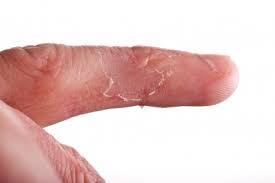
Hand Infections
Hand infections can result from various causes, including bacteria, fungi, or viruses, and typically affect the skin, soft tissues, joints, or tendons. These infections may lead to serious complications if left untreated. Common hand infections include cellulitis, abscesses, paronychia, felon, and septic arthritis. Early recognition and treatment are essential to prevent long-term damage.
---
20 Causes of Hand Infections
1. Cuts or Wounds: Open cuts or abrasions that become infected by bacteria.
2. Puncture Injuries: Deep puncture wounds from sharp objects like needles or nails.
3. Bite Wounds: Human or animal bites can introduce bacteria into the hand.
4. Scratches: Scratches from animals, especially cats, can introduce harmful bacteria.
5. Burns: Burns that blister or leave the skin exposed are prone to infection.
6. Surgery: Post-surgical infections from contamination during or after surgery.
7. Infected Hangnails: Hangnails that become inflamed or infected due to bacteria.
8. Diabetes: Poor circulation in diabetics can make hand wounds more prone to infection.
9. Fungal Infections: Fungal growth, such as from contaminated water, can affect the skin.
10. Ingrown Nails: Ingrown fingernails can become infected with bacteria or fungi.
11. Contaminated Water: Exposure to dirty water or handling raw food can introduce harmful bacteria.
12. Skin Conditions: Pre-existing skin conditions like eczema can break the skin barrier, allowing infection.
13. Foreign Objects: Splinters or other objects embedded in the skin can lead to infection.
14. Inadequate Hand Hygiene: Poor hand hygiene can lead to bacterial growth on the skin.
15. Use of Contaminated Tools: Using unclean or improperly sterilized tools, such as manicure tools, can introduce infections.
16. Immunocompromised State: People with weakened immune systems are more susceptible to infections.
17. Drug Injection: Injecting drugs, particularly with unsterile needles, can lead to serious infections.
18. Contact with Infected Individuals: Direct contact with infected individuals can spread infections like MRSA.
19. Contact Dermatitis: Skin reactions that break the skin can allow bacteria to enter.
20. Poor Nail Care: Lack of proper nail hygiene, such as trimming or cleaning, can promote infection.
---
20 Signs and Symptoms of Hand Infections
1. Redness: A red area around the infection site.
2. Swelling: Inflammation and swelling of the infected area.
3. Pain: Localized pain or tenderness around the infection.
4. Pus or Discharge: Pus-filled abscess or discharge from the infected wound.
5. Warmth: The infected area feels warm to the touch due to inflammation.
6. Fever: Fever or chills, particularly with more severe infections.
7. Throbbing Pain: A deep, throbbing pain, especially in infections like felon.
8. Blisters: Blisters or vesicles may form over the infected area.
9. Skin Breakdown: The skin may break open, ooze, or ulcerate in more severe cases.
10. Lymphangitis: Red streaks moving from the infected site toward the arm indicate a spreading infection.
11. Numbness or Tingling: Nerve involvement can cause numbness or tingling in the hand.
12. Joint Stiffness: Stiffness in nearby joints, indicating the infection may have spread.
13. Weak Grip Strength: Weakness or difficulty gripping objects.
14. Swollen Lymph Nodes: Enlarged and tender lymph nodes in the arm or under the arm.
15. Discoloration: The infected skin may turn a darker color if not treated.
16. Fatigue: Generalized fatigue or malaise, often due to systemic infection.
17. Difficulty Moving Fingers: Pain or stiffness when moving fingers or hand joints.
18. Nail Discoloration: Infections around the nails (paronychia) may cause the nail to discolor.
19. Crusting or Scabbing: Formation of scabs or crusty lesions over the infection site.
20. Bad Odor: Foul-smelling discharge from the infected area.
---
10 Effects of Hand Infections
1. Tissue Damage: Infections can cause necrosis (tissue death) if untreated.
2. Loss of Hand Function: Severe infections can result in loss of hand movement or strength.
3. Chronic Pain: Persistent pain due to tendon or joint involvement from the infection.
4. Scarring: Deep infections can lead to permanent scarring on the skin.
5. Amputation: In extreme cases, infections that are not treated can result in the need for amputation.
6. Septic Arthritis: Joint infections may lead to arthritis in the hand.
7. Spread to Other Areas: Infections can spread to the arm or other parts of the body through the bloodstream.
8. Sepsis: Severe infections may lead to a life-threatening condition called sepsis.
9. Osteomyelitis: Bone infection if the bacteria spread to the underlying bone.
10. Abscess Formation: Pockets of pus (abscesses) may form, requiring drainage or surgery.
---
Prevention of Hand Infections
1. Practice Good Hygiene: Wash hands regularly with soap and water, especially after touching contaminated surfaces.
2. Proper Wound Care: Clean and cover cuts, scrapes, or wounds promptly with antiseptics and bandages.
3. Avoid Biting Nails or Cuticles: Nail-biting can introduce bacteria into the skin.
4. Use Gloves for Protection: Wear gloves when handling sharp objects, gardening, or dealing with chemicals.
5. Keep Nails Trimmed: Maintain proper nail hygiene to prevent infections around the nails.
6. Avoid Sharing Personal Items: Do not share nail clippers, razors, or towels to reduce the spread of bacteria.
7. Sterilize Tools: Ensure that any tools used for manicures or medical procedures are sterilized.
8. Vaccination: Stay up-to-date with vaccinations, such as tetanus shots, especially after injuries.
9. Boost Immune Health: Maintain a healthy immune system through proper diet, exercise, and rest to fight off infections.
10. Seek Immediate Medical Attention: Early medical care for cuts, bites, or punctures can prevent infection.
Hand infections can escalate quickly if not addressed, so proper hygiene and early intervention are essential to prevent complications.