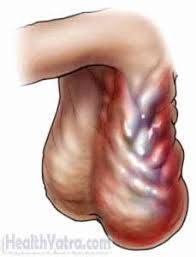
Varicocele
A varicocele is the abnormal enlargement of veins within the scrotum, similar to varicose veins that occur in the legs. It is a common condition, especially in males aged 15–25 years.
---
Causes
1. Venous Valve Dysfunction:
Malfunctioning valves in the veins that drain blood from the testicles can cause blood to pool, leading to swelling.
2. Anatomical Factors:
The left testicular vein is more commonly affected due to its anatomy, as it drains into the left renal vein at a perpendicular angle, which can increase pressure.
3. Increased Abdominal Pressure:
Heavy lifting, chronic coughing, or straining during bowel movements may exacerbate vein dilation.
4. Unknown Causes:
In some cases, the exact reason for varicocele development is unclear.
---
Signs and Symptoms
1. Visible or Palpable Enlarged Veins:
A "bag of worms" sensation or appearance in the scrotum, often on the left side.
2. Scrotal Discomfort:
Dull or aching pain in the scrotum, which may worsen with prolonged standing or physical activity.
3. Testicular Asymmetry:
The affected testicle may appear smaller due to reduced blood flow and heat stress.
4. Infertility Issues:
Some men discover varicocele when seeking evaluation for fertility problems.
5. No Symptoms:
Many varicoceles are asymptomatic and discovered during routine exams.
---
Effects
1. Reduced Testicular Function:
Impaired sperm production, motility, and quality due to increased scrotal temperature and reduced oxygen supply.
2. Infertility:
Varicoceles are a leading cause of male infertility, especially in cases of low sperm count or quality.
3. Testicular Atrophy:
The affected testicle may shrink over time.
4. Chronic Pain:
Discomfort can interfere with daily activities and physical performance.
---
Solutions
1. Observation and Monitoring:
Asymptomatic varicoceles or those not affecting fertility may not require treatment.
2. Lifestyle Adjustments:
Wearing supportive underwear to reduce discomfort.
Avoid prolonged standing or heavy lifting to reduce strain.
3. Medications:
Pain relievers like ibuprofen or acetaminophen for mild pain.
4. Surgical Treatment (Indicated for significant symptoms or infertility):
Varicocelectomy: Surgical ligation of the affected veins to redirect blood flow to normal veins.
Percutaneous Embolization: A minimally invasive procedure where a coil or solution is used to block the abnormal veins.
5. Assisted Reproductive Techniques:
For men with infertility, in-vitro fertilization (IVF) or intracytoplasmic sperm injection (ICSI) may be considered.
---
Prevention
While varicocele cannot always be prevented, early detection and treatment can help manage complications.
Regular self-exams and annual medical check-ups can help detect changes in the scrotum early.
If you suspect a varicocele, consult a healthcare provider for a proper evaluation and personalized treatment plan.



No comments yet
Be the first to share your thoughts!