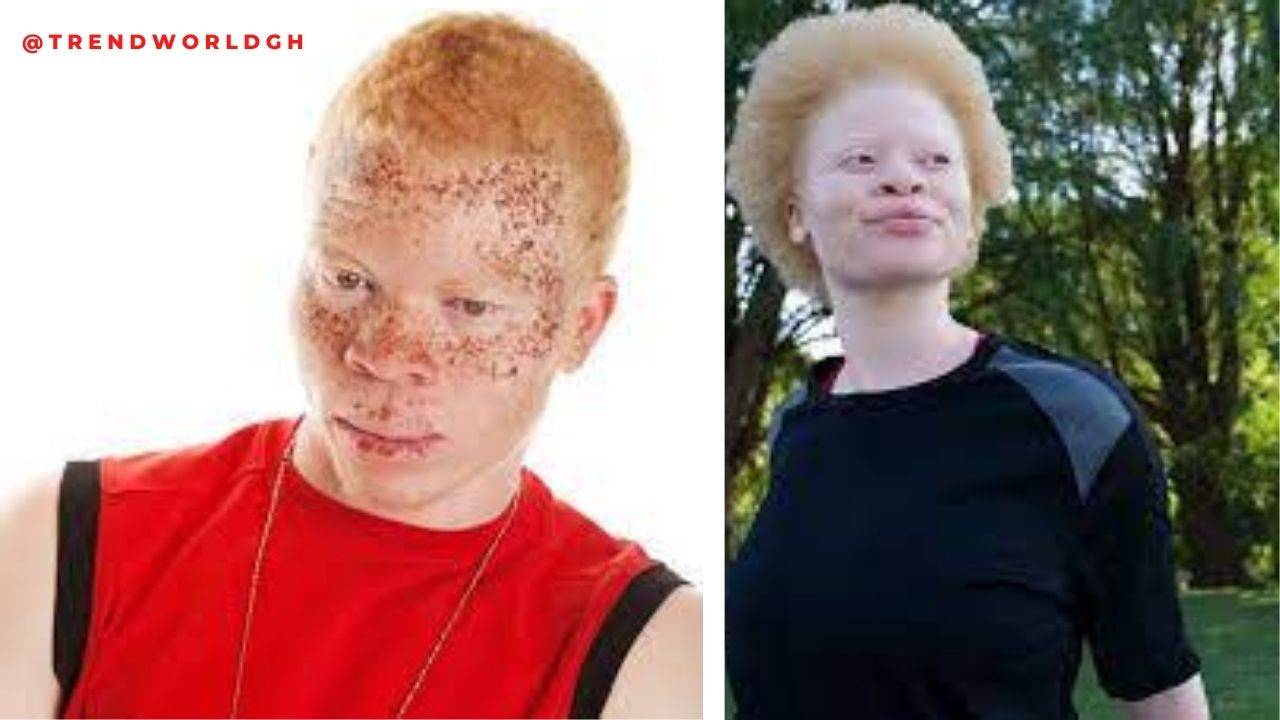
Albinism is a rare genetic condition caused by mutations of certain genes that affect the amount of melanin your body produces. Melanin controls the pigmentation (color) of your skin, eyes and hair. People with albinism have extremely pale skin, eyes and hair. They are at an increased risk of vision, skin and social issues.
Albinism is a defect in one of several genes that produce or distribute melanin, the pigment that gives skin, eyes, and hair their coloring. The defect may result in the absence of melanin production or a reduced amount of melanin production.
For most types of albinism, both parents must carry the gene in order for their child to develop the condition. Most people with albinism have parents who are only carriers of the gene and don’t have symptoms of the condition.
Below are the types of albinism :
1. Oculocutaneous albinism (OCA)
Oculocutaneous albinism (OCA) is a group of rare inherited disorders characterized by a reduction or complete lack of melanin pigment in the skin, hair and eyes. These conditions are caused by mutations in specific genes that are necessary for the production of melanin pigment in specialized cells called melanocytes but there are several type which are listed below.
OCA1.
OCA1 is caused by a defect in the tyrosinase enzyme and there are two subtypes of OCA1:
OCA1a. People with OCA1a have a complete absence of melanin. People with this subtype have white hair, very pale skin, and light eyes.
OCA1b. People with OCA1b produce some melanin. They have light-colored skin, hair, and eyes. Their coloring may increase as they age.
OCA2.
OCA2 is less severe than OCA1. It’s caused by a defect in the OCA2 gene that results in reduced melanin production. People with OCA2 are born with light coloring and skin. Their hair may be yellow, blond, or light brown and it's most common in people of African descent and Native Americans.
2. Ocular albinism
Ocular albinism is a genetic condition that primarily affects the eyes. This condition reduces the coloring (pigmentation) of the iris, which is the colored part of the eye, and the retina, which is the light-sensitive tissue at the back of the eye. Pigmentation in the eye is essential for normal vision.
Unlike some other forms of albinism, ocular albinism does not significantly affect the color of the skin and hair. People with this condition may have a somewhat lighter complexion than other members of their family, but these differences are usually minor.
3. Hermansky-Pudlak syndrome (HPS)
Hermansky-Pudlak syndrome (HPS) is a rare, hereditary disorder that consists of two characteristics: decreased pigmentation (albinism) with visual impairment, and blood platelet dysfunction with prolonged bleeding. Some patients have lung fibrosis, colitis, or an abnormal storage of a fatty-like substance (ceroid lipofuscin) in various tissues of the body.
4.Chédiak-Higashi's Syndrome
Chédiak-Higashi syndrome is a rare, autosomal recessive syndrome characterized by impaired lysis of phagocytized bacteria, resulting in recurrent bacterial respiratory and other infections and oculocutaneous albinism. Genetic testing for LYST mutations can confirm the diagnosis.
5. Griscelli syndrome
Griscelli syndrome is an inherited condition characterized by unusually light (hypopigmented) skin and light silvery-gray hair starting in infancy. Researchers have identified three types of this disorder, which are distinguished by their genetic cause and pattern of signs and symptoms.
What are the symptoms of albinism ?
People with albinism have the following symptoms:
an absence of color in the skin, hair, or eyes which are mostly lighter than normal coloring of the skin, hair, or eyes patches of skin that have an absence of color Albinism occurs with vision problems, which may include:
strabismus, or crossed eyes photophobia, or sensitivity to light nystagmus, or involuntary rapid eye movements impaired vision or blindness astigmatism.
Can Albinism be cured ?
Because albinism is a genetic disorder, it can't be cured but it's treatment focuses on getting proper eye care and monitoring skin for signs of abnormalities.
NB: Albinism has no race or nationality but a genetic disorder.
Thank you for reading.















No comments yet
Be the first to share your thoughts!