Herpes Simplex Virus (HSV)
Herpes Simplex Virus (HSV) is a contagious virus that causes infections in various parts of the body, most commonly around the mouth (oral herpes) or genitals (genital herpes). It has two main types:
1. HSV-1: Primarily causes oral herpes (cold sores).
2. HSV-2: Primarily causes genital herpes.
---
Causes of HSV
HSV is transmitted through direct contact with an infected person. Common causes include:
HSV-1 (Oral Herpes)
Kissing or skin-to-skin contact.
Sharing utensils, lip balms, or razors with someone who has an active cold sore.
Touching the infected area and then touching other parts of the body.
HSV-2 (Genital Herpes)
Sexual contact (vaginal, anal, or oral) with an infected person.
Direct contact with genital sores or shedding virus from the skin, even without visible sores.
Triggers for Recurrence (Both Types):
Stress.
Illness or weakened immune system.
Hormonal changes (e.g., menstruation).
Fatigue.
Sun exposure.
---
Signs and Symptoms
HSV-1 (Oral Herpes):
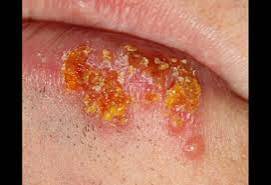
Cold Sores or Fever Blisters: Painful, fluid-filled blisters around the mouth or lips.
Tingling or Itching: May occur before blisters appear.
Sore Throat: Especially during the first outbreak.
Swollen Gums or Lymph Nodes: Accompanying signs in initial infections.
HSV-2 (Genital Herpes):
Painful Blisters or Ulcers: On or around the genitals, buttocks, or thighs.
Itching or Tingling: Often precedes blister formation.
Painful Urination: If sores are near the urethra.
Flu-Like Symptoms: Fever, headache, and muscle aches during initial outbreaks.
---
Effects
1. Physical Pain:
Sores can cause significant discomfort, affecting eating, drinking, or urination.
2. Recurrent Outbreaks:
Even after the initial infection subsides, the virus remains dormant and can reactivate periodically.
3. Emotional Stress:
Social stigma and recurrent symptoms may lead to anxiety or depression.
4. Increased Risk of Transmission:
Can be passed to sexual partners or newborns during delivery (neonatal herpes).
5. Complications (Rare):
Herpes Keratitis: Infection of the eyes, potentially affecting vision.
Herpes Encephalitis: Inflammation of the brain, which is life-threatening.
---
Prevention and Management
Avoid direct contact with active lesions.
Use barrier methods like condoms during sexual activity.
Take antiviral medications (e.g., acyclovir or valacyclovir) as prescribed to reduce outbreaks and transmission risk.
Click to join our official channel
 blogpay
blogpay























Total Comments: 0