How to Prevent Diabetes Mellitus (Type 1 & 2)
Introduction:
Diabetes Mellitus, commonly known as diabetes, is a chronic metabolic disorder characterized by elevated blood sugar levels. Type 1 and Type 2 diabetes are the two main forms, each with distinct causes and risk factors. While genetics and certain uncontrollable factors play a role in diabetes development, adopting a healthy lifestyle can significantly reduce the risk. This comprehensive guide explores effective strategies to prevent both Type 1 and Type 2 diabetes, empowering individuals to take charge of their health and well-being.
Understanding Diabetes Mellitus:
Before diving into prevention strategies, it's essential to understand the two primary types of diabetes:
1. Type 1 Diabetes:
- Type 1 diabetes, often diagnosed in childhood or adolescence, results from the immune system attacking the insulin-producing beta cells in the pancreas.
- Individuals with Type 1 diabetes require lifelong insulin therapy to manage blood sugar levels.
- Prevention of Type 1 diabetes focuses more on early detection and management rather than prevention since the exact cause is still unknown.
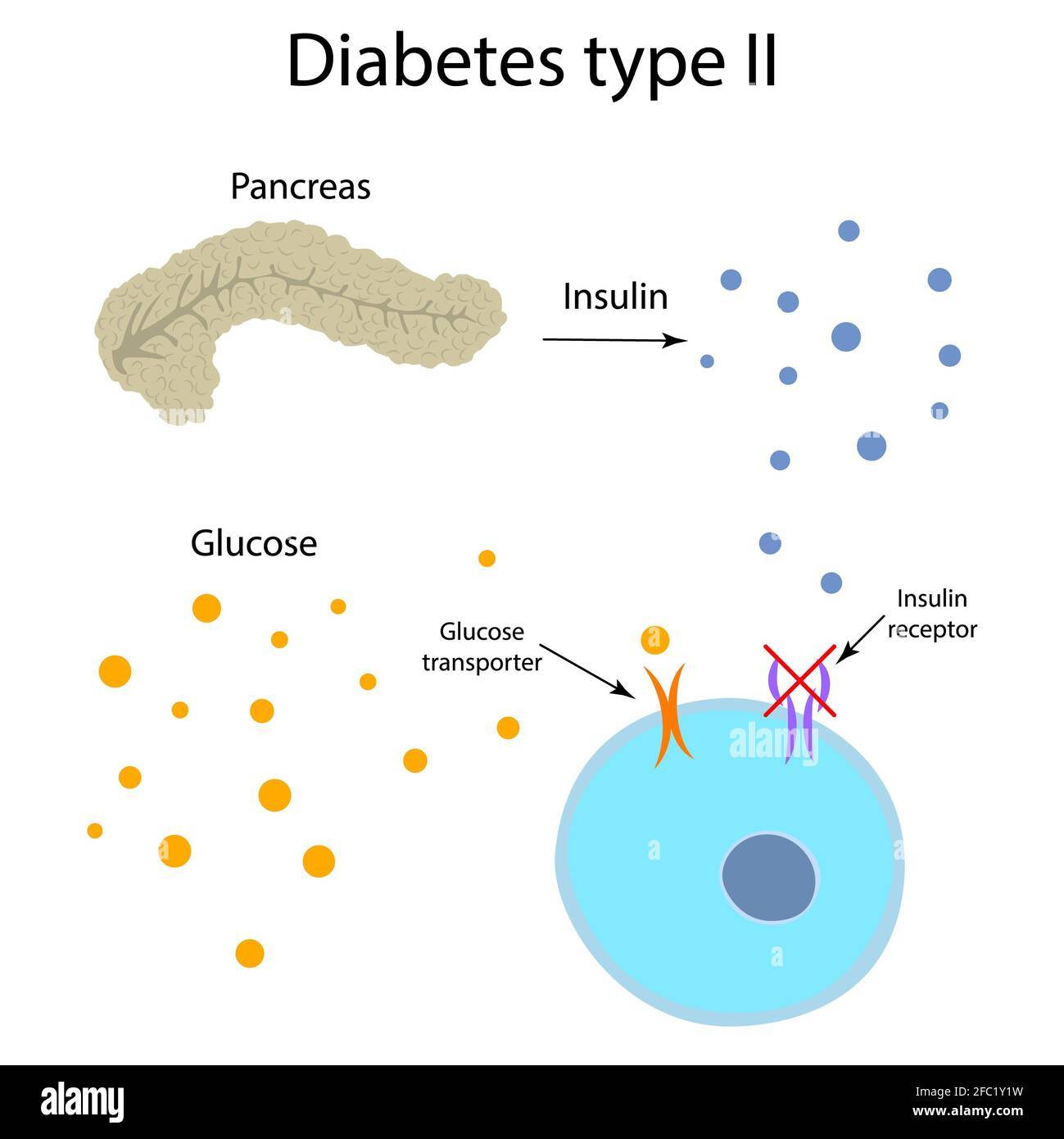
2. Type 2 Diabetes:
- Type 2 diabetes typically develops in adulthood, although it's increasingly diagnosed in children and adolescents due to rising obesity rates.
