Here's a comprehensive look at Parkinson's disease, including its potential causes, signs, effects, and solutions:
1. Causes of Parkinson’s Disease
The exact cause of Parkinson's disease is still unknown, but several factors are believed to contribute to its development:
1. Genetics – Mutations in genes such as LRRK2, PARK7, and SNCA are linked to Parkinson's.
2. Environmental Toxins – Exposure to pesticides, herbicides, or heavy metals can increase risk.
3. Age – Risk rises with age, especially over 60.
4. Gender – Men are more likely than women to develop Parkinson's.
5. Head Injuries – Repeated head trauma may be linked to Parkinson’s.
6. Oxidative Stress – Imbalance in free radicals can damage cells.
7. Low Dopamine Levels – Loss of dopamine-producing neurons is a hallmark of Parkinson's.
8. Inflammation – Chronic inflammation in the brain may contribute to disease progression.
9. Rural Living – People in rural areas may be more exposed to pesticides.
10. Mitochondrial Dysfunction – Abnormal function of cellular energy production can contribute to neuron death.
11. Air Pollution – Exposure to pollutants has been associated with neurodegenerative disorders.
12. Dietary Factors – Low intake of antioxidants might contribute to higher oxidative stress.
13. Gut Health Issues – Certain gut bacteria are linked to Parkinson's development.
14. Low Vitamin D Levels – Vitamin D deficiency has been linked to higher Parkinson's risk.
15. Autoimmune Diseases – Conditions like rheumatoid arthritis may increase risk.
16. Occupational Exposure – Contact with certain industrial chemicals may increase susceptibility.
17. Melatonin Deficiency – Low melatonin levels may affect dopamine regulation.
18. Chronic Stress – Long-term stress may contribute to brain inflammation.
19. Viral Infections – Certain viral infections could lead to neuroinflammation.
20. Sedentary Lifestyle – Lack of physical activity may contribute to increased risk.
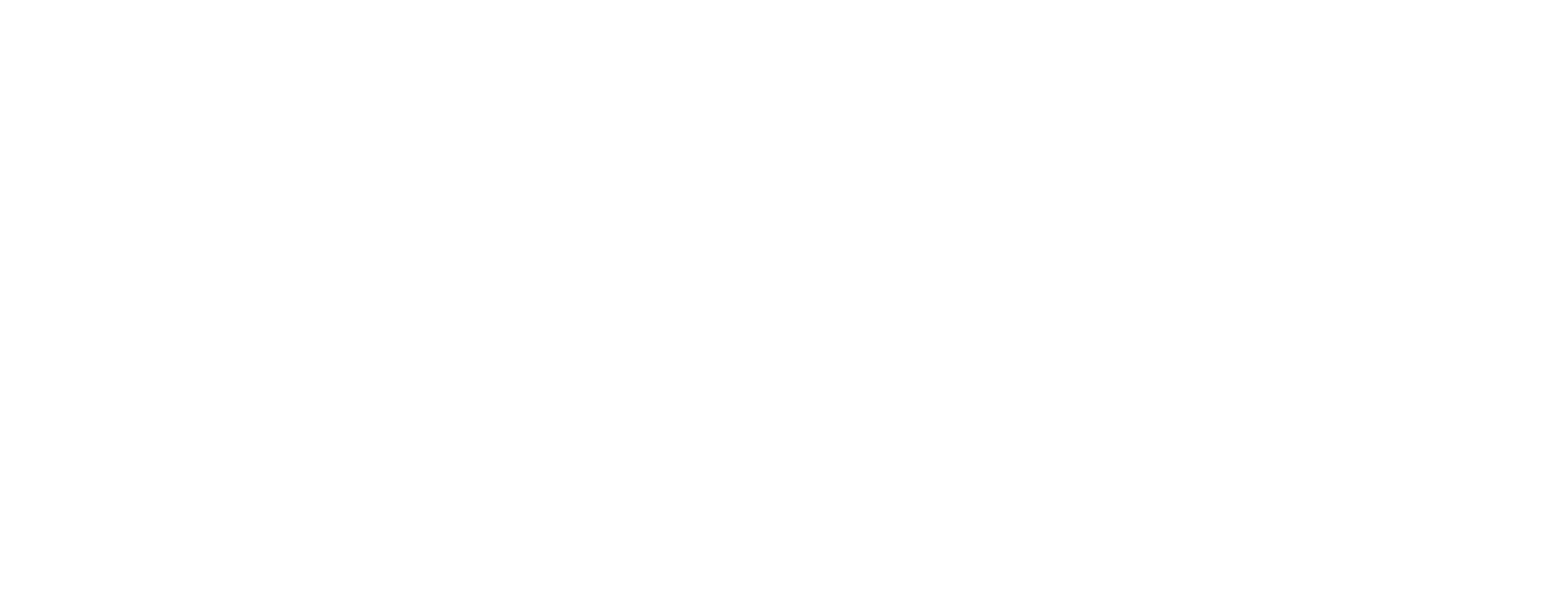
2. Signs of Parkinson’s Disease
The symptoms of Parkinson's disease can vary in severity and often worsen as the disease progresses:
