Pneumonia: Understanding the Causes, Symptoms, Diagnosis, Treatment Options, and Prevention Strategies
Pneumonia is a serious and potentially life-threatening infection that inflames the air sacs in the lungs. It can be caused by a variety of factors, including bacteria, viruses, and fungi. According to the World Health Organization (WHO), pneumonia is the leading cause of death in children under the age of five, accounting for approximately 1.4 million deaths annually. In this article, we will provide an in-depth overview of pneumonia, including its causes, symptoms, diagnosis, treatment options, and prevention strategies.
Causes of Pneumonia
Pneumonia can be caused by a variety of factors, including:
1. Bacterial pneumonia: This is the most common type of pneumonia, accounting for approximately 80% of cases. The most common bacterial causes of pneumonia include Streptococcus pneumoniae, Haemophilus influenzae, and Klebsiella pneumoniae.
2. Viral pneumonia: This type of pneumonia is caused by viruses, such as the flu virus, respiratory syncytial virus (RSV), and adenovirus.
3. Fungal pneumonia: This type of pneumonia is caused by fungi, such as Pneumocystis jirovecii, which is a common cause of pneumonia in people with weakened immune systems.
4. Parasitic pneumonia: This type of pneumonia is caused by parasites, such as Plasmodium falciparum, which is a common cause of pneumonia in people with malaria.
Symptoms of Pneumonia
The symptoms of pneumonia can vary depending on the cause and severity of the infection. Common symptoms include:
- Coughing, which may produce phlegm or pus
- Fever, which may be high
- Chills
- Shortness of breath or difficulty breathing
- Chest pain or discomfort
- Fatigue or weakness
- Headache
- Sweating
- Nausea or vomiting
Diagnosis of Pneumonia
Diagnosing pneumonia typically involves a combination of physical examination, medical history, and diagnostic tests. The following tests may be used to diagnose pneumonia:
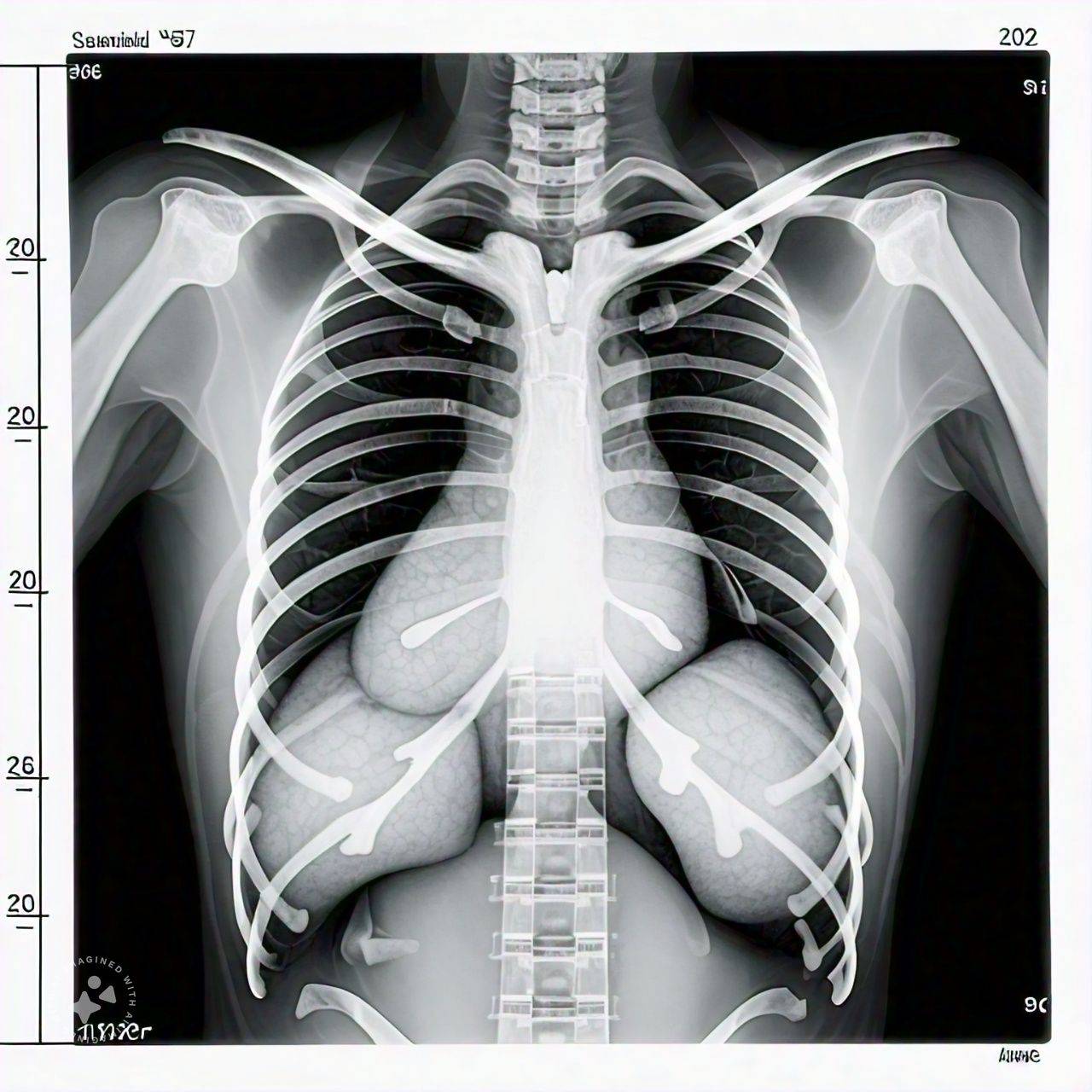
- Chest X-ray: This is the most common imaging test used to diagnose pneumonia.
