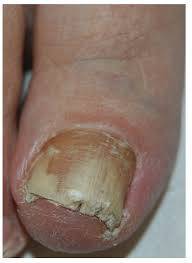
Onychomycosis
Onychomycosis, commonly referred to as nail fungus, is a fungal infection that affects the toenails or fingernails. It can cause significant discomfort and cosmetic concerns if untreated.
---
Causes
1. Fungal Organisms (Dermatophytes): The most common cause, often Trichophyton rubrum.
2. Yeasts: Such as Candida species.
3. Non-Dermatophyte Molds: Less common but can also infect nails.
4. Risk Factors:
Warm, moist environments (sweaty feet, tight shoes).
Poor nail hygiene.
Walking barefoot in communal areas like pools or gyms.
Nail trauma.
Diabetes or circulatory issues.
Weakened immune system.
---
Signs and Symptoms
1. Thickened Nails: Nails become abnormally thick and difficult to trim.
2. Discoloration: Yellow, white, brown, or green discoloration.
3. Brittle or Crumbly Nails: Nails may split, crack, or break easily.
4. Separation: Nail may detach from the nail bed (onycholysis).
5. Distorted Shape: Nails may become misshapen over time.
6. Foul Odor: In severe cases, the infection can produce an unpleasant smell.
7. Pain or Discomfort: Particularly when wearing shoes or using affected fingers.
---
Effects
1. Aesthetic Concerns: Discolored, deformed nails may cause embarrassment.
2. Pain: Thickened nails can press against shoes, leading to discomfort.
3. Secondary Infections: The fungal infection can spread to the surrounding skin or other nails.
4. Impairment: Difficulty using affected fingers or toes for daily activities.
5. Complications in Health Conditions: Worsens for people with diabetes, leading to foot ulcers or infections.
---
Solutions
1. Preventive Measures
Keep nails clean and dry.
Avoid walking barefoot in communal areas.
Use breathable socks and well-ventilated footwear.
Trim nails properly to avoid trauma.
Disinfect nail tools regularly.
2. Medical Treatments
Topical Antifungal Medications:
E.g., Ciclopirox, Efinaconazole, or Amorolfine. Useful for mild cases.
Oral Antifungal Drugs:
E.g., Terbinafine or Itraconazole. Effective for severe or widespread infections.
Combination Therapy: Using both oral and topical treatments for stubborn cases.
Laser Therapy: Targets fungal cells without damaging surrounding tissues.
3. Home Remedies (For Mild Cases)
Tea Tree Oil: Natural antifungal properties. Apply diluted oil to the nail.
Vinegar Soak: A mix of water and vinegar to inhibit fungal growth.
Hydrogen Peroxide: To clean and disinfect the affected area.
4. Surgical or Advanced Options
Nail Removal: In severe cases, the entire nail may be removed to allow treatment.
Permanent Removal: For recurring infections, the nail matrix can be destroyed.
5. Consult a Specialist
A dermatologist or podiatrist can provide tailored treatments and guidance.
---
Early treatment improves outcomes and prevents the spread of onychomycosis. Consistency with treatment is essential, as nail fungus often requires several months to fully resolve.