Prostate Cancer Prevention: Strategies, Myths, and Facts
Introduction:
Prostate cancer is one of the most common cancers affecting men worldwide. According to statistics, it is the second most common cancer in men after skin cancer. While the exact cause of prostate cancer remains unknown, there are several risk factors that have been identified, including age, family history, ethnicity, and lifestyle factors. Despite these risk factors, there are steps that men can take to reduce their risk of developing prostate cancer. In this article, we will explore various strategies for preventing prostate cancer, debunk some myths surrounding the disease, and provide evidence-based information on how to minimize risk.
Understanding Prostate Cancer:
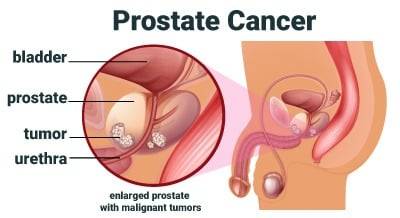
The prostate is a small gland located below the bladder and in front of the rectum in men. It plays a crucial role in the reproductive system by producing fluid that nourishes and transports sperm. Prostate cancer occurs when abnormal cells in the prostate gland grow and multiply uncontrollably, forming a tumor. If left untreated, prostate cancer can spread to other parts of the body, leading to serious complications and even death.
Risk Factors for Prostate Cancer:
Several factors can increase a man's risk of developing prostate cancer. These include:
1. Age: Prostate cancer is rare in men under 40, but the risk increases significantly with age. Most cases are diagnosed in men over the age of 65.
2. Family History: Men with a family history of prostate cancer, especially a father or brother with the disease, are at higher risk.
3. Ethnicity: African American men have a higher risk of developing prostate cancer compared to men of other ethnicities. They are also more likely to develop aggressive forms of the disease.
4. Lifestyle Factors: Certain lifestyle choices, such as a poor diet high in saturated fats, obesity, lack of physical activity, and smoking, have been linked to an increased risk of prostate cancer.
Preventive Measures:
While some risk factors for prostate cancer, such as age and family history, cannot be changed, there are several preventive measures that men can take to reduce their risk of developing the disease:
1. Maintain a Healthy Diet:
- Eat a balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins.
- Limit intake of red and processed meats, which have been linked to an increased risk of prostate cancer.
- Incorporate foods rich in antioxidants, such as tomatoes, broccoli, and green tea, which may help protect against prostate cancer.
2. Exercise Regularly:
- Aim for at least 30 minutes of moderate to vigorous physical activity most days of the week.
- Regular exercise can help maintain a healthy weight, reduce inflammation, and improve overall health, lowering the risk of prostate cancer.
3. Maintain a Healthy Weight:
- Obesity has been associated with an increased risk of prostate cancer and more aggressive forms of the disease.
- Aim to achieve and maintain a healthy weight through a combination of diet and exercise.
4. Get Regular Screenings:
- Early detection is key to successful treatment of prostate cancer.
- Talk to your doctor about the pros and cons of prostate cancer screening, including the prostate-specific antigen (PSA) test and digital rectal exam (DRE).
- The decision to undergo screening should be based on individual risk factors and preferences, and should involve a discussion with a healthcare professional.
5. Limit Alcohol Consumption:
- Heavy alcohol consumption has been linked to an increased risk of prostate cancer.
- If you choose to drink alcohol, do so in moderation. Limit consumption to no more than two drinks per day for men.
6. Don't Smoke:
- Smoking has been linked to an increased risk of developing aggressive forms of prostate cancer.
- If you smoke, seek help to quit. Quitting smoking has numerous health benefits, including reducing the risk of cancer.
Debunking Myths:
There are several myths and misconceptions surrounding prostate cancer prevention. It's important to separate fact from fiction to make informed decisions about your health:
Myth #1: Taking Supplements Can Prevent Prostate Cancer.
Fact: While some studies have suggested that certain supplements, such as vitamin E and selenium, may reduce the risk of prostate cancer, the evidence is inconclusive. In fact, high doses of these supplements may even increase the risk of developing the disease.
Myth #2: Having a Vasectomy Increases the Risk of Prostate Cancer.
Fact: Research has not found a conclusive link between vasectomy and prostate cancer. While some studies have suggested a slight increase in risk, others have found no association.
Myth #3: Prostate Cancer Is Always Fatal.
Fact: While prostate cancer can be serious, especially if not detected early, many men diagnosed with the disease do not die from it. With advances in treatment and early detection, the survival rate for prostate cancer is relatively high.
Myth #4: Only Older Men Need to Worry About Prostate Cancer.
Fact: While prostate cancer is more common in older men, it can occur at any age. Younger men with a family history of prostate cancer or other risk factors should be aware of their risk and talk to their doctor about screening options.
Conclusion:
While the exact cause of prostate cancer remains unknown, there are steps that men can take to reduce their risk of developing the disease. By adopting a healthy lifestyle, getting regular screenings, and staying informed about prostate cancer prevention, men can take control of their health and lower their risk of this common and potentially deadly cancer. Remember, early detection is key, so don't hesitate to talk to your doctor about your risk factors and screening options.



No comments yet
Be the first to share your thoughts!