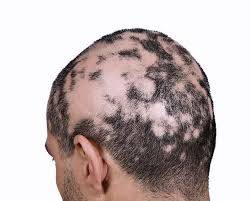
Alopecia Areata
Alopecia areata is an autoimmune condition where the body's immune system attacks hair follicles, causing hair loss. It can occur on the scalp, face, or other parts of the body.
---
Causes
1. Autoimmune response: The immune system mistakenly attacks hair follicles.
2. Genetics: Family history of autoimmune diseases increases risk.
3. Environmental factors: Stress, infections, or injuries might trigger it.
4. Other autoimmune diseases: Commonly associated with conditions like vitiligo, thyroid disorders, or rheumatoid arthritis.
---
Signs and Symptoms
1. Patchy Hair Loss: Round or oval bald patches on the scalp or body.
2. Exclamation Mark Hairs: Short hairs tapering at the base near the bald areas.
3. Nail Changes: Ridges, dents, or brittleness in fingernails or toenails.
4. Regrowth and Relapse: Hair may regrow in affected areas but can fall out again.
5. Widespread Loss (in severe cases):
Alopecia totalis: Complete scalp hair loss.
Alopecia universalis: Loss of all body hair, including eyebrows and eyelashes.
---
Effects
1. Emotional Impact: Anxiety, depression, and low self-esteem due to visible hair loss.
2. Social Challenges: Difficulty with social interactions or stigmatization.
3. Physical Sensitivity: Loss of hair can make the skin more vulnerable to sunburn, cold, or irritants.
4. Chronic Recurrence: Episodes may recur unpredictably.
---
Solutions and Treatments
While there is no permanent cure, the following options can help manage alopecia areata:
Medical Treatments
1. Corticosteroids:
Injections into bald areas to reduce immune response.
Topical creams or ointments for less severe cases.
2. Minoxidil (Rogaine):
Over-the-counter treatment to stimulate hair growth.
3. Immunotherapy:
Topical application of chemicals to provoke an allergic reaction and stimulate hair regrowth.
4. JAK Inhibitors:
Newer oral or topical medications (e.g., tofacitinib) targeting specific immune pathways.
5. Anthralin:
A topical tar-like substance that reduces inflammation in the scalp.
Lifestyle and Support
1. Wigs and Hairpieces:
Cosmetic solutions for covering bald patches.
2. Stress Management:
Techniques like yoga, meditation, or counseling to reduce triggers.
3. Nutritional Support:
A diet rich in vitamins (e.g., biotin, zinc) to promote overall hair health.
4. Support Groups:
Joining communities for emotional support and coping strategies.
Natural Remedies (Limited Evidence)
1. Essential Oils: Lavender, rosemary, or peppermint oil may improve scalp health.
2. Aloe Vera or Onion Juice: Claimed to stimulate hair regrowth.
3. Acupuncture: May help reduce stress and promote hair health.
---
Prevention
While alopecia areata cannot always be prevented, minimizing stress, maintaining a balanced diet, and monitoring other autoimmune conditions may help reduce the severity or frequency of episodes. Regular check-ups with a dermatologist are essential for effective management.