Urinary Tract Infections: Causes, Symptoms, Treatment, and Prevention
Introduction:
Urinary Tract Infections (UTIs) are one of the most common bacterial infections affecting millions of people worldwide each year. Despite their prevalence, UTIs often go undiagnosed or untreated, leading to discomfort, complications, and even serious health issues. In this comprehensive guide, we will delve into the various aspects of UTIs, including their causes, symptoms, treatment options, and preventive measures.
Understanding Urinary Tract Infections:
1. Anatomy of the Urinary Tract:
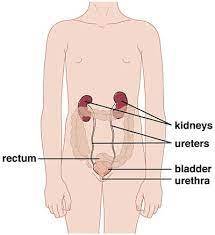
- To understand UTIs, it's crucial to grasp the anatomy of the urinary tract. The urinary tract consists of organs responsible for producing, storing, and eliminating urine from the body. These organs include the kidneys, ureters, bladder, and urethra.
- Each part of the urinary tract plays a specific role in the excretion process. The kidneys filter waste products and excess fluids from the blood to produce urine. This urine then travels through the ureters to the bladder for storage. When the bladder is full, urine is expelled through the urethra during urination.
2. What is a Urinary Tract Infection (UTI)?
- A UTI occurs when bacteria enter the urinary tract and multiply, leading to infection. While UTIs can affect any part of the urinary tract, they most commonly occur in the lower urinary tract, which includes the bladder and urethra.
- The majority of UTIs are caused by bacteria, with Escherichia coli (E. coli) being the most common culprit. However, other bacteria such as Klebsiella, Proteus, and Enterococcus can also cause UTIs.
3. Types of Urinary Tract Infections:
- UTIs can be classified based on the location within the urinary tract and the severity of the infection. The main types of UTIs include:
- Cystitis: This type of UTI affects the bladder and is often characterized by symptoms such as frequent urination, urgency, and discomfort or pain in the pelvic region.
- Pyelonephritis: Pyelonephritis is a more severe UTI that affects the kidneys. Symptoms may include fever, chills, back pain, nausea, and vomiting.
- Urethritis: Urethritis is an infection of the urethra and can cause symptoms such as pain or burning during urination and discharge.
4. Causes and Risk Factors:
- Several factors can increase the risk of developing a UTI. These include:
- Gender: Women are more prone to UTIs than men due to their shorter urethra, which allows bacteria easier access to the bladder.
- Sexual Activity: Sexual intercourse can introduce bacteria into the urinary tract, increasing the risk of infection.
- Urinary Catheterization: Individuals with urinary catheters are at a higher risk of developing UTIs due to the introduction of bacteria into the urinary tract.
- Diabetes: Poorly controlled diabetes can weaken the immune system, making individuals more susceptible to infections, including UTIs.
- Urinary Tract Abnormalities: Structural abnormalities in the urinary tract can hinder the flow of urine and increase the risk of UTIs.
5. Symptoms of Urinary Tract Infections:
- The symptoms of a UTI can vary depending on the location and severity of the infection. Common symptoms include:
- Pain or burning sensation during urination
- Frequent urination
- Urgency to urinate
- Cloudy or strong-smelling urine
- Blood in the urine (hematuria)
- Pelvic pain (in women)
- Back pain (in cases of kidney involvement)
6. Diagnosis:
- Diagnosing a UTI typically involves a combination of medical history review, physical examination, and laboratory tests. These may include:
- Urinalysis: This test examines a urine sample for the presence of bacteria, white blood cells, and other indicators of infection.
- Urine Culture: A urine culture is performed to identify the specific bacteria causing the infection and determine the most effective antibiotic treatment.
7. Treatment Options:
- The treatment of UTIs usually involves antibiotics to eradicate the underlying bacterial infection. The choice of antibiotic and duration of treatment depend on factors such as the type of bacteria identified, the severity of symptoms, and the individual's medical history.
- Commonly prescribed antibiotics for UTIs include trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole, nitrofurantoin, ciprofloxacin, and amoxicillin-clavulanate.
- In addition to antibiotics, pain relievers such as ibuprofen or acetaminophen may be recommended to alleviate discomfort associated with UTI symptoms.
8. Complications:
- While most UTIs can be effectively treated with antibiotics, complications can arise if the infection is left untreated or becomes recurrent. Potential complications of UTIs include:
- Kidney damage: Untreated or severe UTIs can lead to kidney infection (pyelonephritis), which may cause permanent kidney damage.
- Sepsis: In rare cases, UTIs can progress to sepsis, a life-threatening condition characterized by an overwhelming immune response to infection.
- Recurrent Infections: Some individuals may experience recurrent UTIs, which can significantly impact quality of life and may require long-term management strategies.
9. Prevention Strategies:
- Fortunately, there are several steps individuals can take to reduce their risk of developing UTIs:
- Stay Hydrated: Drinking plenty of water helps flush bacteria out of the urinary tract.
- Practice Good Hygiene: Wiping from front to back after using the bathroom can prevent the spread of bacteria from the anus to the urethra.
- Urinate After Sex: Emptying the bladder after sexual intercourse can help flush out bacteria introduced during intercourse.
- Avoid Irritants: Certain products, such as perfumed soaps, douches, and feminine hygiene sprays, can irritate the urinary tract and increase the risk of infection.
- Cranberry Products: Some studies suggest that cranberry products may help prevent UTIs by preventing bacteria from adhering to the urinary tract lining, although more research is needed to confirm their effectiveness.
Conclusion:
Urinary Tract Infections are common bacterial infections that can cause significant discomfort and, if left untreated, may lead to serious complications. By understanding the causes, symptoms, treatment options, and preventive measures associated with UTIs, individuals can take proactive steps to maintain urinary tract health and reduce their risk of infection. If you suspect you have a UTI or experience symptoms such as painful urination or frequent urination, it's essential to seek medical attention promptly for proper diagnosis and treatment. With timely intervention and proper management, UTIs can be effectively treated, helping to alleviate symptoms and prevent complications.



No comments yet
Be the first to share your thoughts!