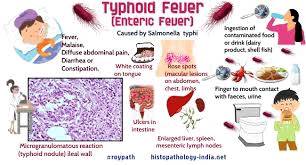
TYPHOID FEVER

WELCOM TO MADEK ZINC HERBAL(THE USE OF LOCAL HERBS WILL MAKE YOU LAUGH)Acknowledgements ........................................................................................................ viiChapter 1: The organism, the disease and transmission ....................................... 1 1.1 The organism ............................................................................ ........................... 1 1.2 The disease ........................................................................................................... 1 1.3 Contamination and transmission ....................................................................... 4 Chapter 2: Diagnosis of typhoid fever ....................................................................... 7 2.1 Specimens ............................................................................................................. 7 2.2 Microbiological procedures ............................................................................... 9 2.3 Serological procedures...................................................................................... 11 2.4 Antimicrobial susceptibility test for typhoid fever organisms .................... 16 2.5 Storage of typhoid fever organisms ................................................................ 17 2.6 Quality control .................................................................................................. 17 Chapter 3: Treatment of typhoid fever ................................................................... 19 3.1 General management ........................................................................................ 19 3.2 Antimicrobial therapy ....................................................................................... 19 3.3 Management of complications ......................................................................... 22 3.4 Management of carriers.................................................................................... 23 Chapter 4: Prevention of typhoid fever ................................................................... 25 4.1 Safe water........................................................................................................... 25 4.2 Food safety ......................................................................................................... 25 4.3 Sanitation ............................................................................................................ ACKNOWLEDGEMENTThe author is greatly indebted to our LORD CHRIST for all the physical and spiritual resources and feasible provided, and by whose grace the publishing work has been possible. I also wish to express my profound gratitude to all OSSEC agricultural and General science students their contribution and also to readers whose corrective contributions has helped to shape this herbal tips.Chapter 1:The organism, the disease and transmissionTyphoid fever is caused by Salmonella typhi, a Gram-negative bacterium. A very similarbut often less severe disease is caused by Salmonella serotype paratyphi A.The nomenclature for these bacteria is confused because the criteria for designatingbacteria as individual species are not clear. Two main views on the nomenclature of thegenus Salmonella have been discussed. Le Minor and Popoff suggested that two speciesshould be recognized: Salmonella bongori and Salmonella enterica. S. enterica includedsix subspecies, of which subspecies I (one) contained all the pathogens of warm-bloodedanimals. S. typhi was a serotype within subspecies I: Salmonella enterica subspecies Iserotype typhi. This proposal was rejected by the International Judicial Commissionbecause the name was not well known to clinicians and its use might cause accidentsendangering health or life. The original rules therefore remain in force. Ezaki andcolleagues have noted in the International Journal of Systematic and EvolutionaryMicrobiology that the correct nomenclature for the causal agent of typhoid fever isSalmonella typhi and have requested that the current subspecific status of serotypeparatyphi A should be raised to specific status, i.e. Salmonella paratyphi A.S. typhi has several unique features, the genetic basis of many of which is known asa result of early genetic studies and the recent sequencing of the whole genome.Although many genes are shared with E. coli and at least 90% with S. typhimurium,there are several unique clusters of genes known as pathogenicity islands and manymore single genes that seem to have been acquired by S. typhi during evolution.S. typhi can be identified in the laboratory by several biochemical and serological tests(see Chapter 2). One of the most specific is that of polysaccharide capsule Vi, which ispresent in about 90% of all freshly isolated S. typhi and has a protective effect againstthe bactericidal action of the serum of infected patients. This capsule provides the basisfor one of the commercially available vaccines (see Chapter 4).
Vi antigen is present insome other bacteria (Citrobacter freundii, Salmonella paratyphi C and Salmonelladublin) but not in exactly the same genetic context. The ratio of disease caused byS. typhi to that caused by S. paratyphi is about 10 to 1 in most of the countries wherethis matter has been studied.1.2 The diseaseDuring an acute infection, S. typhi multiplies in mononuclear phagocytic cells beforebeing released into the bloodstream. After ingestion in food or water, typhoid organismspass through the pylorus and reach the small intestine. We CONTINUE .....https://madekzinc.blogspot.com/2022/09/typhoid-fever.html




No comments yet
Be the first to share your thoughts!