- Blood tests: Blood tests may be used to check for signs of infection, such as a high white blood cell count.
- Sputum test: A sputum test may be used to check for the presence of bacteria or other microorganisms in the lungs.
- Pulse oximetry: This test measures the level of oxygen in the blood.
Treatment Options for Pneumonia
The treatment options for pneumonia depend on the cause and severity of the infection. The following treatments may be used:
- Antibiotics: These are the primary treatment for bacterial pneumonia.
- Antiviral medications: These may be used to treat viral pneumonia.
- Antifungal medications: These may be used to treat fungal pneumonia.
- Oxygen therapy: This may be used to help increase oxygen levels in the blood.
- Mechanical ventilation: This may be used in severe cases of pneumonia to help support breathing.
Prevention Strategies for Pneumonia
Preventing pneumonia is crucial, especially for high-risk groups, such as older adults, young children, and people with weakened immune systems. The following prevention strategies may be used:
- Vaccination: Getting vaccinated against pneumonia can help prevent the infection.
- Practicing good hygiene: Practicing good hygiene, such as washing hands frequently, can help reduce the risk of transmission.
- Avoiding close contact: Avoiding close contact with people who are sick with pneumonia can help reduce the risk of transmission.
- Quitting smoking: Quitting smoking can help reduce the risk of developing pneumonia.
- Managing underlying health conditions: Managing underlying health conditions, such as diabetes and heart disease, can help reduce the risk of developing pneumonia.
Conclusion
Pneumonia is a serious and potentially life-threatening infection that can be caused by a variety of factors. Understanding the causes, symptoms, diagnosis, treatment options, and prevention strategies is crucial for managing the infection and reducing the risk of complications. By getting vaccinated, practicing good hygiene, avoiding close contact with people who are sick, quitting smoking, and managing underlying health conditions, individuals can help reduce their risk of developing pneumonia.Pneumonia: Understanding the Causes, Symptoms, Diagnosis, Treatment Options, and Prevention Strategies
Pneumonia is a serious and potentially life-threatening infection that inflames the air sacs in the lungs. It can be caused by a variety of factors, including bacteria, viruses, and fungi. According to the World Health Organization (WHO), pneumonia is the leading cause of death in children under the age of five, accounting for approximately 1.4 million deaths annually. In this article, we will provide an in-depth overview of pneumonia, including its causes, symptoms, diagnosis, treatment options, and prevention strategies.
Causes of Pneumonia
Pneumonia can be caused by a variety of factors, including:
1. Bacterial pneumonia: This is the most common type of pneumonia, accounting for approximately 80% of cases. The most common bacterial causes of pneumonia include Streptococcus pneumoniae, Haemophilus influenzae, and Klebsiella pneumoniae.
2. Viral pneumonia: This type of pneumonia is caused by viruses, such as the flu virus, respiratory syncytial virus (RSV), and adenovirus.
3. Fungal pneumonia: This type of pneumonia is caused by fungi, such as Pneumocystis jirovecii, which is a common cause of pneumonia in people with weakened immune systems.
4. Parasitic pneumonia: This type of pneumonia is caused by parasites, such as Plasmodium falciparum, which is a common cause of pneumonia in people with malaria.
Symptoms of Pneumonia
The symptoms of pneumonia can vary depending on the cause and severity of the infection. Common symptoms include:
- Coughing, which may produce phlegm or pus
- Fever, which may be high
- Chills
- Shortness of breath or difficulty breathing
- Chest pain or discomfort
- Fatigue or weakness
- Headache
- Sweating
- Nausea or vomiting
Diagnosis of Pneumonia
Diagnosing pneumonia typically involves a combination of physical examination, medical history, and diagnostic tests. The following tests may be used to diagnose pneumonia:
- Chest X-ray: This is the most common imaging test used to diagnose pneumonia.
