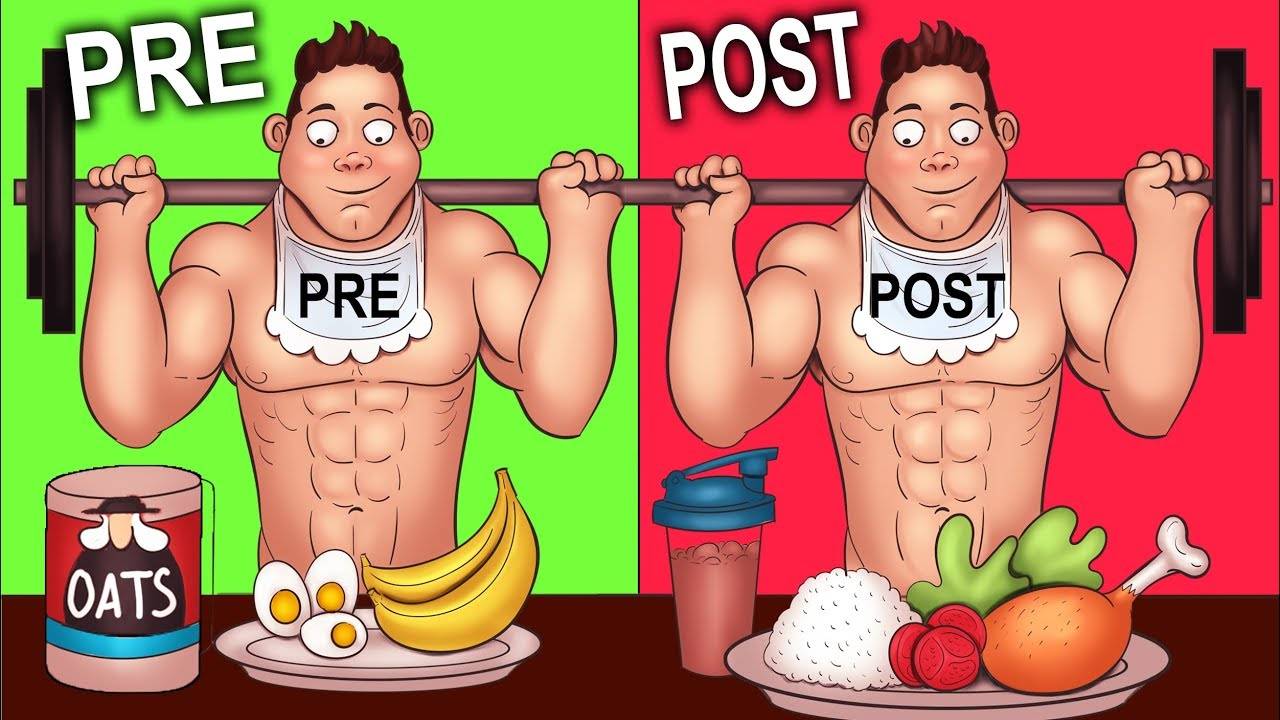
What You Should Eat Before and After Workouts for Maximum Impact
Whether you’re a fitness enthusiast or just starting your exercise journey, proper nutrition is key to getting the most out of your workouts. Eating the right foods at the right times can boost your performance and speed up recovery. This guide breaks down everything you need to know about pre- and post-workout nutrition to fuel your body effectively.
Why Nutrition is Important for Workouts
Pre-Workout Nutrition:
Prepares your body by providing the energy needed for exercise. Carbohydrates act as your main energy source, while protein helps preserve muscle mass.
Post-Workout Nutrition:
Aids in muscle repair and glycogen replenishment while reducing soreness, preparing you for your next workout.
Pre-Workout Nutrition: Laying the Groundwork
Timing Matters
2-3 Hours Before Exercise:
Eat a balanced meal with plenty of carbs, moderate protein, and minimal fat.
Example: Grilled chicken with quinoa or oatmeal with banana and almonds.
30-60 Minutes Before Exercise:
Opt for a light snack to prevent hunger and provide a quick energy boost.
Example: A banana with peanut butter or a small protein smoothie.
What to Eat Before a Workout
1. Carbohydrates:
Your body’s main energy source. Aim for 1-4 grams of carbs per kilogram of body weight about 1-2 hours before working out.
2. Protein:
Helps repair and protect muscles. Include 15-20 grams of protein in your pre-workout snack.
3. Fats:
Limit fat intake before exercise as it slows digestion and could cause discomfort during your workout.
Examples of Pre-Workout Snacks
- Greek yogurt with berries.
- Whole-grain toast with a boiled egg.
- A piece of fruit like an apple or banana.
During the Workout (If Needed)
For workouts under an hour, water is usually sufficient to stay hydrated. However, for longer or more intense sessions, you might need:
- Carbohydrates: Consume 30-90 grams per hour from sources like bananas, raisins, or sports drinks.
- Electrolytes: Replenish minerals lost through sweat, especially in hot or humid conditions.
Post-Workout Nutrition: Enhancing Recovery
Timing is Key
Eat within 30-60 minutes after exercise to maximize recovery and replenish glycogen stores. Waiting longer than two hours can significantly slow recovery.
What to Eat After a Workout
1. Protein:
Essential for muscle repair and growth. Aim for 20-40 grams of high-quality protein post-workout.
2. Carbohydrates:
Replenishes energy stores. Consume 25-30 grams of carbs for effective recovery.
3. Fats:
While not crucial, small amounts of healthy fats like avocado or nuts can be included.
Examples of Post-Workout Meals
- A protein shake with a banana.
- Grilled salmon with sweet potatoes.
- Greek yogurt topped with granola and honey.
Hydration
Drink 16-24 ounces of water for every pound of body weight lost during exercise. For longer or high-intensity workouts, consider electrolyte-rich drinks.
Tailoring Nutrition to Your Workout Goals
1. Endurance Activities (e.g., running, cycling):
Prioritize carbs for sustained energy. A 4:1 ratio of carbs to protein is ideal.
2. Strength Training (e.g., weightlifting):
Focus on protein for muscle repair, using a 2:1 ratio of carbs to protein.
3. General Fitness:
A balanced 3:1 ratio of carbs to protein works well for most recreational activities.
Avoid These Common Nutrition Mistakes
Skipping Meals:
Exercising on an empty stomach can lower performance and lead to muscle loss.
Eating Too Much Fat:
High-fat meals before or after exercise can slow digestion and nutrient absorption.
Neglecting Hydration:
Dehydration can cause fatigue, cramps, and reduced performance.
Practical Tips for Everyday Athletes
1. Meal Prep:
Plan and prepare your meals ahead of time to stay consistent.
2. Portion Control:
Adjust portion sizes to match your workout intensity and goals.
3. Listen to Your Body:
Everyone’s nutritional needs are different. Experiment with different foods and timings to find what works best for you.
Pre- and post-workout nutrition is a vital part of any fitness routine. Eating carbohydrates and protein before exercise gives you the energy to perform, while focusing on protein and carbs afterward helps with recovery. Don’t forget to stay hydrated and time your meals for maximum benefit.
By following these strategies, you’ll enhance your workout performance, recover faster, and feel more energized. Start today, and tailor your nutrition plan to meet your unique fitness needs.
For more detailed guidance, check resources like the American Heart Association or Cleveland Clinic.