Cataracts: Causes, Symptoms, Treatment, and Prevention
Introduction:
Cataracts are a common eye condition that affects millions of people worldwide, especially as they age. Despite its prevalence, there's often confusion about what cataracts are, how they develop, and what can be done to treat or prevent them. In this comprehensive guide, we'll delve into the intricacies of cataracts, covering everything from their causes and symptoms to treatment options and preventative measures.
**What are Cataracts?**
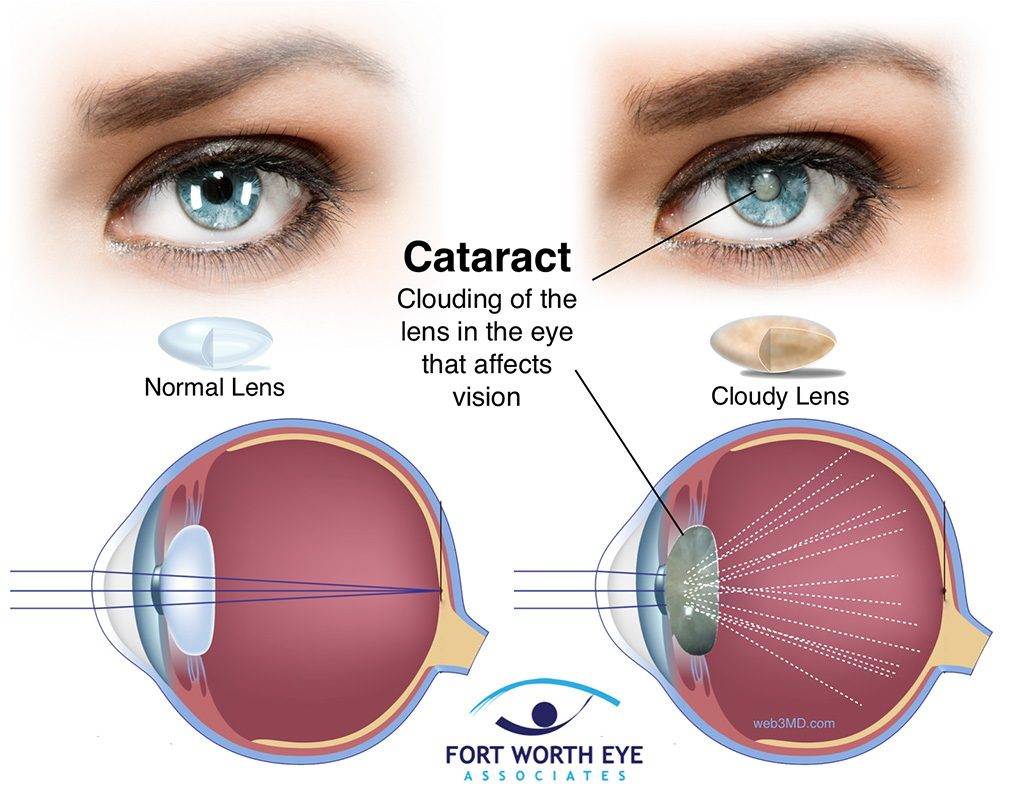
Cataracts refer to the clouding of the lens in the eye, leading to blurred vision and, if left untreated, potentially causing blindness. The lens, normally transparent, becomes cloudy due to the buildup of protein, hindering the passage of light to the retina, which is crucial for clear vision.
**Types of Cataracts:**
There are several types of cataracts, each classified based on its location within the eye or the circumstances surrounding its development:
1. **Age-Related Cataracts**: The most common type, age-related cataracts occur as a natural part of the aging process, usually manifesting in individuals over the age of 50.
2. **Congenital Cataracts**: These cataracts are present at birth or develop during childhood due to genetic factors, infection during pregnancy, or other developmental issues.
3. **Secondary Cataracts**: Secondary cataracts may develop as a result of other medical conditions like diabetes, exposure to certain medications (such as corticosteroids), or following eye surgery.
4. **Traumatic Cataracts**: These cataracts occur due to eye injuries and can develop immediately after the injury or years later.
5. **Radiation Cataracts**: Exposure to certain types of radiation, such as those used in cancer treatment, can lead to the development of cataracts.
Understanding the type of cataract one has is essential for determining the appropriate treatment approach.
**Causes of Cataracts:**
While cataracts primarily develop due to aging, several other factors can contribute to their formation:
1. **Age**: The natural aging process leads to changes in the proteins within the lens, making it less transparent over time.
2. **Ultraviolet Radiation**: Prolonged exposure to UV radiation from sunlight increases the risk of cataracts.
