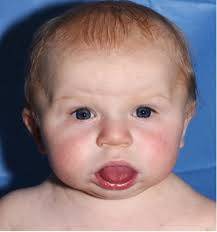
Macroglossia is a condition characterized by an abnormally large tongue, which can affect speech, chewing, swallowing, and breathing. It can be congenital (present at birth) or acquired later in life, depending on the underlying cause.
---
Causes
Macroglossia may arise due to several factors, including:
Congenital Causes:
1. Genetic Disorders - Conditions like Down syndrome, Beckwith-Wiedemann syndrome, and mucopolysaccharidoses can cause an enlarged tongue.
2. Hemangiomas or Lymphangiomas - Benign growths or vascular malformations in the tongue.
3. Cretinism (Congenital Hypothyroidism) - Can cause tissue enlargement, including the tongue.
Acquired Causes:
1. Acromegaly - Excess growth hormone leads to tissue enlargement, including the tongue.
2. Amyloidosis - Deposition of amyloid proteins in the tongue tissues.
3. Trauma or Inflammation - Chronic inflammation or injury can lead to tongue enlargement.
4. Hypothyroidism - In adults, this can lead to swelling of the tongue due to mucopolysaccharide accumulation.
5. Tumors - Benign or malignant tumors in the tongue tissue.
6. Allergic Reactions - Severe allergic responses can lead to tongue swelling (angioedema).
---
Signs and Symptoms
1. Enlarged Tongue - The tongue appears visibly larger than normal, often protruding from the mouth.
2. Difficulty Speaking (Dysarthria) - Speech may be slurred or unclear due to tongue size.
3. Chewing and Swallowing Problems - Difficulty managing food and saliva.
4. Drooling - Inability to keep saliva within the mouth due to tongue size.
5. Teeth Marks - Indentations on the sides of the tongue caused by constant pressure against the teeth.
6. Airway Obstruction - In severe cases, macroglossia can cause difficulty breathing or sleep apnea.
7. Facial Changes - Chronic macroglossia may lead to changes in facial appearance or jaw alignment, especially in children.
---
Effects
1. Speech Impairments - Difficulty articulating words clearly.
2. Nutritional Problems - Trouble chewing or swallowing can impact nutrition.
3. Orthodontic Issues - Malocclusion (misaligned teeth) or jaw deformities may develop.
4. Breathing Problems - Sleep apnea or airway obstruction in severe cases.
5. Self-Esteem Concerns - Visible tongue enlargement may lead to social discomfort.
---
Solutions and Management
Non-Surgical Management:
1. Treat Underlying Causes
Hypothyroidism: Use thyroid hormone replacement therapy.
Acromegaly: Treat with medications, surgery, or radiation to manage growth hormone levels.
Amyloidosis: Manage the underlying systemic condition with appropriate treatments.
2. Speech Therapy
Helps improve articulation and communication for those with speech difficulties.
3. Orthodontic Care
Braces or other appliances can manage dental and jaw issues caused by macroglossia.
4. Allergy Management
Treat angioedema with antihistamines, corticosteroids, or epinephrine in case of severe allergic reactions.
Surgical Solutions:
1. Glossectomy
Partial removal of tongue tissue to reduce size, often recommended for severe cases impacting breathing, speech, or swallowing.
2. Corrective Surgery for Malformations
For vascular abnormalities or tumors, surgical excision may be required.
---
Supportive Care:
1. Soft Diet
Eating soft foods that are easy to chew and swallow can minimize discomfort.
2. Good Oral Hygiene
Clean the tongue and teeth properly to prevent infections caused by food trapping.
3. Regular Monitoring
Regular checkups with a healthcare provider to track tongue size and related issues.
---
When to See a Doctor
Seek medical attention if macroglossia:
Interferes with breathing, eating, or speaking.
Is accompanied by other symptoms like fatigue, unexplained weight gain, or systemic signs of illness.
Occurs suddenly or progresses rapidly.
Prompt evaluation and treatment can prevent complications and improve quality of life.


No comments yet
Be the first to share your thoughts!