1. Tremors – Shaking or tremor in hands, arms, legs, or jaw.
2. Bradykinesia – Slowness of movement, making everyday tasks difficult.
3. Muscle Stiffness – Rigidity in the limbs or body.
4. Impaired Balance – Difficulty maintaining posture or balance.
5. Masked Facial Expression – Reduced facial expressions or "mask-like" appearance.
6. Micrographia – Small, cramped handwriting.
7. Difficulty Walking – Shuffling gait or difficulty with mobility.
8. Speech Changes – Soft, monotone, or slurred speech.
9. Reduced Arm Swing – One arm may not swing naturally while walking.
10. Postural Instability – Increased risk of falls due to poor posture.
11. Swallowing Difficulties – Dysphagia, or difficulty swallowing.
12. Sleep Disorders – REM sleep behavior disorder, insomnia, or excessive daytime sleepiness.
13. Cognitive Changes – Memory problems, confusion, or difficulty concentrating.
14. Depression – High rates of depression and anxiety.
15. Urinary Issues – Problems with bladder control.
16. Constipation – Slowed digestion leading to constipation.
17. Loss of Smell – Reduced or loss of sense of smell (often an early sign).
18. Fatigue – Persistent feelings of tiredness or low energy.
19. Dizziness – May feel lightheaded or dizzy upon standing.
20. Pain or Discomfort – Pain in specific parts of the body, often due to muscle rigidity.
3. Effects of Parkinson’s Disease
Parkinson's disease affects not only motor function but also mental and emotional health:
1. Loss of Independence – Increasing reliance on others for daily activities.
2. Reduced Quality of Life – Physical limitations impact social and personal life.
3. Emotional Distress – Depression and anxiety from dealing with disease limitations.
4. Cognitive Impairment – Dementia or memory issues in advanced stages.
5. Increased Fall Risk – Mobility and balance issues can lead to frequent falls.
6. Social Isolation – Avoidance of social activities due to symptoms.
7. Speech and Communication Challenges – Difficulty speaking clearly.
8. Sleep Disruption – Insomnia and REM sleep behavior disorder impact rest.
9. Economic Burden – Medical expenses and lost income.
10. Caregiver Strain – Family members and caregivers experience emotional and financial stress.
4. Solutions and Management
While Parkinson’s disease is incurable, various strategies can help manage symptoms and improve quality of life:
1. Medication – Drugs like levodopa, dopamine agonists, and MAO-B inhibitors can help manage symptoms.
2. Physical Therapy – Exercises that improve flexibility, strength, and balance can reduce mobility issues.
3. Speech Therapy – Helps with communication issues and can address voice volume and clarity.
4. Occupational Therapy – Techniques to make daily tasks easier and safer.
5. Dietary Adjustments – A balanced diet with antioxidants and fiber can support general health and alleviate constipation.
6. Exercise – Regular physical activity, like walking, swimming, or yoga, to improve movement.
7. Deep Brain Stimulation (DBS) – A surgical treatment that implants electrodes to reduce symptoms.
8. Mental Health Support – Counseling or medication for managing depression and anxiety.
9. Sleep Management – Practicing good sleep hygiene and, if necessary, using medication to address sleep disorders.
10. Support Groups – Joining groups for social and emotional support, helping both patients and caregivers manage stress and improve well-being.
These solutions can help individuals with Parkinson's lead a better-quality life and manage the progression of symptoms.Jí oo
 blogpay
blogpay

























Total Comments: 0