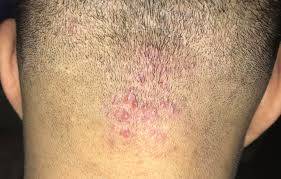
Folliculitis
Folliculitis is an inflammation or infection of hair follicles, which can occur anywhere on the skin where hair grows. It is often caused by bacteria, fungi, or other irritants and can range from mild to severe.
---
Causes
1. Bacterial Infections:
Most commonly caused by Staphylococcus aureus.
2. Fungal Infections:
Malassezia or other fungi can infect the follicles, especially in humid environments.
3. Viral Infections:
Herpes simplex virus can sometimes lead to folliculitis.
4. Irritants:
Tight clothing, shaving, or friction from equipment can irritate hair follicles.
5. Hot Tub Folliculitis:
Caused by Pseudomonas aeruginosa, often from contaminated hot tubs or pools.
6. Weakened Immune System:
People with diabetes, HIV/AIDS, or other conditions that impair immunity are more susceptible.
---
Signs and Symptoms
1. Red Bumps or Pimples:
Small red or white-headed bumps around hair follicles.
2. Itching or Burning:
The affected area may feel itchy or tender.
3. Swelling:
Surrounding skin may appear swollen or inflamed.
4. Pus Formation:
Infected bumps may become filled with pus and break open.
5. Crusting:
Healed lesions may crust over.
6. Scarring or Dark Spots:
Severe cases can lead to permanent scarring or post-inflammatory hyperpigmentation.
---
Effects
1. Discomfort and Pain:
Itching, tenderness, or pain can interfere with daily activities.
2. Skin Damage:
Repeated or severe infections may cause scarring or pigmentation changes.
3. Cosmetic Concerns:
Visible bumps and scars can affect self-esteem.
4. Chronic or Recurrent Infections:
Folliculitis can become persistent without proper treatment.
---
Solutions and Treatments
Mild Cases
1. Hygiene and Skincare:
Cleanse the affected area gently with warm water and antibacterial soap.
2. Warm Compresses:
Apply warm compresses to reduce swelling and promote drainage.
3. Over-the-Counter (OTC) Products:
Topical antibiotics (e.g., mupirocin) or antifungal creams.
Benzoyl peroxide cleansers for mild bacterial folliculitis.
Moderate to Severe Cases
1. Topical Medications:
Antibiotics: Mupirocin or clindamycin for bacterial infections.
Antifungal Creams: For fungal folliculitis (e.g., ketoconazole or clotrimazole).
2. Oral Medications:
Antibiotics: Oral doxycycline or cephalexin for widespread or severe infections.
Antifungal Pills: Oral fluconazole or itraconazole for fungal causes.
3. Antiviral Medications:
For folliculitis caused by herpes simplex (e.g., acyclovir).
4. Steroid Creams:
Reduce inflammation in non-infectious folliculitis, such as from irritation.
---
Lifestyle and Home Remedies
1. Avoid Tight Clothing:
Wear loose, breathable fabrics to reduce friction and irritation.
2. Shaving Techniques:
Use clean razors, shave in the direction of hair growth, and avoid frequent shaving.
3. Stay Clean and Dry:
Keep the affected area clean and avoid excessive moisture.
4. Exfoliation:
Use gentle exfoliants to prevent clogged follicles (avoid during active infections).
5. Avoid Sharing Personal Items:
Do not share towels, razors, or other personal items.
---
Preventive Measures
1. Proper Hygiene:
Wash regularly, especially after sweating.
2. Avoid Irritants:
Minimize the use of oily or heavy skin products that can clog follicles.
3. Disinfect Hot Tubs and Pools:
Ensure proper maintenance to avoid contamination.
4. Strengthen Immune System:
Manage underlying conditions and maintain a healthy lifestyle.
---
When to See a Doctor
Symptoms persist for more than a few days.
Folliculitis spreads or becomes widespread.
Painful, pus-filled lesions or boils develop.
Scarring or pigmentation changes occur.
With appropriate care and treatment, folliculitis is usually manageable and resolves without long-term complications.



No comments yet
Be the first to share your thoughts!