The human mind comprises of right around 80 billion neurons that contrast in capacity, structure, and availability with different neurons. Because of this intricacy, the mind can play out different complex undertakings. Researchers have recognized a few kinds of neurons, yet they don't have the foggiest idea how this intricacy emerges during the mental health's.
Claude Desplan, Silver Professor of Biology at NYU and the review's senior creator, said, "Knowing how the human cerebrum creates could permit us in the future to rehash these formative cycles in the lab to produce explicit sorts of neurons in a Petri dish-and possibly relocate them inpatients-or to set off neuronal undifferentiated cells in living beings to produce and supplant missing neurons."
Concentrating on the human cerebrum is an inconceivably perplexing undertaking. That is the reason researchers rely upon model living beings, like mice and flies, to investigate the complex instruments engaged with the mind's cycles.
In another review, researchers at New York University have recognized the total series of 10 factors that direct the improvement of synapse types in the visual arrangement of organic product flies-remembering for what request these neurons create.
Worldly designing is the manner by which brain immature microorganisms produce various neurons over the long run. By communicating various particles named worldly record factors, or tTFs-that control the declaration of explicit qualities in every window of time, brain foundational microorganisms produce various neurons.
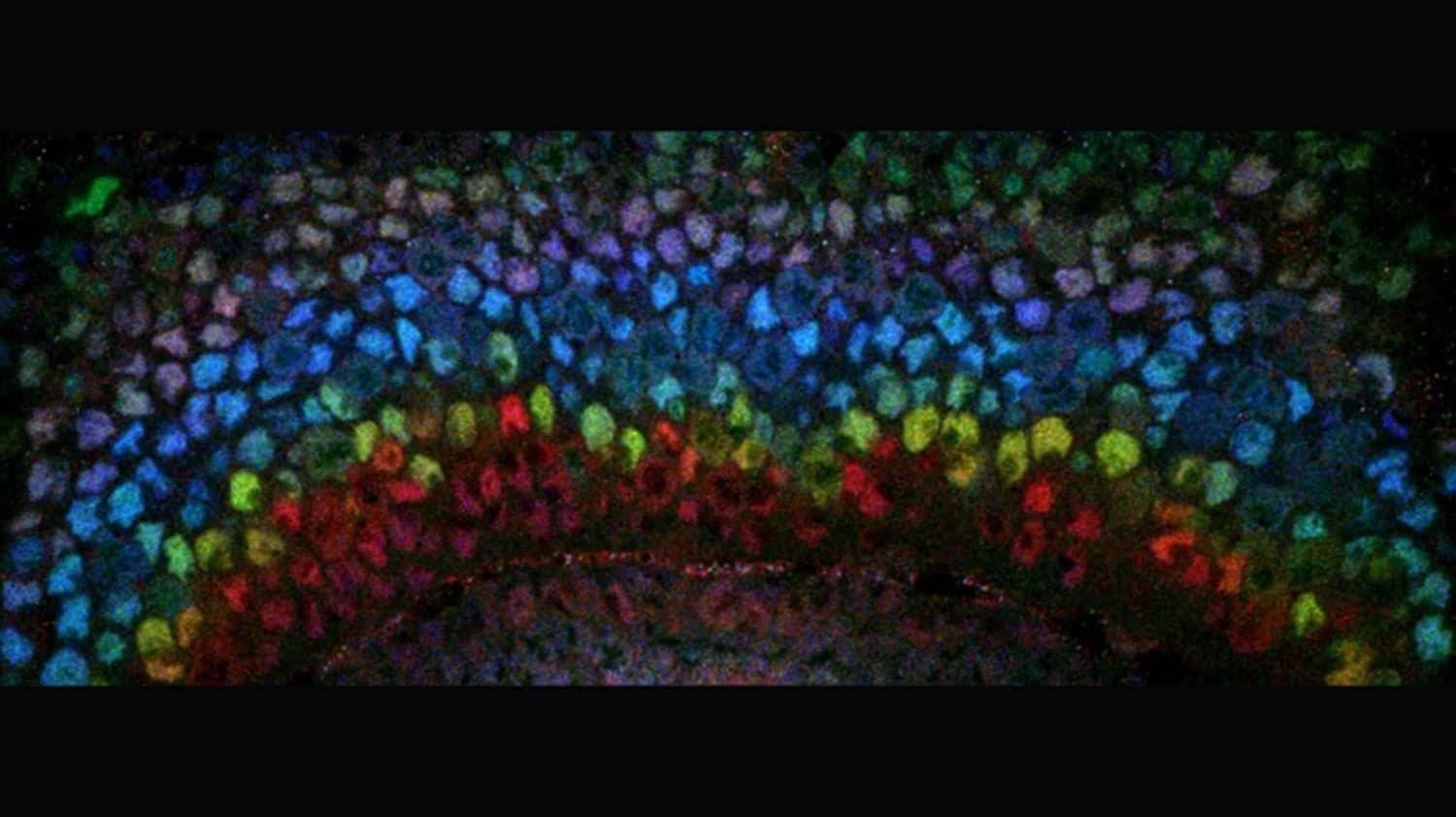
Researchers concentrated on the minds of the organic product fly Drosophila to uncover the total arrangement of tTFs expected to create the approximately 120 neuron kinds of the medulla, a particular cerebrum structure in the visual arrangement of flies. Utilizing mRNA sequencing, they acquired the transcriptome of in excess of 50,000 individual cells that were then assembled into the majority of the cell types present in the creating medulla.
Zeroing in on brain immature microorganisms, researchers distinguished the total arrangement of tTFs that characterize the various windows of time in this cerebrum locale and the hereditary organization that controls the statement of these different tTFs that permit this worldly outpouring to advance.
One of the review's lead creators, Nikolaos Konstantinides, said, "A few tTFs had been recently recognized in the mind's visual framework utilizing accessible antibodies; we have presently distinguished the thorough series of 10 tTFs that can indicate all the neuron types in this cerebrum locale."
Researchers later pinpointed the hereditary connections that permit the worldly fountain to advance and how this movement connects with the "birth request" of all neurons in the medulla, connecting explicit transient windows with the age of specific neurons. This fountain is fundamental for creating total brain variety of mind districts in a cliché request.
Isabel Holguera, a postdoctoral individual in NYU's Department of Biology and one of the review's co-first creators, expressed, "Impedance of the transient fountain movement prompts diminished neuronal variety, henceforth modifying mental health."
Researchers concentrated on the underlying system of brain immature microorganisms developing into neurons. This stage is known as separation. This cycle for fly and human cortical neurons is practically comparable, with indistinguishable quality articulation designs during phases of separation.
Co-first creator Anthony Rossi said, "Our discoveries propose that understanding the systems of neuron improvement in flies can produce knowledge for the same interaction in people."



No comments yet
Be the first to share your thoughts!