How to Prevent Polycystic Kidney Disease
Introduction:
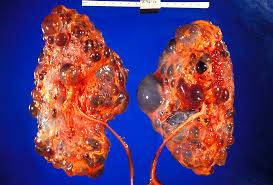
Polycystic Kidney Disease (PKD) is a genetic disorder characterized by the growth of numerous cysts in the kidneys. These cysts can interfere with kidney function, leading to complications such as high blood pressure, kidney stones, and ultimately, kidney failure. While PKD is an inherited condition and cannot be completely prevented, there are steps individuals can take to manage the disease and reduce its impact on their health. In this comprehensive guide, we'll explore various strategies for preventing and managing PKD, ranging from lifestyle modifications to medical interventions.
Understanding Polycystic Kidney Disease:
Before delving into prevention strategies, it's essential to understand the underlying causes and manifestations of PKD. PKD is primarily caused by genetic mutations that affect the development and function of the kidneys. There are two main types of PKD: Autosomal Dominant Polycystic Kidney Disease (ADPKD) and Autosomal Recessive Polycystic Kidney Disease (ARPKD).
ADPKD is the most common form of PKD, accounting for about 90% of cases. It typically manifests in adulthood and is characterized by the gradual enlargement of cysts in the kidneys over time. ARPKD, on the other hand, is a rare form of PKD that usually presents in infancy or childhood. Both types of PKD can lead to kidney failure if left untreated.
Preventive Measures and Management Strategies:
While PKD cannot be prevented entirely, individuals with a family history of the disease or those diagnosed with PKD can take proactive steps to manage their condition and reduce the risk of complications. Here are some preventive measures and management strategies:
1. Genetic Testing and Counseling:
If you have a family history of PKD or are at risk of inheriting the disease, genetic testing can help determine whether you carry the responsible gene mutation. Genetic counseling can provide valuable information about the likelihood of passing PKD to future generations and assist individuals in making informed decisions about family planning.
2. Regular Monitoring and Screening:
Early detection of PKD and its complications is crucial for effective management. Regular monitoring through imaging tests such as ultrasound or MRI can help track the progression of cyst growth and identify any associated complications, such as high blood pressure or kidney stones. Routine blood and urine tests can also provide valuable insights into kidney function.
3. Blood Pressure Management:
High blood pressure is a common complication of PKD and can accelerate the progression of kidney damage. Managing blood pressure through lifestyle modifications (such as a low-sodium diet, regular exercise, and stress reduction techniques) and medication can help preserve kidney function and reduce the risk of cardiovascular events.
4. Maintain a Healthy Lifestyle:
Adopting a healthy lifestyle can play a significant role in managing PKD and reducing the risk of complications. This includes:
- Following a balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins.
- Limiting intake of processed foods, saturated fats, and added sugars.
- Staying hydrated by drinking an adequate amount of water throughout the day.
- Avoiding tobacco products and excessive alcohol consumption.
- Engaging in regular physical activity to maintain a healthy weight and promote overall well-being.
5. Kidney Stone Prevention:
Individuals with PKD are at increased risk of developing kidney stones due to the presence of cysts in the kidneys. To prevent kidney stones, it's essential to:
- Stay well-hydrated by drinking plenty of water.
- Limit consumption of foods high in oxalates, such as spinach, nuts, and chocolate.
- Monitor calcium intake and consider dietary adjustments or supplements as needed.
- Avoid excessive intake of foods high in purines, such as organ meats and shellfish.
6. Medication and Medical Interventions:
In some cases, medication may be prescribed to manage symptoms associated with PKD, such as pain, high blood pressure, or urinary tract infections. Additionally, certain medical interventions may be considered to address complications or slow the progression of kidney damage. These may include:
- Cyst drainage or aspiration to relieve pain or discomfort caused by large cysts.
- Surgical removal of cysts or affected portions of the kidneys in severe cases.
- Dialysis or kidney transplantation for individuals with advanced kidney failure.
7. Participation in Clinical Trials:
Clinical trials offer opportunities to explore new treatments and interventions for PKD. By participating in clinical research, individuals with PKD can contribute to the advancement of medical knowledge and access potentially innovative therapies not yet available to the general public.
Conclusion:
While Polycystic Kidney Disease cannot be completely prevented, proactive management strategies can help individuals with PKD maintain kidney function, reduce the risk of complications, and improve their overall quality of life. By embracing a healthy lifestyle, adhering to recommended screening guidelines, and working closely with healthcare providers, individuals can take control of their health and minimize the impact of PKD on their well-being. Moreover, ongoing research and advancements in treatment hold promise for future generations affected by this challenging condition.



No comments yet
Be the first to share your thoughts!