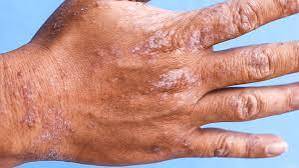
Eczema
Eczema, or atopic dermatitis, is a chronic skin condition that causes inflammation, redness, and itching. It often starts in childhood but can affect individuals of any age.
---
Causes
The exact cause of eczema is not fully understood, but it is believed to result from a combination of genetic, environmental, and immune system factors.
1. Genetic Factors:
Family history of eczema, allergies, or asthma increases the risk.
Mutations in the filaggrin gene, which helps maintain the skin barrier.
2. Environmental Triggers:
Allergens (pollen, dust mites, pet dander).
Irritants (soaps, detergents, fragrances).
Weather changes (cold, dry air or heat).
Sweating or excessive dryness.
3. Immune Dysregulation:
Overactive immune responses to triggers lead to inflammation.
4. Other Triggers:
Stress.
Hormonal changes (e.g., during pregnancy or menstruation).
Certain foods (dairy, nuts, or wheat in some cases).
---
Signs and Symptoms
1. Itching: Often severe and persistent, especially at night.
2. Redness and Inflammation: Skin appears red, swollen, and irritated.
3. Dry, Scaly Skin: Affected areas may flake or peel.
4. Rash: Commonly found on the face, hands, elbows, knees, or neck.
5. Thickened or Cracked Skin: Chronic scratching can cause skin thickening (lichenification).
6. Weeping or Crusting: In severe cases, fluid may ooze from the affected area.
---
Effects
1. Physical Discomfort: Constant itching and skin irritation can interfere with daily activities.
2. Sleep Disturbances: Nighttime itching often disrupts sleep.
3. Infection: Repeated scratching can lead to bacterial infections, such as Staphylococcus aureus.
4. Emotional Impact: Anxiety, depression, or low self-esteem due to the appearance of the skin.
5. Chronic Nature: Eczema often flares up periodically, requiring ongoing management.
---
Solutions
1. Preventive Measures
Moisturize Regularly: Use fragrance-free, hypoallergenic emollients or ointments.
Avoid Triggers: Identify and avoid allergens, irritants, and harsh products.
Use Gentle Skin Products: Choose mild, unscented soaps, and detergents.
Wear Protective Clothing: Soft fabrics like cotton to avoid skin irritation.
Control Temperature and Humidity: Use humidifiers in dry climates.
2. Medical Treatments
Topical Corticosteroids: Reduce inflammation and itching during flare-ups.
Calcineurin Inhibitors: Non-steroid creams like tacrolimus or pimecrolimus for sensitive areas.
Antihistamines: Reduce itching and help with sleep.
Antibiotics: Treat secondary infections if present.
Phototherapy: Controlled exposure to ultraviolet (UV) light for severe cases.
Oral Medications: For severe eczema, options include systemic corticosteroids or immunosuppressants like cyclosporine.
3. Home Remedies
Oatmeal Baths: Soothe irritated skin and reduce inflammation.
Coconut Oil: Acts as a natural moisturizer with antimicrobial properties.
Aloe Vera Gel: Calms redness and itching.
Cold Compresses: Relieve itching and swelling.
4. Lifestyle Modifications
Stress Management: Practice relaxation techniques such as yoga, meditation, or counseling.
Dietary Adjustments: Identify and avoid foods that trigger flare-ups.
5. Long-Term Care
Maintain consistent skin care routines, even during remission periods.
Work with a dermatologist to develop a tailored management plan.
---
Key Takeaways
Eczema is a chronic condition but can be managed with proper care.
Early intervention and consistent treatment reduce flare-ups and improve quality of life.
Avoiding triggers and maintaining skin hydration are crucial for long-term management.