3. **Smoking and Alcohol**: Research suggests that smoking and excessive alcohol consumption can accelerate the development of cataracts.
4. **Medical Conditions**: Conditions such as diabetes, hypertension, and obesity are associated with an increased risk of cataracts.
5. **Eye Trauma**: Any injury to the eye can potentially lead to the development of cataracts.
6. **Genetics**: Family history may play a role in predisposing individuals to cataracts.
Understanding these risk factors can help individuals take proactive steps to minimize their chances of developing cataracts.
**Symptoms of Cataracts:**
The symptoms of cataracts can vary depending on the type and severity of the condition. Common symptoms include:
1. **Blurred Vision**: One of the most common symptoms, blurred vision occurs as the lens becomes cloudier, making it difficult to see clearly.
2. **Sensitivity to Light**: Individuals with cataracts may experience increased sensitivity to bright lights or glare.
3. **Difficulty Seeing at Night**: Night vision may be particularly affected, making it challenging to drive or navigate in low-light conditions.
4. **Fading Colors**: Colors may appear duller or less vibrant as cataracts progress.
5. **Double Vision**: Cataracts can cause double vision in one eye.
6. **Frequent Changes in Eyeglass Prescription**: As cataracts worsen, individuals may find that their prescription glasses need to be updated more frequently.
It's essential to seek medical attention if you experience any of these symptoms, as early detection and treatment can prevent further vision loss.
**Diagnosis of Cataracts:**
Diagnosing cataracts typically involves a comprehensive eye examination performed by an ophthalmologist. The following tests may be conducted:
1. **Visual Acuity Test**: This test measures how well you can see at various distances using an eye chart.
2. **Slit-Lamp Examination**: A slit lamp is used to examine the structures of the eye, including the lens, under high magnification.
3. **Retinal Examination**: The doctor may use dilating eye drops to examine the retina and optic nerve at the back of the eye.
4. **Tonometry**: This test measures the pressure inside the eye and can help detect conditions like glaucoma, which may coexist with cataracts.
Once diagnosed, the doctor will discuss treatment options based on the severity of the cataracts and the individual's overall eye health.
**Treatment Options for Cataracts:**
The treatment for cataracts typically involves surgical intervention, as there are no medications or eye drops that can reverse the condition. The most common surgical procedure for cataracts is called phacoemulsification, which involves the following steps:
1. **Anesthesia**: Before the surgery, the eye is numbed using local anesthesia to ensure the patient's comfort.
2. **Incision**: A small incision is made in the cornea to access the lens.
3. **Phacoemulsification**: An ultrasound probe is inserted into the eye to break up the cloudy lens into small pieces, which are then removed from the eye.
4. **Lens Replacement**: Once the natural lens is removed, an artificial intraocular lens (IOL) is implanted to restore clear vision.
Cataract surgery is considered safe and highly effective, with a success rate of over 95%. Most patients experience significant improvement in their vision following the procedure and can resume their normal activities within a few days.
In some cases, especially if the cataracts are in the early stages and not significantly impacting vision, the doctor may recommend monitoring the condition and delaying surgery until it becomes necessary.
**Preventing Cataracts:**
While cataracts are primarily age-related and inevitable for many individuals, there are steps you can take to reduce your risk or slow their progression:
1. **Protect Your Eyes from UV Radiation**: Wear sunglasses that block 100% of UV rays when outdoors, and use broad-brimmed hats for added protection.
2. **Quit Smoking**: If you smoke, quitting can reduce your risk of cataracts and numerous other health problems.
3. **Limit Alcohol Consumption**: Moderating your alcohol intake may help lower your risk of developing cataracts.
4. **Maintain a Healthy Diet**: Eating a diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and antioxidants may help protect against cataracts.
5. **Manage Chronic Conditions**: Keeping conditions like diabetes and hypertension under control can reduce your risk of developing cataracts.
6. **Regular Eye Exams**: Schedule routine eye exams with an ophthalmologist to monitor your eye health and detect cataracts early.
By incorporating these lifestyle habits into your daily routine, you can take proactive steps to protect your vision and reduce your risk of developing cataracts.
**Conclusion:**
Cataracts are a common eye condition that can significantly impact an individual's quality of life if left untreated. However, with early detection and appropriate treatment, most people can regain clear vision and resume their normal activities. Understanding the causes, symptoms
, and treatment options for cataracts is essential for maintaining optimal eye health and preserving vision as we age. By taking proactive steps to protect our eyes and seeking regular eye care, we can minimize the impact of cataracts and enjoy clear vision well into our later years.



No comments yet
Be the first to share your thoughts!