- This form of diabetes occurs when the body becomes resistant to insulin or fails to produce enough insulin to regulate blood sugar effectively.
- Lifestyle factors, such as poor diet, sedentary lifestyle, obesity, and genetics, significantly contribute to the development of Type 2 diabetes.
Now, let's explore evidence-based strategies to prevent both types of diabetes:
Preventing Type 1 Diabetes:
1. Early Detection: While prevention of Type 1 diabetes isn't currently possible, early detection through regular health check-ups and screenings can help manage the condition effectively. Recognizing symptoms like increased thirst, frequent urination, unexplained weight loss, and fatigue is crucial for timely diagnosis and intervention.
2. Immune System Support: Although the exact cause of Type 1 diabetes remains unclear, evidence suggests that autoimmune factors play a significant role. Supporting immune health through a balanced diet rich in vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants may help modulate immune function and reduce the risk of autoimmune disorders.
3. Genetic Counseling: Since genetics contribute to the risk of Type 1 diabetes, individuals with a family history of the condition may benefit from genetic counseling. Understanding genetic predispositions can inform preventive measures and early intervention strategies.
Preventing Type 2 Diabetes:
1. Maintain a Healthy Weight:
- Obesity is a major risk factor for Type 2 diabetes. Adopting a healthy weight through a balanced diet and regular exercise can significantly reduce the risk.
- Focus on portion control, consume a variety of nutrient-dense foods, and limit intake of processed foods, sugary beverages, and high-fat foods.
- Incorporate regular physical activity into your routine, aiming for at least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity exercise per week.
2. Balanced Diet:
- Emphasize whole foods, including fruits, vegetables, whole grains, lean proteins, and healthy fats, in your diet.
- Monitor carbohydrate intake and choose complex carbohydrates with a low glycemic index to prevent blood sugar spikes.
- Limit intake of added sugars, refined carbohydrates, and saturated fats, which can contribute to insulin resistance and weight gain.
3. Regular Exercise:
- Engage in a combination of aerobic exercise, strength training, and flexibility exercises to improve insulin sensitivity, lower blood sugar levels, and maintain a healthy weight.
- Find activities you enjoy and aim for consistency rather than intensity. Even small increments of physical activity throughout the day can make a difference.
4. Manage Stress:
- Chronic stress can contribute to insulin resistance and disrupt blood sugar regulation. Incorporate stress-reduction techniques such as mindfulness, meditation, deep breathing exercises, and hobbies into your daily routine.
- Prioritize adequate sleep, as sleep deprivation can impair glucose metabolism and increase the risk of Type 2 diabetes.
5. Avoid Tobacco and Limit Alcohol:
- Smoking increases the risk of Type 2 diabetes and complicates its management by contributing to cardiovascular complications.
- Limit alcohol consumption, as excessive alcohol intake can disrupt blood sugar levels and increase the risk of weight gain and insulin resistance.
6. Regular Health Check-ups:
- Schedule regular health screenings to monitor blood sugar levels, blood pressure, cholesterol levels, and other risk factors associated with diabetes.
- Early detection of prediabetes allows for timely intervention through lifestyle modifications and, if necessary, medication.
Conclusion:
Preventing diabetes, whether Type 1 or Type 2, requires a proactive approach to health that encompasses balanced nutrition, regular physical activity, stress management, and healthy lifestyle choices. While some risk factors like genetics may be beyond our control, adopting evidence-based preventive strategies can significantly reduce the risk of developing diabetes and its associated complications. By empowering individuals with knowledge and resources, we can collectively work towards a healthier future, free from the burden of diabetes mellitus.



No comments yet
Be the first to share your thoughts!