Rifle Basics: Understanding Parts and Functions
Firearms are categorized based on their design and functionality, each serving specific purposes. Among them, rifles stand out for their versatility, making them a preferred choice for military, law enforcement, hunting, and competitive shooting. Their ability to engage targets from short to long distances, combined with durability and precision, makes them one of the most widely used firearms.
One specialized category is the sniper rifle, commonly used by military and law enforcement tactical units. These rifles offer extreme accuracy over long distances when operated by trained professionals.
In civilian applications, rifles are popular among hunters, particularly those targeting large game. Unlike shotguns, which are effective at close range, rifles allow hunters to engage targets from a greater distance, making them ideal for situations where animals are difficult to approach. Rifles are also widely used in sports shooting, from beginner-level BB gun training to professional Olympic-level competitions.
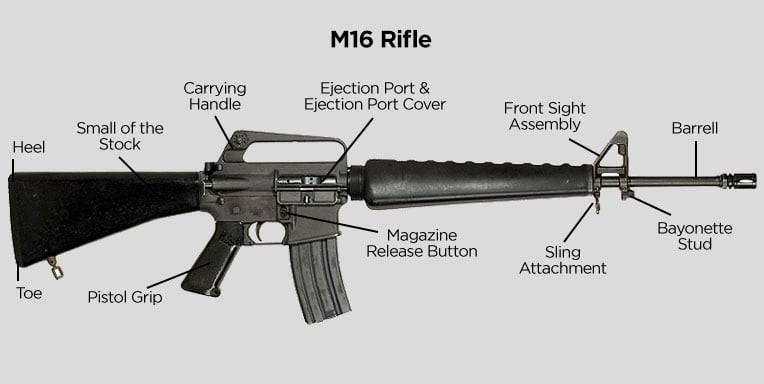
Among the most recognizable combat rifles is the M-16, along with its civilian counterpart, the AR-15. These rifles share many common components, with the key difference being that the M-16 has select-fire capability, allowing for automatic or burst-fire modes, whereas the AR-15 is limited to semi-automatic fire.
Key Components of a Rifle and Their Functions
Muzzle Compensator / Flash Suppressor
Located at the tip of the barrel, these components help manage recoil and reduce muzzle movement when firing. The muzzle compensator redirects hot gases to minimize upward barrel movement, while the flash suppressor disperses gases to reduce visible flash, aiding in concealment.
Handguard
Encasing the barrel, the handguard provides a secure grip while protecting the shooter’s hand from heat generated during firing.
Carry Handle
Positioned on top of the rifle behind the handguard, the carry handle allows for easy one-handed transport.
Charging Handle
Located just behind the carry handle, the charging handle is used to cycle the bolt and chamber a round. Pulling and releasing it loads a cartridge into the firing chamber, preparing the weapon to fire.
Sights (Front & Rear)
The front post and rear ghost ring sights aid in aiming. These are adjustable, allowing shooters to fine-tune their accuracy, a process known as zeroing the weapon.
Magazine Well & Magazine Release Button
The magazine well is a rectangular opening below the carry handle that holds the magazine, which stores ammunition. The magazine release button allows for quick removal and replacement of a magazine.
Bolt Catch
This mechanism holds the bolt open after the last round is fired. Once a fresh magazine is inserted, pressing the bolt catch releases the bolt, chambering a new round.
Selector Lever
This safety mechanism determines the firing mode of the rifle. On civilian models, it typically has two positions:
Safe – Prevents the weapon from firing.
Semi-Automatic – Fires one round per trigger pull.
Military models may have additional settings:
Three-Round Burst – Fires up to three rounds per trigger squeeze.
Full-Auto – Allows continuous fire as long as the trigger is held down.
Stock & Grip
Rifles come with different stock designs, including fixed stocks for stability and collapsible stocks for adjustability. Grips also vary, with pistol grips being common on tactical rifles and stock grips on traditional hunting rifles.



No comments yet
Be the first to share your thoughts!