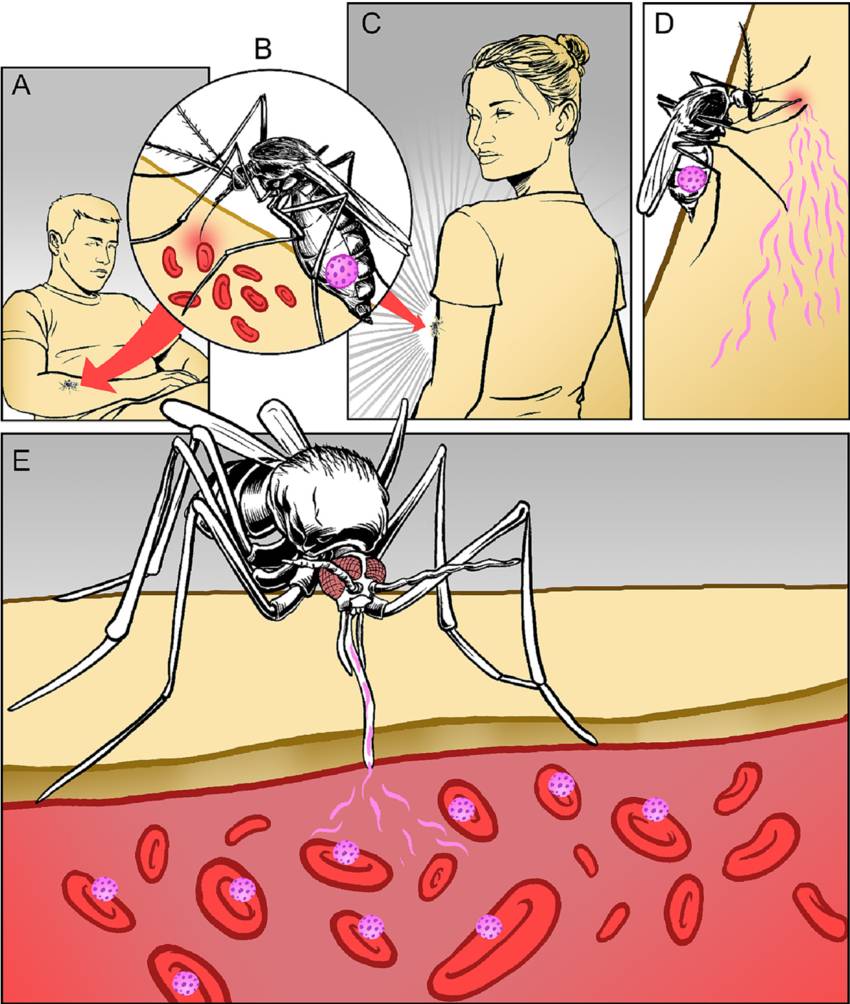
Malaria is a life-threatening disease caused by parasites that are transmitted to humans through the bites of infected female Anopheles mosquitoes. The parasites belong to the *Plasmodium genus*, with *Plasmodium falciparum* and *Plasmodium vivax* being the most common species causing malaria in humans.
Symptoms of malaria typically include fever, chills, headache, nausea, vomiting, muscle pain, and fatigue. If left untreated, the infection can progress to severe malaria, which can cause serious health complications such as anemia, respiratory distress, *organ failure* , and even *death* .
Malaria is preventable and treatable. Preventive measures include using insecticide-treated mosquito nets, indoor residual spraying, and taking antimalarial medications when traveling to areas where malaria is prevalent(widespread). Treatment involves antimalarial drugs, with the choice of medication depending on the specific Plasmodium species and the severity of the infection.
HOW DOES LACK OF SANITATION LEADS TO MALARIA?
While lack of sanitation itself does not directly cause malaria, it can contribute to conditions that promote the breeding of Anopheles mosquitoes, which are the vectors of the disease. Here’s how poor sanitation can indirectly lead to an increased risk of malaria:
1. **Standing Water**: Poor sanitation often results in the accumulation of stagnant water in and around living areas. Common sources include uncovered water containers, clogged drains, and poorly managed waste disposal sites. These stagnant water bodies provide ideal breeding grounds for Anopheles mosquitoes.
2. **Poor Drainage Systems**: Inadequate or poorly maintained drainage systems can lead to waterlogging and the creation of puddles and pools of water. These stagnant water bodies are potential mosquito breeding sites.
3. **Waste Accumulation**: Accumulation of garbage and waste materials can create microenvironments that retain water, offering additional breeding sites for mosquitoes.
4. **Open Defecation**: In areas with poor sanitation infrastructure, open defecation can contribute to environmental contamination and water pollution. While not directly linked to malaria, it can create unsanitary conditions that may attract mosquitoes and other disease vectors.
Improving sanitation can help reduce the prevalence of mosquito breeding sites, thereby lowering the risk of malaria transmission. Measures include proper waste management, ensuring effective drainage, covering water storage containers, and eliminating any stagnant water sources in residential areas.
SIGN AND SYMPTOMS OF MALARIA.
Malaria presents a range of symptoms that typically appear 10-15 days after an infective mosquito bite. The signs and symptoms can vary depending on the species of Plasmodium causing the infection and the severity of the disease. Common signs and symptoms include:
1. **Fever**: Often characterized by cycles of chills, followed by a high fever, and then sweating as the fever drops.
2. **Chills**: Intense shivering and feeling very cold.
3. **Headache**: Persistent and severe headaches.
4. **Nausea and Vomiting**: Feeling nauseous and vomiting.
5. **Muscle Pain**: Generalized body aches and muscle pain.
6. **Fatigue**: Extreme tiredness and weakness.
7. **Sweating**: Profuse sweating as the fever breaks.
8. **Anemia**: Caused by the destruction of red blood cells, leading to a shortage of oxygen in the body.
9. **Jaundice**: Yellowing of the skin and eyes due to liver dysfunction and the breakdown of red blood cells.
In severe cases, malaria can progress to more serious symptoms and complications, including:
1. **Cerebral Malaria**: Seizures, confusion, and loss of consciousness due to the infection affecting the brain.
2. **Respiratory Distress**: Difficulty breathing or shortness of breath.
3. **Organ Failure**: Severe malaria can lead to kidney or liver failure, and cardiovascular collapse.
4. **Severe Anemia**: Critically low levels of red blood cells.
5. **Hypoglycemia**: Abnormally low blood sugar levels, which can be particularly dangerous in pregnant women and young children.
6. **Acidosis**: Accumulation of acid in the blood and tissues, which can be life-threatening.
Prompt diagnosis and treatment are crucial to managing malaria and preventing complications. If malaria is suspected, especially after travel to an endemic area, it is important to seek medical attention immediately.
Some Countries With Malaria Infection
1. Nigeria
2. Uganda
3. Mozambique
4. Ghana
5. Colombia
Some Countries Without Malaria
1. United States
2. Canada
3. Japan
4. South Korea
5. Qatar
Efforts to eliminate malaria have been successful in many regions due to widespread use of insecticide-treated nets, indoor residual spraying, effective antimalarial drugs, and robust public health systems. However, continued vigilance and preventive measures are necessary to maintain malaria-free status and prevent reintroduction.
By putting all the objectives learned into practice in our societies, we can leave a good and a healthy life, and also having a malaria free environment as well. Try to share the link to at least 3 people or groups for others to also get the chance to read this educative article. Let's promote a healthy future, sharing is caring.


No comments yet
Be the first to share your thoughts!