- Blood tests: Blood tests may be used to check for signs of infection, such as a high white blood cell count.
- Sputum test: A sputum test may be used to check for the presence of bacteria or other microorganisms in the lungs.
- Pulse oximetry: This test measures the level of oxygen in the blood.
Treatment Options for Pneumonia
The treatment options for pneumonia depend on the cause and severity of the infection. The following treatments may be used:
- Antibiotics: These are the primary treatment for bacterial pneumonia.
- Antiviral medications: These may be used to treat viral pneumonia.
- Antifungal medications: These may be used to treat fungal pneumonia.
- Oxygen therapy: This may be used to help increase oxygen levels in the blood.
- Mechanical ventilation: This may be used in severe cases of pneumonia to help support breathing.
Prevention Strategies for Pneumonia
Preventing pneumonia is crucial, especially for high-risk groups, such as older adults, young children, and people with weakened immune systems. The following prevention strategies may be used:
- Vaccination: Getting vaccinated against pneumonia can help prevent the infection.
- Practicing good hygiene: Practicing good hygiene, such as washing hands frequently, can help reduce the risk of transmission.
- Avoiding close contact: Avoiding close contact with people who are sick with pneumonia can help reduce the risk of transmission.
- Quitting smoking: Quitting smoking can help reduce the risk of developing pneumonia.
- Managing underlying health conditions: Managing underlying health conditions, such as diabetes and heart disease, can help reduce the risk of developing pneumonia.
Conclusion
Pneumonia is a serious and potentially life-threatening infection that can be caused by a variety of factors. Understanding the causes, symptoms, diagnosis, treatment options, and prevention strategies is crucial for managing the infection and reducing the risk of complications. By getting vaccinated, practicing good hygiene, avoiding close contact with people who are sick, quitting smoking, and managing underlying health conditions, individuals can help reduce their risk of developing pneumonia.Pneumonia: Understanding the Causes, Symptoms, Diagnosis, Treatment Options, and Prevention Strategies
Pneumonia is a serious and potentially life-threatening infection that inflames the air sacs in the lungs. It can be caused by a variety of factors, including bacteria, viruses, and fungi. According to the World Health Organization (WHO), pneumonia is the leading cause of death in children under the age of five, accounting for approximately 1.4 million deaths annually. In this article, we will provide an in-depth overview of pneumonia, including its causes, symptoms, diagnosis, treatment options, and prevention strategies.
Causes of Pneumonia
Pneumonia can be caused by a variety of factors, including:
1. Bacterial pneumonia: This is the most common type of pneumonia, accounting for approximately 80% of cases. The most common bacterial causes of pneumonia include Streptococcus pneumoniae, Haemophilus influenzae, and Klebsiella pneumoniae.
2. Viral pneumonia: This type of pneumonia is caused by viruses, such as the flu virus, respiratory syncytial virus (RSV), and adenovirus.
3. Fungal pneumonia: This type of pneumonia is caused by fungi, such as Pneumocystis jirovecii, which is a common cause of pneumonia in people with weakened immune systems.
4. Parasitic pneumonia: This type of pneumonia is caused by parasites, such as Plasmodium falciparum, which is a common cause of pneumonia in people with malaria.
Symptoms of Pneumonia
The symptoms of pneumonia can vary depending on the cause and severity of the infection. Common symptoms include:
- Coughing, which may produce phlegm or pus
- Fever, which may be high
- Chills
- Shortness of breath or difficulty breathing
- Chest pain or discomfort
- Fatigue or weakness
- Headache
- Sweating
- Nausea or vomiting
Diagnosis of Pneumonia
Diagnosing pneumonia typically involves a combination of physical examination, medical history, and diagnostic tests. The following tests may be used to diagnose pneumonia:
- Chest X-ray: This is the most common imaging test used to diagnose pneumonia.
- Blood tests: Blood tests may be used to check for signs of infection, such as a high white blood cell count.
- Sputum test: A sputum test may be used to check for the presence of bacteria or other microorganisms in the lungs.
- Pulse oximetry: This test measures the level of oxygen in the blood.
Treatment Options for Pneumonia
The treatment options for pneumonia depend on the cause and severity of the infection. The following treatments may be used:
- Antibiotics: These are the primary treatment for bacterial pneumonia.
- Antiviral medications: These may be used to treat viral pneumonia.
- Antifungal medications: These may be used to treat fungal pneumonia.
- Oxygen therapy: This may be used to help increase oxygen levels in the blood.
- Mechanical ventilation: This may be used in severe cases of pneumonia to help support breathing.
Prevention Strategies for Pneumonia
Preventing pneumonia is crucial, especially for high-risk groups, such as older adults, young children, and people with weakened immune systems. The following prevention strategies may be used:
- Vaccination: Getting vaccinated against pneumonia can help prevent the infection.
