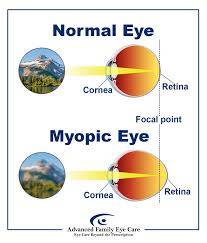
Near-sightedness also known as short sightedness and Myopia is a refractive error or eye disorder where light rays focus in front of, instead of on the retina. Myopia is the most common type eye disorder and is estimated to affect 1. 5 billion people. Both hereditary and environmental factors are essential for the growth of the Ocular tissues responsible for determining the refractive factor of the eye. Uncorrected Myopia is one of the most common causes of vision impairment globally along with Cataracts, Macular Degeneration and Vitamin-A deficiency. Myopia has been variously designated Simple, Physiologic, Pathologic, Progressive, Malignant, Degenerative, Congenital and acquired. A) Aetiology :- Congenital Myopia is generally amalgamated with an increase in axial length and overall globe size. b) High degree of error:- The refractive error may be up to -10D. Generally the error is of about 8-10D,which mostly remains constant. c) Clinical fundus changes are seen. C) Diagnosis:- Unilateral Congenital Myopia is frequently discovered either by routine screening eye examination or after a strabismus develops because of the associated amblyopia. D) Treatment:- Early diagnosis and correction of Congenital Myopia is coverable to help the child to expand normal distant vision and perception of the World. Even then it may not always be possible for these children to acquire 6/6 visual acuity in either eye.
E) Prognosis:- The prognosis for good vision and normal binocularity is poor in unilateral cases, if the myopia is acute. Developmental Myopia-commonest variety School Myopia (School going age 8-12 years) Simple or Developmental Myopia also known as Physiological Myopia, is the Commonest variety. It is deliberated as a Physiological error not associated with any eye problems. some factors associated with Simple Myopia are as follows:- a)Axial type of Simple Myopia may signify just a Physiological variation in the length of the eyeball or it may be associated with impertinent neurological growth during childhood. b) Curvatural type of Simple Myopia is considered to be due to underdevelopment of the eyeball c) Roll of Genetics :- Genetics plays an important role in the biological variation of the development of eye, as appearance of myopia is more in children with the both parent myopic (20%) than the children with one parent myopic (10%) and children with no parent myopic (5%). Most of the patients are rather both Hypermetropic, but during advancement the normal mark is overshooted and the child becomes myopic. Simple myopia generally begins between 7 and 10 years of the age and may develop during the years of growth usually at about -5D or less and it never exceeds -8D. 3) Asthenopic Symptom occur in patient with small degree of Myopia. Myopic eyes are large and prominent. No degenerative changes are seen. Pathological myopia, as the name indicates is a rapidly progressive error which starts in childhood at 5-10 years of age and results in high Myopia (7-6)D during early adult life which is generally associated with degenerative changes in the eye. It is obvious that the Pathological myopia results from a rapid axial growth of the eyeball which is outside the normal biological variations of the development. a)Role of heredity:- It is now substantiated that genetic factors play an important role in the aetiology as the progressive myopia is familial, more general in certain races like Japanese, Chinese, Arabians.
It is presumed that heredity-linked growth of retina is the determinant in the progression of myopia. The increased axial length, degenerative changes in retina and choroid, vitreous changes and pathological Complications are determined by various genes. b)Though the Role of general growth process minor, can’t be denied in the progress of myopia. With affect the general growth process may also have some influence of the progression of MYOPIA 1)Defective vision, uncorrectable loss of vision may occur due to Progressive degenerative changes. 6) Degenerative changes in retina choroid are common in Progressive Myopia. Retinal tear, Haemorrhage and even Retinal detachment may be seen as complications of Myopic chorioretinal degeneration. It is important that these Degenerative changes in the fundus are not necessarily comparable with the degree of myopia, for they may be more marked when the Myopia is slight and less marked when the error is very. : Fundus changes in Pathological Myopia 2) Complicated cataract, vitreous haemorrhage, choroidal haemorrhage, nuclear sclerosis may occur. 3)POAG is not a complication but a common association of Pathological Myopia. Corneal Curvatural Myopia develops in many cases of increase of corneal curvature in some conditions such as keratoconus. Lenticular Curvatural Myopia may also occur due to increase of lenticular curvature in some conditions such as Lenticonus anterior and posterior. Nuclear Sclerosis may also develop more and more hyper-refringentpari passu,which occurs a progressive myopia. G)Night Myopia:- The shift from photopic to scotopic vision twilight is associated with developed sensitivity to the shorter wavelengths of light.



No comments yet
Be the first to share your thoughts!