Psoriasis: Causes, Symptoms, and Treatment Options
Introduction:
Psoriasis is a chronic autoimmune condition that affects millions of people worldwide. Characterized by red, itchy, and scaly patches on the skin, psoriasis can have a significant impact on a person's quality of life. Despite being relatively common, many misconceptions surround this condition. In this comprehensive guide, we'll explore the causes, symptoms, and treatment options for psoriasis, shedding light on this often misunderstood condition.
Understanding Psoriasis:
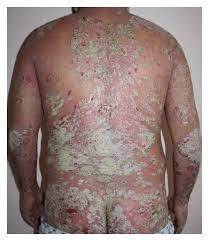
Psoriasis is a chronic autoimmune disorder that causes rapid growth of skin cells. Normally, skin cells grow deep within the skin and rise to the surface over the course of a month, where they are shed and replaced by new cells. However, in individuals with psoriasis, this process is accelerated, leading to the buildup of skin cells on the surface. This rapid turnover results in the formation of thick, red patches known as plaques, which are often covered with silvery scales.
Causes of Psoriasis:
The exact cause of psoriasis is not fully understood, but it is believed to involve a combination of genetic, environmental, and immune system factors. Family history plays a significant role, with about one-third of people with psoriasis having a family member with the condition. Certain environmental triggers, such as stress, infections, and injuries to the skin, can also exacerbate symptoms or trigger flare-ups in susceptible individuals.
Immune System Dysfunction:
One of the key factors in psoriasis development is dysfunction of the immune system. In psoriasis, the immune system mistakenly attacks healthy skin cells, triggering inflammation and causing the rapid turnover of skin cells. This inflammatory response leads to the characteristic symptoms of redness, itching, and scaling associated with psoriasis.
Types of Psoriasis:
Psoriasis can manifest in several different forms, each with its own unique characteristics. The most common form is plaque psoriasis, which accounts for about 80% of cases. Plaque psoriasis presents as raised, red patches covered with silvery scales, typically occurring on the elbows, knees, scalp, and lower back.
Other types of psoriasis include:
1. Guttate psoriasis: Characterized by small, dot-like lesions that often develop after a bacterial or viral infection.
2. Inverse psoriasis: Occurs in skin folds such as the armpits, groin, and under the breasts, appearing as smooth, red patches.
3. Pustular psoriasis: Presents as pus-filled blisters surrounded by red skin, typically on the hands and feet.
4. Erythrodermic psoriasis: A rare and severe form of psoriasis that causes widespread redness and shedding of the skin.
Symptoms of Psoriasis:
The symptoms of psoriasis can vary depending on the type and severity of the condition. Common symptoms include:
1. Red patches of skin covered with silvery scales.
2. Itching, burning, or soreness in affected areas.
3. Thickened, pitted, or ridged nails.
4. Dry, cracked skin that may bleed.
5. Joint pain and swelling in some cases (psoriatic arthritis).
Psoriasis can have a significant impact on a person's physical and emotional well-being. The visible nature of the condition can lead to feelings of self-consciousness, embarrassment, and even depression in some individuals. Additionally, the chronic nature of psoriasis means that it requires ongoing management to control symptoms and prevent flare-ups.
Diagnosis:
Diagnosing psoriasis typically involves a physical examination by a healthcare professional. The characteristic appearance of the skin lesions is usually sufficient for a diagnosis to be made. In some cases, a skin biopsy may be performed to confirm the diagnosis and rule out other skin conditions.
Treatment Options:
While there is currently no cure for psoriasis, there are several treatment options available to help manage symptoms and improve quality of life. Treatment approaches may vary depending on the type and severity of psoriasis, as well as individual patient preferences and medical history. Some common treatment options include:
1. Topical treatments: These include creams, ointments, and lotions applied directly to the skin to reduce inflammation and slow the growth of skin cells. Common topical medications include corticosteroids, vitamin D analogs, and retinoids.
2. Phototherapy: Also known as light therapy, phototherapy involves exposing the skin to ultraviolet light under medical supervision. This can help reduce inflammation and slow the growth of skin cells.
3. Oral medications: In cases of moderate to severe psoriasis, oral medications such as methotrexate, cyclosporine, or acitretin may be prescribed to help suppress the immune system and reduce symptoms.
4. Biologic therapies: Biologic drugs are a newer class of medications that target specific parts of the immune system involved in the development of psoriasis. These drugs are typically administered by injection or intravenous infusion and can be highly effective in controlling symptoms.
In addition to medical treatments, lifestyle modifications can also play a role in managing psoriasis. These may include avoiding triggers such as stress, smoking, and excessive alcohol consumption, as well as adopting a healthy diet and maintaining a healthy weight.
Living with Psoriasis:
Living with psoriasis can be challenging, but with proper management and support, many people are able to lead fulfilling lives. It's important for individuals with psoriasis to work closely with their healthcare team to develop a treatment plan that meets their needs and addresses their specific symptoms.
Support groups and online communities can also provide valuable support and encouragement for individuals living with psoriasis. These forums allow people to connect with others who understand their experiences and can offer advice, tips, and emotional support.
In conclusion, psoriasis is a chronic autoimmune condition that affects millions of people worldwide. While there is currently no cure, there are many treatment options available to help manage symptoms and improve quality of life. By understanding the causes, symptoms, and treatment options for psoriasis, individuals can take control of their condition and live well with psoriasis.
Closing Thoughts:
Psoriasis is a complex and often misunderstood condition that can have a significant impact on physical and emotional well-being. By raising awareness and understanding of psoriasis, we can help reduce stigma, improve access to treatment, and support those living with this chronic condition. With ongoing research and advancements in treatment, the future looks promising for individuals living with psoriasis.



No comments yet
Be the first to share your thoughts!