- Practicing good hygiene: Practicing good hygiene, such as washing hands frequently, can help reduce the risk of transmission.
- Avoiding close contact: Avoiding close contact with people who are sick with pneumonia can help reduce the risk of transmission.
- Quitting smoking: Quitting smoking can help reduce the risk of developing pneumonia.
- Managing underlying health conditions: Managing underlying health conditions, such as diabetes and heart disease, can help reduce the risk of developing pneumonia.
Conclusion
Pneumonia is a serious and potentially life-threatening infection that can be caused by a variety of factors. Understanding the causes, symptoms, diagnosis, treatment options, and prevention strategies is crucial for managing the infection and reducing the risk of complications. By getting vaccinated, practicing good hygiene, avoiding close contact with people who are sick, quitting smoking, and managing underlying health conditions, individuals can help reduce their risk of developing pneumonia.Pneumonia: Understanding the Causes, Symptoms, Diagnosis, Treatment Options, and Prevention Strategies
Pneumonia is a serious and potentially life-threatening infection that inflames the air sacs in the lungs. It can be caused by a variety of factors, including bacteria, viruses, and fungi. According to the World Health Organization (WHO), pneumonia is the leading cause of death in children under the age of five, accounting for approximately 1.4 million deaths annually. In this article, we will provide an in-depth overview of pneumonia, including its causes, symptoms, diagnosis, treatment options, and prevention strategies.
Causes of Pneumonia
Pneumonia can be caused by a variety of factors, including:
1. Bacterial pneumonia: This is the most common type of pneumonia, accounting for approximately 80% of cases. The most common bacterial causes of pneumonia include Streptococcus pneumoniae, Haemophilus influenzae, and Klebsiella pneumoniae.
2. Viral pneumonia: This type of pneumonia is caused by viruses, such as the flu virus, respiratory syncytial virus (RSV), and adenovirus.
3. Fungal pneumonia: This type of pneumonia is caused by fungi, such as Pneumocystis jirovecii, which is a common cause of pneumonia in people with weakened immune systems.
4. Parasitic pneumonia: This type of pneumonia is caused by parasites, such as Plasmodium falciparum, which is a common cause of pneumonia in people with malaria.
Symptoms of Pneumonia
The symptoms of pneumonia can vary depending on the cause and severity of the infection. Common symptoms include:
- Coughing, which may produce phlegm or pus
- Fever, which may be high
- Chills
- Shortness of breath or difficulty breathing
- Chest pain or discomfort
- Fatigue or weakness
- Headache
- Sweating
- Nausea or vomiting
Diagnosis of Pneumonia
Diagnosing pneumonia typically involves a combination of physical examination, medical history, and diagnostic tests. The following tests may be used to diagnose pneumonia:
- Chest X-ray: This is the most common imaging test used to diagnose pneumonia.
- Blood tests: Blood tests may be used to check for signs of infection, such as a high white blood cell count.
- Sputum test: A sputum test may be used to check for the presence of bacteria or other microorganisms in the lungs.
- Pulse oximetry: This test measures the level of oxygen in the blood.
Treatment Options for Pneumonia
The treatment options for pneumonia depend on the cause and severity of the infection. The following treatments may be used:
- Antibiotics: These are the primary treatment for bacterial pneumonia.
- Antiviral medications: These may be used to treat viral pneumonia.
- Antifungal medications: These may be used to treat fungal pneumonia.
- Oxygen therapy: This may be used to help increase oxygen levels in the blood.
- Mechanical ventilation: This may be used in severe cases of pneumonia to help support breathing.
Prevention Strategies for Pneumonia
Preventing pneumonia is crucial, especially for high-risk groups, such as older adults, young children, and people with weakened immune systems. The following prevention strategies may be used:
- Vaccination: Getting vaccinated against pneumonia can help prevent the infection.
- Practicing good hygiene: Practicing good hygiene, such as washing hands frequently, can help reduce the risk of transmission.
- Avoiding close contact: Avoiding close contact with people who are sick with pneumonia can help reduce the risk of transmission.
- Quitting smoking: Quitting smoking can help reduce the risk of developing pneumonia.
- Managing underlying health conditions: Managing underlying health conditions, such as diabetes and heart disease, can help reduce the risk of developing pneumonia.
Conclusion
Pneumonia is a serious and potentially life-threatening infection that can be caused by a variety of factors. Understanding the causes, symptoms, diagnosis, treatment options, and prevention strategies is crucial for managing the infection and reducing the risk of complications. By getting vaccinated, practicing good hygiene, avoiding close contact with people who are sick, quitting smoking, and managing underlying health conditions, individuals can help reduce their risk of developing pneumonia.



No comments yet
Be the first to share your thoughts!