 blogpay
blogpay
- Home
- Trending
-
- Category
- Arts & Entertainment
- Asante Kingdom
- Autos & Vehicles
- Beauty & Fitness
- Books & Literature
- Business & Industrial
- Computers & Electronics
- Education
- Finance
- Food & Drink
- Games
- Health
- Hobbies & Leisure
- Home & Garden
- Internet & Telcom
- Jobs & Education
- Law & Government
- News
- Online Communities
- People & Society
- Pets & Animals
- Poetry
- Politics
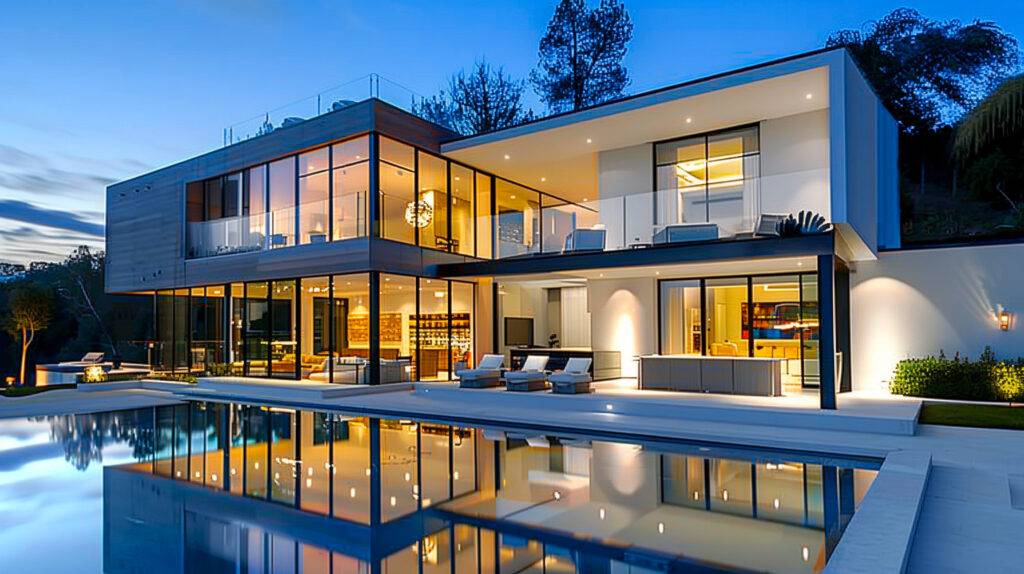
- Real Estates
- Relationships
- Religion
- Science
- Shopping
- Sports
- Technology
- Travel
- Advertisements
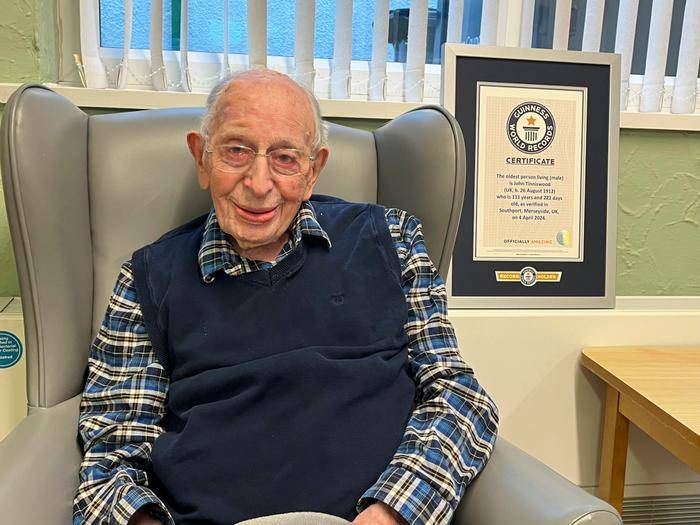



























Total Comments: 0