heart to destroy areas of abnormal electrical tissue causing arrhythmias.
5. **Implantable Devices**: Devices like pacemakers and implantable cardioverter-defibrillators (ICDs) can help regulate heart rhythm and deliver electric shocks if dangerous arrhythmias occur.
6. **Surgery**: In some cases, surgical procedures may be necessary to correct underlying heart conditions or implant devices to manage arrhythmias.
**Prevention and Management**
Preventing and managing arrhythmias often involves a combination of lifestyle modifications, regular medical follow-ups, and adherence to treatment plans. Some key strategies include:
1. **Regular Exercise**: Engaging in regular physical activity can strengthen the heart and improve overall cardiovascular health.
2. **Healthy Diet**: Consuming a balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, lean proteins, and healthy fats can support heart health and reduce the risk of arrhythmias.
3. **Stress Management**: Practicing relaxation techniques such as deep breathing, meditation, or yoga can help reduce stress and promote heart health.
4. **Regular Medical Check-ups**: Routine check-ups with healthcare providers are essential for monitoring heart health, detecting arrhythmias early, and adjusting treatment plans as needed.
5. **Medication Adherence**: It's crucial to take prescribed medications as directed and to communicate with healthcare providers about any side effects or concerns.
6. **Avoiding Triggers**: Identifying and avoiding triggers such as caffeine, alcohol, and stressors that can exacerbate arrhythm



No comments yet
Be the first to share your thoughts!