Traumatic Brain Injury (TBI): Causes, Symptoms, Treatment, and Recovery
Introduction
Traumatic Brain Injury (TBI) is a significant public health concern worldwide, with potentially debilitating consequences for individuals and their families. It occurs when a sudden trauma causes damage to the brain, disrupting its normal function. TBIs can range from mild to severe, with outcomes varying widely depending on the extent of the injury and promptness of treatment. In this comprehensive guide, we will delve into the various aspects of traumatic brain injury, including its causes, symptoms, diagnosis, treatment options, and strategies for rehabilitation and recovery.
Understanding Traumatic Brain Injury
Traumatic Brain Injury, often referred to as the "silent epidemic," encompasses a broad spectrum of injuries resulting from external forces acting upon the brain. These forces can be caused by various incidents, including falls, vehicle accidents, sports injuries, assaults, or blasts in military combat. The severity of a TBI is typically categorized as mild, moderate, or severe, based on the extent of damage and the duration of altered consciousness.
Causes of Traumatic Brain Injury
TBIs can result from both closed and penetrating head injuries. Closed head injuries occur when the head undergoes sudden acceleration and deceleration or experiences blunt force trauma, leading to brain damage without any penetration of the skull. Penetrating head injuries, on the other hand, involve foreign objects entering the skull and directly damaging brain tissue.
Common causes of TBIs include:
1. Falls: Falls are the leading cause of traumatic brain injury, particularly among young children and older adults.
2. Motor Vehicle Accidents: Car, motorcycle, and bicycle accidents are significant contributors to TBIs, especially those involving high speeds or lack of proper safety measures.
3. Violence: Intentional acts of violence, such as assaults and gunshot wounds, can result in severe traumatic brain injuries.
4. Sports Injuries: Contact sports like football, soccer, and boxing pose a risk of TBIs due to collisions, tackles, or falls.
5. Explosive Blasts: Military personnel are at risk of TBIs due to exposure to explosive blasts during combat operations.
Symptoms of Traumatic Brain Injury
The symptoms of TBI can vary widely depending on the severity and location of the injury. While some symptoms may appear immediately after the trauma, others might manifest days or even weeks later. Common symptoms of TBI include:
- Physical Symptoms: Headaches, nausea or vomiting, dizziness, blurred vision, sensitivity to light or noise, fatigue, and sleep disturbances.
- Cognitive Symptoms: Memory problems, difficulty concentrating, confusion, slowed thinking, and impaired judgment.
- Emotional Symptoms: Mood swings, irritability, anxiety, depression, and feelings of sadness or hopelessness.
- Sensory Symptoms: Loss of smell or taste, ringing in the ears (tinnitus), and changes in hearing or vision.
- Motor Symptoms: Weakness or paralysis in limbs, coordination problems, and tremors.
Diagnosis of Traumatic Brain Injury
Diagnosing a traumatic brain injury often involves a comprehensive evaluation by medical professionals, including a physical examination, neurological assessment, and imaging tests. Common diagnostic tools used to assess TBIs include:
- Glasgow Coma Scale (GCS): A standardized tool used to assess the level of consciousness based on eye, verbal, and motor responses.
- CT Scan (Computed Tomography): A type of X-ray that provides detailed images of the brain's structure, allowing healthcare providers to detect bleeding, swelling, or other abnormalities.
- MRI (Magnetic Resonance Imaging): An imaging technique that produces detailed images of the brain's soft tissues, helping to identify subtle injuries that may not be visible on a CT scan.
- Neurological Examination: A series of tests to assess reflexes, sensation, coordination, and cognitive function, which can help determine the extent of brain damage.
Treatment of Traumatic Brain Injury
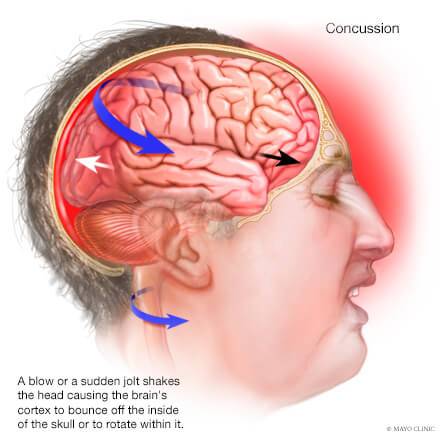
The treatment of traumatic brain injury depends on the severity of the injury and its associated symptoms. In cases of mild TBI, also known as a concussion, treatment may involve rest, pain management, and monitoring for any worsening symptoms. For moderate to severe TBIs, more intensive interventions may be required, including:
- Hospitalization: Patients with moderate to severe TBIs may require hospitalization for close monitoring and medical management.
- Medications: Medications may be prescribed to control symptoms such as pain, seizures, inflammation, or agitation.
- Surgery: In cases of severe TBI, surgery may be necessary to remove hematomas (blood clots), repair skull fractures, or relieve pressure on the brain caused by swelling.
- Rehabilitation: Rehabilitation programs play a crucial role in helping individuals recover from traumatic brain injury. These programs may include physical therapy, occupational therapy, speech therapy, and cognitive rehabilitation to improve motor function, cognitive skills, and overall quality of life.
Prognosis and Recovery
The prognosis for individuals with traumatic brain injury can vary widely depending on factors such as the severity of the injury, the age and overall health of the patient, and the effectiveness of treatment and rehabilitation efforts. While some individuals may experience a full recovery, others may face long-term challenges or disabilities. The recovery process following a traumatic brain injury can be complex and may involve multiple stages, including:
- Acute Care: Immediate medical treatment and stabilization following the injury, typically in an emergency department or intensive care unit.
- Rehabilitation: Intensive therapy and rehabilitation aimed at maximizing function and independence, often conducted in specialized rehabilitation centers or outpatient settings.
- Long-Term Care: Ongoing support and management of symptoms, disabilities, and complications that may persist after the initial injury.
Conclusion
Traumatic Brain Injury is a significant public health issue with far-reaching implications for individuals, families, and society as a whole. By understanding the causes, symptoms, diagnosis, treatment, and recovery of TBI, we can better support those affected by these injuries and work towards preventing future incidents. Through ongoing research, education, and advocacy efforts, we can strive to improve outcomes for individuals with traumatic brain injury and enhance their quality of life.



No comments yet
Be the first to share your thoughts!