How to Prevent Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD)
Introduction:
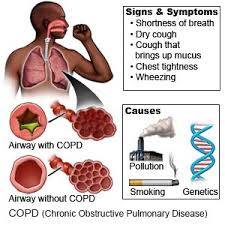
Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD) is a progressive lung disease that makes it hard to breathe. It encompasses various conditions such as emphysema, chronic bronchitis, and refractory (non-reversible) asthma. COPD is a leading cause of morbidity and mortality worldwide, with smoking being the primary risk factor. However, exposure to pollutants, genetic predisposition, and respiratory infections also contribute to its development. While COPD is a chronic and progressive condition, there are steps individuals can take to prevent its onset or slow its progression. This article aims to provide a comprehensive guide on how to prevent COPD.
Understanding COPD:
Before diving into prevention strategies, it's crucial to understand COPD and its risk factors. COPD is characterized by airflow limitation due to inflammation and structural changes in the lungs. The most common symptoms include breathlessness, chronic cough, and excessive sputum production. Over time, COPD can significantly impair quality of life and lead to complications such as respiratory infections, pulmonary hypertension, and heart disease.
Risk Factors:
1. Smoking: Tobacco smoke is the leading cause of COPD. Smokers are at a significantly higher risk of developing COPD compared to non-smokers. Additionally, exposure to secondhand smoke can also contribute to the development of the disease.
2. Environmental Exposure: Prolonged exposure to pollutants such as industrial fumes, biomass smoke, and indoor air pollutants can increase the risk of COPD. Occupational exposure to dust, chemicals, and fumes is also a significant risk factor.
3. Genetics: Genetic factors play a role in COPD susceptibility. Alpha-1 antitrypsin deficiency, an inherited condition, predisposes individuals to early-onset COPD, particularly in non-smokers.
4. Respiratory Infections: Recurrent respiratory infections, especially during childhood, can damage the lungs and increase the risk of developing COPD later in life.
Prevention Strategies:
1. Smoking Cessation:
- Quitting smoking is the single most effective way to prevent COPD and slow its progression. Even long-term smokers can benefit from quitting at any age.
- Seek support from healthcare professionals, use nicotine replacement therapy, or join smoking cessation programs to increase your chances of success.
- Create a smoke-free environment at home and avoid places where smoking is permitted to reduce exposure to secondhand smoke.
2. Avoiding Environmental Pollutants:
- Minimize exposure to indoor and outdoor air pollutants by using air purifiers, ensuring proper ventilation, and avoiding areas with high levels of pollution.
- If you work in an environment with potential respiratory hazards, use appropriate personal protective equipment and follow safety protocols to reduce exposure.
3. Occupational Safety:
- Employers should implement measures to protect workers from occupational hazards such as dust, chemicals, and fumes. This may include providing respiratory protective equipment and implementing engineering controls to minimize exposure.
4. Regular Exercise:
- Engage in regular physical activity to improve lung function and overall health. Aerobic exercises such as walking, swimming, and cycling can strengthen respiratory muscles and enhance lung capacity.
- Consult with a healthcare provider before starting any exercise regimen, especially if you have pre-existing respiratory conditions.
5. Healthy Diet:
- Maintain a balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins. Certain nutrients such as antioxidants, omega-3 fatty acids, and vitamin D may have protective effects on lung health.
- Stay hydrated by drinking an adequate amount of water, as dehydration can exacerbate respiratory symptoms.
6. Immunizations:
- Stay up-to-date with vaccinations, including annual flu shots and pneumococcal vaccines. Respiratory infections can exacerbate COPD symptoms and increase the risk of complications.
7. Regular Health Check-ups:
- Schedule regular check-ups with your healthcare provider to monitor lung function and assess COPD risk factors. Early detection and intervention can help prevent or delay the progression of the disease.
8. Medication Adherence:
- If you have existing respiratory conditions such as asthma, make sure to adhere to prescribed medications and treatment plans. Proper management of underlying conditions can reduce the risk of COPD exacerbations.
Conclusion:
Preventing Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD) requires a multifaceted approach that addresses modifiable risk factors and promotes healthy lifestyle habits. Smoking cessation remains the cornerstone of COPD prevention, but efforts to reduce environmental exposures, maintain a healthy diet, exercise regularly, and stay vigilant about respiratory health are equally important. By adopting these preventive measures, individuals can reduce their risk of developing COPD and improve their overall lung health and quality of life. Remember, prevention is always better than cure, and taking proactive steps today can lead to better respiratory outcomes tomorrow.



No comments yet
Be the first to share your thoughts!