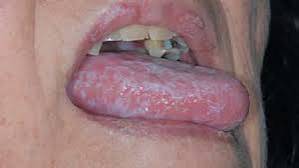
Oral Lichen Planus (OLP)
Oral lichen planus is a chronic inflammatory condition that affects the mucous membranes of the mouth. It often appears as white, lacy patches or painful sores and is linked to an autoimmune response.
---
Causes of Oral Lichen Planus
The exact cause of OLP is unknown, but it is believed to involve an autoimmune reaction where the immune system attacks the mucous membranes. Possible triggers include:
1. Autoimmune Disorders:
The immune system mistakenly attacks healthy oral tissues.
2. Genetic Predisposition:
Family history of autoimmune conditions.
3. Stress or Anxiety:
May exacerbate symptoms.
4. Certain Medications:
NSAIDs, beta-blockers, or antimalarials.
5. Dental Materials:
Amalgam fillings or other metals may irritate tissues.
6. Infections:
Hepatitis C virus has been associated with OLP.
7. Allergic Reactions:
To certain foods or oral hygiene products.
8. Hormonal Changes:
More common in postmenopausal women.
9. Tobacco and Alcohol Use:
Can irritate the mucous membranes.
10. Chronic Irritation:
From rough dental appliances or sharp teeth edges.
---
Signs of Oral Lichen Planus
Common Symptoms
1. White, lacy patches on the inner cheeks, gums, tongue, or lips.
2. Red, swollen tissues in the affected areas.
3. Painful sores or ulcers.
4. Burning or stinging sensation, especially when eating spicy or acidic foods.
5. Sensitivity to hot or cold foods.
6. Dry mouth.
7. Bleeding gums if ulcers are irritated.
8. Metallic or altered taste in the mouth.
9. Difficulty chewing or swallowing.
10. Persistent soreness or discomfort.
---
Effects of Oral Lichen Planus
Short-Term Effects
1. Pain or discomfort during eating or drinking.
2. Difficulty speaking due to sores or swelling.
3. Anxiety or stress about persistent symptoms.
Long-Term Effects
4. Chronic pain or irritation.
5. Weight loss due to difficulty eating.
6. Secondary infections if ulcers become infected.
7. Risk of oral cancer in severe, untreated cases.
8. Impact on quality of life due to ongoing symptoms.
---
Solutions and Management of Oral Lichen Planus
Home Care and Lifestyle Changes
1. Avoid Trigger Foods:
Stay away from spicy, acidic, or hot foods that may irritate the lesions.
2. Good Oral Hygiene:
Use a soft-bristled toothbrush and avoid abrasive toothpaste.
3. Stop Smoking and Alcohol:
Reduces irritation and inflammation.
4. Stress Management:
Practice relaxation techniques like yoga, meditation, or therapy.
Medical Treatments
5. Topical Corticosteroids:
Reduce inflammation and pain (e.g., clobetasol, triamcinolone).
6. Immunosuppressive Medications:
Tacrolimus or cyclosporine for severe cases.
7. Antihistamines:
Relieve itching and discomfort.
8. Antifungal Medications:
Prevent secondary fungal infections like oral thrush.
9. Pain Relievers:
Over-the-counter or prescribed pain medications.
Professional Treatments
10. Phototherapy:
UV light therapy for resistant cases.
11. Biopsy:
To confirm the diagnosis and rule out oral cancer.
12. Regular Monitoring:
Routine dental and medical check-ups to assess lesion changes.
Natural Remedies
13. Aloe Vera Gel:
Apply directly to reduce inflammation and soothe sores.
14. Honey:
Antibacterial properties can help prevent infections.
15. Saltwater Rinses:
Use warm saltwater to keep the mouth clean.
Preventive Measures
16. Avoid Known Irritants:
Identify and eliminate allergens, such as specific toothpaste or foods.
17. Use Alcohol-Free Mouthwash:
To avoid irritation.
---
When to Seek Medical Help
If lesions persist for more than two weeks.
Symptoms worsen or interfere with eating, speaking, or drinking.
If there are any signs of tissue changes that could indicate malignancy.
Early diagnosis and consistent management are essential to controlling oral lichen planus and preventing complications.