### Understanding Logarithms: The Exponent Concept
A **logarithm** is a mathematical concept that answers the question: **To what power must a given base be raised to produce a specific number?** It is a fundamental tool in algebra, calculus, and many fields of science and engineering.
---
#### The Definition of a Logarithm
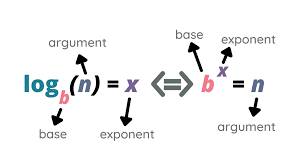
The logarithmic expression is written as:
\[
\log_b(y) = x
\]
This means that \( b^x = y \), where:
- \( b \) is the **base** (a positive number, \( b > 0 \), and \( b \neq 1 \)).
- \( y \) is the **result** or the number you're trying to reach.
- \( x \) is the **logarithm**, or the power/exponent to which the base \( b \) must be raised to produce \( y \).
---
#### Examples
1. \(\log_2(8) = 3\): Here, the base \( 2 \) must be raised to the power \( 3 \) to produce \( 8 \), since \( 2^3 = 8 \).
2. \(\log_{10}(1000) = 3\): The base \( 10 \) raised to \( 3 \) gives \( 1000 \), as \( 10^3 = 1000 \).
---
#### Types of Logarithms
1. **Common Logarithm (\( \log \))**:
- Base \( 10 \).
- Frequently used in science and engineering.
- Example: \(\log(1000) = 3\) (implies base 10).
2. **Natural Logarithm (\( \ln \))**:
- Base \( e \) (Euler's number, approximately \( 2.718 \)).
- Used in calculus and natural growth models.
- Example: \(\ln(e^2) = 2\).
3. **Binary Logarithm**:
- Base \( 2 \).
- Common in computer science and information theory.
- Example: \(\log_2(16) = 4\).
---
#### Properties of Logarithms
Logarithms have several important properties that simplify calculations:
1. **Product Rule**:
\[
\log_b(xy) = \log_b(x) + \log_b(y)
\]
2. **Quotient Rule**:
\[
\log_b\left(\frac{x}{y}\right) = \log_b(x) - \log_b(y)
\]
3. **Power Rule**:
\[
\log_b(x^k) = k \cdot \log_b(x)
\]
4. **Change of Base Formula**:
\[
\log_b(y) = \frac{\log_k(y)}{\log_k(b)}
\]
This allows you to convert logarithms to a more convenient base.
---
#### Applications of Logarithms
1. **Science**: Understanding phenomena that scale exponentially, such as sound intensity (decibels) or the pH scale in chemistry.
2. **Engineering**: Logarithms simplify complex multiplications into additions, useful in circuit design and signal processing.
3. **Computer Science**: Efficiently solving problems involving powers of two, such as data storage and algorithm complexity analysis.
4. **Finance**: Calculating compound interest and growth rates over time.
5. **Statistics**: Transforming data to manage skewed distributions.
---
#### Conclusion
Logarithms are powerful mathematical tools that connect exponential growth to linear functions. By providing a way to "reverse" exponentiation, they simplify many real-world problems involving multiplication, division, and scaling. Understanding logarithms is essential for mastering mathematics and applying it effectively in various scientific and practical domains.



No comments yet
Be the first to share your thoughts!